Historical time is the historical references used to organize the most important events and major changes in societies and civilizations.
It's a way of counting time from the action of human beings on Earth, by the experiences that a people, nation or all of humanity have gone through.
Historical time is marked by great events, such as wars, fall of empires, great constructions, great epidemics and regime changes.
Historical times mark different forms of political, economic, social and cultural organization of civilizations and may vary between social groups.
Difference between historical time and chronological time
The chronological time is the clock time and of the calendars, this time is measured in exact and constant fractions of time: a day is always 24 hours, an hour is always sixty minutes, and a year is always 12 months.
Chronological time began to be measured by natural phenomena such as the position of the sun and the phases of the moon. Then man created instruments to control time, such as the hourglass, clock and calendar.
Unlike chronological time, historical time is the time marked by big events, for example:
- Development and decline of great civilizations;
- Emergence of writing;
- Discovery of the American continent;
- First and Second World Wars;
- Cold War;
- French Revolution and Industrial Revolution.
Historical time does not respect the predictability and rigor of calendars or clocks, it is imprecise and unpredictable and its counting considers the sequence of events of short and long duration.
There are different ways to count historical time
Time is a cultural creation and each civilization develops different ways to understand and count it, which can be observed in the different existing calendars.
Considering the three major existing monotheistic religions, we have 3 different calendars:
Christian or Gregorian Calendar
The Catholic Church calendar starts with the birth of Jesus Christ during the Ancient Age. This is one of the major milestones for counting time in our civilization.
The year of Christ's birth is considered year 0. All the years preceding his birth are counted in descending order and bring together the letters a. C (before Christ).
Jewish or Hebrew Calendar
The Jewish calendar began in the year 3761 a. C, which according to Jewish tradition was the year of Adam's creation. This means that in 2020, we would be in the year 5780 or 5781 (depending on the month) of the Hebrew calendar.
This calendar is also divided into 12 months, but these months do not correspond to the same division of months as the Christian calendar.
Muslim Calendar
The Muslim calendar is used by the Islamic religion and begins in the year 622 of the Christian calendar, that is, 622 years after the birth of Christ.
This is the year that marks the date that Mohammed fled from Mecca to Medina, an event known as hegira. This calendar is based on the phases of the moon and is also 12 months old.
Time was perceived differently in some civilizations
Our civilization is mainly based on the Gregorian calendar, which is organized in a linear fashion with a beginning, middle and end. The beginning is marked by the birth of Jesus Christ and the end, according to the Bible, will be marked by his return.
Other civilizations, however, understand time differently. To the Mayans and Aztecs, for example, the weather happened in cycles that repeated themselves, so their calendar was circular.
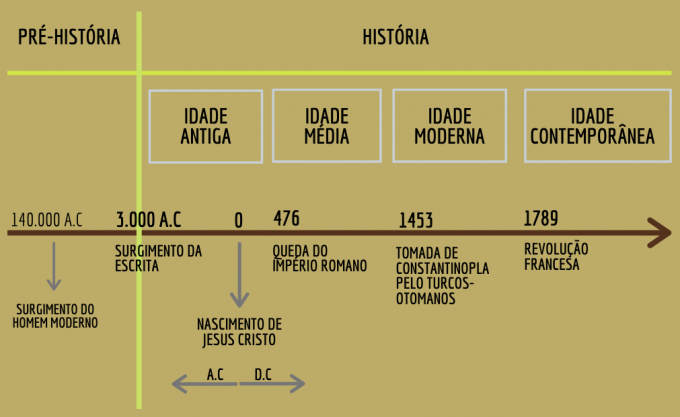
Human history timeline
The historical time of our civilization is divided into major phases, as described in the timeline:
In each of these phases, civilization had common characteristics that allow its classification:
Prehistory
Prehistory corresponds to the entire period prior to the emergence of writing and it is usually divided into two phases: the Stone Age and the Metal Age.
- Stone Age: begins about 2 million years ago, with the emergence of the genus Homo and extends to about 5,000 BC. C, when the Metal Age begins;
- Age of Metals: marks the period when hominids began to make objects out of metal. This phase lasts until the middle of 3000 BC. C, when writing appears.
Old age
The Ancient Age comes with the writing and it's the period of first civilizations, characterized by complex and hierarchically structured political and social organizations.
During this period, the eastern civilizations of Egypt, Mesopotamia, Persians, Hebrews and Phoenicians stand out. It is also the period of development of Chinese and Indian civilizations.
In Western civilizations, the greeks and the romans, which had a great influence on the cultural, political and social formation of the entire West.
It was also during this period that the Inca, Mayan, Aztec and Olmec civilizations developed on the American continent.
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages extended from the 5th to the 15th century and was marked by the development of the political and social economic system called feudalism. This phase is divided between the High Middle Ages and the Low Middle Ages:
- High Middle Ages: development and rise of the feudal system;
- low middle age: decline of the feudal system and beginning of the development of capitalism.
Modern age
In the modern age the mercantile capitalism develops as the dominant production system and the absolutism establishes itself as a form of government.
This is the period of great navigations, the discovery of new continents and the colonization and exploration of several countries in Asia, Africa and the Americas by European nations.
Contemporary age
The Contemporary Age begins with the French Revolution, which opens the way for other bourgeois revolutions that put an end to absolutist regimes in Europe.
This phase also stands out for the Industrial Revolution and by the wars of independence carried out in Latin America.
What are other ways to tell time?
We can also come across other ways of counting time, such as biological time, geological time and psychological time.
Biological time
Biological time refers to Life stages, such as birth, development, reproduction and death. This time is different for the human species and for other animals.
While humans can live for around 100 years, some species, such as flies, live between 15 and 30 days. This means that the life and death cycle of a fly respects a time very different from that of a human being.
geological time
Geological time is used to describe the chronology of the Earth geological formation and its changes since the planet formed.
The Earth is believed to have existed for about 4.6 billion years. This means that the entire rock formation on the planet is the result of millions or billions of years of activities in the Earth's crust.
Thus, the time limits used as a reference for geology are enormously greater than those of men, who appeared on Earth only about 130,000 years ago.
psychological time
Psychological time is another type of timekeeping and is related to perception of the passage of time by individuals.
When a person goes through an experience with strong emotional intensity, for example, he can have the feeling that the experience lasted much longer or much less than the chronological time. would score.
Also understand what is the meaning of time.