Mathematical equations are present in several situations in Physics. Galileo Galilei was able to demonstrate that, when two bodies were abandoned from the same height, the force of air resistance (free fall), reach the ground at the same moment, that is, the fall time is the same for both bodies. This experience is valid for bodies of different masses. Through algebra we can establish a mathematical expression capable of calculating the falling time of objects and the height from which they are dropped. Free fall of bodies is considered a Uniformly Varied Motion, as all bodies are accelerated by gravity.
The acceleration due to gravity corresponds to 9.8 m/s², which means that a body in free fall increases its velocity by 9.8 m/s every 1 second.
Equations
Where:
V: speed
t: fall time
g: gravity acceleration
d: distance traveled by the falling body
Example 1
A body is dropped in free fall from a certain height and takes 6 seconds to reach the surface. How fast does the body reach the ground? Consider g = 9.8 m/s²
V = g * t
V = 9.8 * 6
V = 58.8 m/s or 211.68 Km/h
Example 2
A brick falls from a building under construction and hits the ground at a speed of 30 m/s. Calculate the building height and the brick fall time. Consider g = 10 m/s.
time height
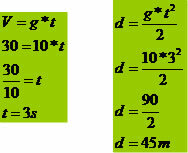
by Mark Noah
Graduated in Mathematics
Brazil School Team
Equations - Math - Brazil School
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/matematica/equacoes-matematicas-no-movimento-queda-livre.htm


