A classification of living beings is studied by a science called taxonomy. Taxonomic classifications take into account physical and physiological individuals to separate them into different groups.
We prepared a list of discursive questions about classification of living beings so you can test your knowledge of taxonomy.
see more
Biology teacher fired after class on XX and XY chromosomes;…
Cannabidiol found in common plant in Brazil brings new perspective…
You can consult the answers and save this list of exercises in PDF at the end of the post!
Discursive questions about classification of living beings
1) What are the seven main taxonomic categories in which living beings are classified? Write in order from largest to smallest group coverage.
2) (UNICAMP) According to the binomial system of nomenclature established by Linnaeus, the scientific name felis catus Applies to all domestic cats such as Angoras, Siamese, Persians, Abyssinians and tabby cats. The Wild Cat (Felis silvestris), the lynx (felis lynx) and the puma or cougar (Felis concolor) are species related to the cat.
a) What genus do all the animals mentioned belong to?
b) Why are all domestic cats designated by the same scientific name?
c) Which of the following names correctly designates the family to which these animals belong: Felinaceae, Felidae, Felini, Felinus or Felidaceae? Justify.
3) (UNICAMP) Leptodactylus labyrinthicus is a seemingly complicated name for an amphibian that occurs in swamps in the State of São Paulo. Justify the use of the scientific name instead of simply “pepper frog”, as the fishermen say.
4) (UFES) See the following image:
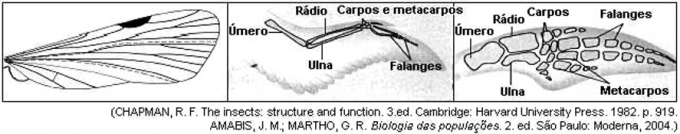
The body structures of different animals may indicate that these species descended from a common ancestor, depending on the anatomical organization and embryonic origin of these structures and regardless of their functions. The figures above represent the wing of an insect, the wing of a bird and the front fin of a dolphin.
Based on the above, do what is asked.
a) Compare the insect wing with that of the bird, in relation to their evolutionary origins and their functions. Explain the evolutionary event involved in the emergence of structures with these conditions.
b) Compare the bird's wing with the dolphin's fin, in relation to their evolutionary origins and functions. Explain the evolutionary event involved in the emergence of structures with these conditions.
c) For Lamarck, the emergence of a fin like that of a dolphin would be due to the development of another type of fin. appendix, which, progressively, in each individual, over generations, would be modified as a result of its use for the swim. The modifications acquired in each individual would be transmitted to their descendants, until, over generations, the appendix became a fin. State whether this hypothesis is correct or not and justify your answer.
5) (UFF-RJ – mod.) Identify the taxonomic category to which each of the mentioned names refers, according to the rules of zoological nomenclature and justify your answer.
The) rattus
B) Ascaris lumbricoides
w) homo sapiens sapiens
d) Anopheles (Nyssorhynchus) darlingi
6) (UFJF-MG) How many and what are the kingdoms of living organisms? Characterize these taxa.
7) (UNIFESP – Mod.) “In a transition area between the Atlantic forest and the cerrado, the pau-d’arco (Tabebuia serratifolia), the box (Tabebuiacasinosides) and some ipês (Tabebuia aurea, tabebuia alba, Cybistax antisyphillitica). The São João vine (Pyrostegia venusta) is also frequent in that region”.
Considering the biological classification criteria, how many genera and how many species are cited in the text?
8) (UFPR) Conceptualize prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells describing at least two characteristics that differentiate them.
9) (UPE – Mod.) The current classification of living beings considers anatomical similarities, chemical composition and genetic structure. Thus, the name of each species must consist of two words: the first designating the genus; and the second, the species. In Brazil, there are about 118 species of primates, being considered the country with the highest number of species. The Amazon is the biome with the greatest diversity, where it is possible to find three of them: Alouatta belzebul, ateles belzebuth It is Ateles paniscus.
