The skeleton is the structure that gives support for the human body and other animals, is formed by bones and cartilage.
Its main functions are to support the body, protect the internal structure, carry out movements and reserve minerals.
The human skeleton is divided into axial It is appendicular, being composed, in an adult person, by 206 bones.
skeleton anatomy
The human skeleton has 206 bones. This number can vary according to age, children generally have more bones than adults.
Human bones can have very different dimensions, being as long as the femur (thigh bone) and the humerus (arm bone), or short (for example: carpal bones in the hands), flat (like the skull) or even with irregular shapes (like the vertebrae).
The largest bone in the human body is the femur. The smallest is the stirrup, which sits inside the ear and is essential for hearing. Bones are made of collagen and mineral saltssuch as calcium, phosphorus and potassium.
See the main human bones:
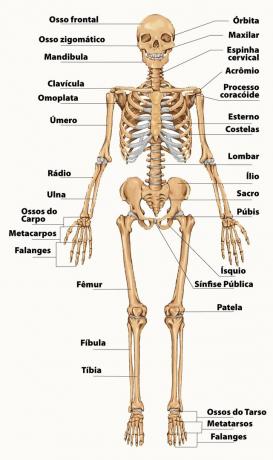

Division of the human skeleton: axial and appendicular
The skeleton is divided into axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton. O axial it is formed by the bones of the main structure of the human body: head, spine and thoracic cage.
In addition to support, the axial skeleton serves especially to protect organs important. In the head, the skull protects the brain, the vertebral column protects the spinal cord, and the ribcage protects the heart and lungs.
O appendicular skeleton It is composed of upper and lower limbs, that is, arms and legs. The bones of the waist and pelvis are also part of this skeleton.
The appendicularis' central function is to ensure mobility and performance of movements. The human skeleton is thus segmented to group the bones according to their main function, helping in the study of the organism.
skeleton function
The skeleton has several essential functions for the functioning of the human body, see what they are:
- body support - it is the skeleton that structures the human body giving it the shape it has;
- organ protection - the skeleton protects human organs from external aggressions. The main organs have a set of bones around them so that they are not so exposed;
- Movement - it is also the skeleton, together with the muscles, that allows the human body to carry out movements. From walking, running, holding objects or even talking;
- mineral storage - it is in the bones that minerals essential for the development of the body are stored, such as calcium and phosphorus;
- muscle support - the skeleton serves as a support for the muscles (and other types of soft tissues), allowing movements to be carried out;
- blood cell production - it is in the bone marrow that blood cells (white and red blood cells and platelets) are produced.
See too: Cardiovascular system, nervous system It is digestive system.