Accelerationgivesgravity is the rate of velocity of a falling body, in free fall, towards the center of the Earth. At sea level, the acceleration of Earth's gravity is, on average, 9.8 m/s². Gravity depends on factors such as the planet's mass and radius and is the same for all bodies, regardless of their masses.
See too: Acceleration — all about this vector physics quantity
What is gravity acceleration?
The acceleration due to gravity is a measure of the variation in velocity of bodies that are dropped from a certain height in relation to the Earth. When an object freefalls, its speed varies at a rate of 9.8 m/s every second. This measure of acceleration is the same for all bodies, even those of different masses, if we disregard the action of dissipative forces, like the drag of air.

How much is the acceleration of gravity worth?
The magnitude of the acceleration of gravity on the surface of the Earthvaries according to the distance we are from the Earth's core. At a distance of approximately 6370 km, when we are at sea level, the terrestrial gravity is, on average, 9.8 m/s². However, this value can vary according to soil density, presence of underground empty spaces, etc.
As we move away from sea level, the gravity acceleration varies in shape inversely proportional squared the distance, therefore, when we are at a height of 6470 km above sea level (12,940 km to the center of the Earth), the value of gravity will be equal to ¼ of its original value, about 2.45 m/s².
See too: Why don't we feel the Earth rotate?
How to calculate gravity acceleration?
the acceleration of gravity can be calculated in different ways. The most common way is through the equations of kinematics related to free fall movement. Below is the formula that relates height to time of fall and which can be used to calculate the local gravity value.

g - gravity acceleration (m/s²)
H - height of fall (m)
t – fall time(s)
In addition to the formula shown above, it is possible to determine the magnitude of gravity's acceleration without knowing the fall time. For this, we apply the principle of conservation of mechanical energy: we say that the whole gravitational potential energy turned into kinetic energy, thus, we have to:
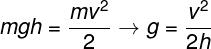
The formula shown above, which relates gravity acceleration to fall height and velocity, can also be obtained from the Torricelli equation.
Gravity Acceleration Formula
The acceleration of gravity can be obtained in other ways besides the kinematic equations, as shown above. One of them is through the use of the law of universal gravitation, in Isaac Newton. According to this law, the acceleration of gravity can be obtained with the following formula:
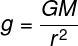
G – constant of universal gravitation (6.67408.10-11Nm²/kg²)
M – Earth mass (kg)
r – radius of the Earth (m)
Gravity Acceleration Exercises
Question 1 — Knowing that the acceleration of gravity on the Moon's surface is approximately 1/5 of the Earth's gravity, it is correct to state that:
a) for two identical abandoned bodies of the same height on the Moon and on Earth, the falling time of the object falling on the Moon will be five times less than the time of the object falling on Earth.
b) for two identical abandoned bodies of the same height on the Moon and on Earth, the velocity of the object that falls on the moon, immediately before touching the ground, will be five times smaller than the object falling on the Earth.
c) the fall time for two identical bodies abandoned from the same height on the Moon and Earth will be the same.
d) none of the alternatives.
Resolution:
When released on the Moon, an object will be subject to a gravity five times that of Earth. In this way, the speed at which this body will reach the ground will be five times slower, so the correct alternative is the letter B.
Question 2 — A bowling ball and a feather are released from the same height, in a region where a partial vacuum is created. Disregarding the action of any frictional forces between the objects and the air, mark the correct alternative.
a) Pen and bowling ball will hit the ground together.
b) The bowling ball will reach the ground before the penalty.
c) The penalty will reach the ground with a speed slower than that of the bowling ball.
d) The bowling ball will reach the ground with a speed slower than the penalty.
Resolution:
Since air resistance can be neglected, the pen and bowling ball will both fall subject to the same acceleration, so they will hit the ground at the same time. Thus, the correct alternative is the letter A.
By Rafael Hellerbrock
Physics teacher
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/aceleracao-da-gravidade.htm