Based on these considerations and the principles that govern this classification, what is the degree of kinship of Ateles paniscus It is ateles belzebuth?
10) (UFC 2009) Some insects have both pairs of wings developed, while others have modifications this condition, replacing the second pair of wings with structures known as dumbbells, used to stabilize the flight. The condition of the well-developed hindwings, similar to the forewings, is known as plesiomorphic, that is, primitive, and the condition of the wings transformed into dumbbells is known as apomorphic, that is, derived. Based on the above, answer the following question.
a) Give an example of a plesiomorphic character and its apomorphic counterpart in vertebrates.
b) Modifications throughout evolutionary history, generating apomorphies, occur in individuals that present homologous structures. Cite an example of homology in relation to the plesiomorphic character mentioned in the previous item.
Answer to question 1
Kingdom – phylum – class – order – family – genus – species.
Answer to question 2
a) The animals mentioned belong to the genus Happy.
b) All domestic cats are designated by the same scientific name because they all belong to the same species.
c) The name that designates the family of cats is Felidae. According to scientific nomenclature, family names must be spelled with the ending “idae”.
Answer to question 3
The use of scientific names allows for more efficient communication between people.
This happens because they are written in Latin, a language that is no longer used in the world and, therefore, are not subject to regionalisms, as is the case with popular or vulgar names.
Also, popular names refer to more than one species, depending on the region.
Answer to question 4
a) The wings of insects and birds are analogous organs, as they have the same function, but embryonic origin and structural plan totally different. A bird's wing is a limb composed of bones, muscle, skin, nerves, etc., whereas an insect's wing is a projection of the chitin exoskeleton covering the animal's body.
b) The wings of birds and the fins of dolphins are homologous organs, because, despite having different functions – the wings are adapted to flight and fins to swimming – they have the same embryonic origin and have skeletons with the same plan structural.
The best explanation for this similarity in bone organization is that these animals descended from a common ancestor, from whom they inherited the structural design they share.
c) The assumption that Lamarck it is not correct. Only some tissues, such as muscle, are transformed as a result of their use or disuse; even so, these transformations cannot be passed on to their descendants.
Answer to question 5
a) Gender; name written in Latin form, in italics or underlined, with a capital letter.
b) Species; double name, Latinized, written in italics or underlined, first name capitalized and second name lowercase.
c) Subspecies; name written in italics or underlined, formed by three words, the last one also written with a lowercase initial.
d) Species in which the subgenus stands out; name written in italics or underlined, consisting of three words, the second (referring to the subgenus) between parentheses and with an initial capital letter.
Answer to question 6
monera: unicellular prokaryotes.
Protist: heterotrophic unicellular eukaryotes (protozoans) or unicellular and multicellular eukaryotes that do not form true tissues and that are autotrophs (algae).
fungus: heterotrophic eukaryotes that feed by absorbing nutrients from the environment (including some flagellated groups).
Plantae or Metaphyta: multicellular autotrophs with true tissues.
Animalia or Metazoa: multicellular heterotrophs that feed by ingestion.
Answer to question 7
The text mentions 3 genera and 6 species.
Answer to question 8
The characteristics that differentiate cells eukaryotes in prokaryotes they are:
1- Absence of nuclear envelope (carioteca), organelles membranous and cytoskeleton in prokaryotic cells and the presence of these structures in eukaryotic cells;
2- Presence of a single circular chromosome formed only by DNA in prokaryotic cells and the presence of filamentous chromosomes in pairs, formed by DNA and proteins, in eukaryotic cells.
Answer to question 9
Ateles paniscus It is ateles belzebuth are species closely related at the genus level.
Answer to question 10
a) Plesiomorphic character: four pairs of legs in most reptiles. Apomorphic character: absence of legs in snakes.
b) Anterior and posterior fins of aquatic mammals.
Click here to save this list of discursive questions about classification of living beings in PDF!
Read too:
- List of exercises about the Kingdom Animalia
- List of exercises on food chains
- List of exercises on intraspecific ecological relationships