In situations involving counting problems we can use the PFC (Fundamental Principle of Counting). But in some situations the calculations tend to become complex and cumbersome. In order to facilitate the development of such calculations, some methods and techniques were developed in in order to determine groupings in the counting problems, consisting of the Arrangements and the Combinations.
Let's establish some differences between arrangements and combinations. The arrangements are characterized by the nature and order of the chosen elements. The combinations are characterized by the nature of the elements.
Arrangements
Given the set B = {2, 4, 6, 8}. The groupings of two elements from set B are:
{(2,4), (2,6), (2,8), (4,2), (4,6), (4,8), (6,2), (6,4), (6,8), (8,2), (8,4), (8,6)}
See that each arrangement is different from the other. Therefore, they are characterized:
Due to the nature of the elements: (2.4) ≠ (4.8)
By order of elements: (1,2) ≠ (2.1)
Combination
At a birthday party, ice cream will be served to guests. Strawberry (M), chocolate (C), vanilla (B) and plum (A) flavors will be offered and the guest must choose two of the four flavors. Note that the order in which flavors are chosen does not matter. If the guest chooses strawberry and chocolate {MC} it will be the same as choosing chocolate and strawberry {CM}. In this case, we can have repeated choices, see: {M, B} = {B, M}, {A, C} = {C, A} and so on.
Therefore, in the combination the groupings are characterized only by the nature of the elements.
Example 1 - Simple Arrangements
At one high school, ten students applied to serve as student council president and vice president. In how many different ways can the choice be made?
We have ten students competing for two places, therefore, ten elements taken two by two.
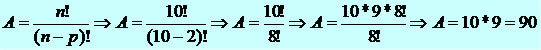
Example 2 - Combinations
Lucas is going on a trip and wants to choose four out of nine shirts. How many different ways can he choose the shirts?
We have nine shirts taken four to four.

by Mark Noah
Graduated in Mathematics
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/matematica/arranjo-ou-combinacao.htm

