We understand by climate change a long-term change in the planet's climate. It is not just a drier year than the previous one, or unseasonable heat, but rather a trend that the climate is not behaving as expected by human beings, causing economic, social and environmental.
Main climate changes
The most talked about climate change is the Global warming, which is the increase in the Earth's average temperature. As stated above, we know that the planet has hotter and colder seasons naturally, however, it is undeniable that this recent increase is already causing and will cause even more social and environmental damage.
Another problem is the acid rain, caused by the emission of pollutants into the atmosphere. As a result, the water in the oceans and rivers, as well as the soil itself, is acidifying. Furthermore, acid rain also causes the corrosion of historical monuments, such as the Colosseum in Rome, or the pyramids in Egypt, causing inestimable cultural loss.
The increase in the number of tornadoes, melting of glaciers, rising ocean levels and the desertification of biomes can also be cited as recent climate changes.

Natural and human causes
The planet's climate has natural variations, which have been observed by humans for a long time. We can mention El Niño and La Niña, Aphelion and Perihelion, the variation in the Earth's tilt, glacial cycles, among many other natural phenomena.
We can say, then, that the climate is not stable. It has small variations known and expected by humans, however, more and more studies by the UN, the IPCC and other international institutions show us that the current climate behavior is no longer so predictable.
Pollution caused by industry and cars, contamination of rivers and oceans, and deforestation are among the main human activities that affect the climate. Whether directly, through the emission of gases, or indirectly, with the extinction of species and destruction of biomes.
Consequences
The consequences can be social, environmental and economic. Normally, they cover the 3 spheres, as they are factors that are interconnected.
A desertification of biomes It is soil loss These are consequences that directly affect the lives of the population, especially the poorest and those who live in rural areas. As a result, agricultural production is compromised, forests are degraded and local fauna is affected.
It is also worth remembering the indigenous, riverside and caiçara populations, who depend directly on natural resources and end up being much more affected.

O melting glaciers and rising sea levels are also examples of global consequences. Even countries that do not emit Greenhouse Gases (GHGs), such as carbon dioxide and methane, are affected. Beaches and islands are submerging, animals are becoming extinct and the entire marine biome is being affected.
In addition, acid rain worsens the situation, as it ends up killing species of algae, marine animals and microorganisms. The soil also becomes acidic, and terrestrial biomes are increasingly affected.
The frequency of tornadoes and hurricanes it is also increasing due to changing air masses, causing even more disasters.
More intense rains and more severe droughts are also among the problems identified, and also cause migration or extinction of animals, changes in biomes and losses in agriculture.
Historical Evolution of Changes
As stated above, the climate is not completely stable, presenting variations throughout the planet's history. However, the patterns observed after the second half of the 20th century do not follow the expected data, as we can see in the image below:
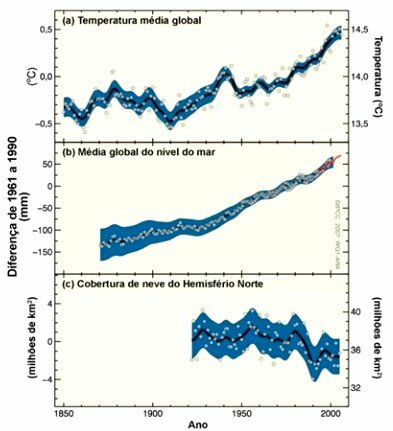
Studies by the IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) demonstrate that these changes coincide with the Industrial Revolution, still in the 18th century. Since then, there has been a large increase in the concentration of greenhouse gases, such as methane (148%) and carbon dioxide (35.3%) on the planet.
With this increase, the consequences began to gain strength to the point that, today, we know that many of them are irreversible, so the fight now revolves around containing the effects to avoid disasters futures.
To achieve this, those most responsible must mobilize: the USA, China and Europe - which are the biggest emitters of gases - are mobilizing to create alternatives that make it possible to continue developing, but causing fewer environmental impacts.
Europe, for example, has already voted to abolish the sale of combustion cars by 2035. Some US states also passed similar measures, giving space for the popularization of electric cars.
China, in turn, is the country that produces the most clean energy and also the one that has the most patents for technologies developed in this area. In solar energy generation alone, it is estimated that by 2025 they will produce twice as much as the USA.
On the other hand, underdeveloped and emerging countries also play a central role in environmental issues. Not in the emission of gases, but in the conservation of forests and water sources.
Brazil is probably the most important country in this regard. In addition to being home to most of the Amazon Rainforest (the largest forest in the world), it is also the country with the most sources of fresh water (12% of the planet's water).
Proposals for the future
Practically all nations in the world publicly recognize the emergency of the climate issue. For this reason, global meetings and agreements are being held to curb climate change.
One of the main current agreements is the Kyoto Protocol, 1997. This document was the first major step towards committing to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, it also created the CDM (Clean Development Mechanism), which serves to create sustainable technologies.
Another important treaty is the Paris Agreement, a kind of continuation of the Kyoto Protocol. Its objective is to slow the planet's warming to a maximum of 2°C by 2030.
The Agreement went through a recent controversy with former American President Donald Trump, who briefly left the agreement in 2020. In 2021, newly elected President Joe Biden rejoins the agreement.
Another agreement that is gaining more and more importance is the COPs - Conference Between the Parties - which are annual meetings to discuss solutions and alternatives to the climate issue. It was from this meeting that the Paris Agreement and other debates to establish local goals emerged.
The already mentioned IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change is another extremely important organization, as it helps monitor data relating to the environment and the socioeconomic impacts of climate change. This way, we have concrete data to be able to outline measures that really aim to reduce the impacts of these changes.

Finally, civil society has also been putting pressure on. We are increasingly seeing protests demanding governments and companies take greater environmental responsibility. It is not enough to create strict environmental laws, monitoring and inspection mechanisms must also be created to guarantee compliance with these laws.
To find out more about the subject:
- Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming.
- Greenhouse effect
- Greenhouse Effect Exercises
- Ice age
- Main environmental problems
- Chemistry at Enem
- Natural sciences and their technologies: Enem
- Enem Geography: subjects that fall the most
Bibliographic references
Silva R. W. C., Paula B. L. 2009. Cause of global warming: anthropogenic versus natural. Terræ Didatica, 5(1):42-49
MARQUES, Vinícius. Climate Change: causes, consequences and prospects for the future.All Matter, [n.d.]. Available in: https://www.todamateria.com.br/mudancas-climaticas-causas-e-consequencias/. Access at:
See too
- Main environmental problems
- Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming
- Enem Geography: subjects that fall the most
- Greenhouse Effect Exercises
- Types of Garbage
- Air pollution
- Global warming
- Greenhouse effect



