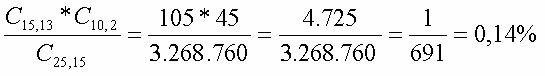When we say “root of an equation”, we are referring to the end result of any equation. 1st degree equations (of the type ax + b = 0, where a and b are real numbers and a≠0) have only one root, a single value for their unknown.
2nd degree equations (of the type ax² + bx + c = 0, where a, b and c are real numbers and a≠0) can have up to two real roots. The number of roots of a 2nd degree equation will depend on the value of the discriminant or delta: ∆.
Complete equations of the 2nd degree are solved by applying Bhaskara's formula:
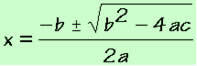
Conditions for the existence of the root of a 2nd degree equation:
No real root: when delta is less than zero. (negative)
∆ < 0
x² - 4x + 5 = 0
∆ = b² - 4ac
∆ = (-4)² - 4*1*5
∆ = 16 – 20
∆ = - 4 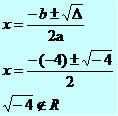
A single real root: when delta equals zero. (null)
∆ = 0
4x² - 4x + 1 = 0
∆ = b² - 4ac
∆ = (-4)² - 4*4*1
∆ = 16 – 16
∆ = 0 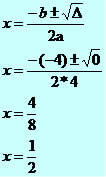
Two real roots: when delta is greater than zero. (positive)
∆ > 0
x² - 5x + 6 = 0
∆ = b² - 4ac
∆ = (-5)² - 4*1*6
∆ = 25 - 24
∆ = 1 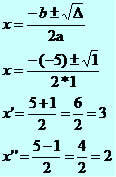
by Mark Noah
Graduated in Mathematics
Brazil School Team
Equation - Math - Brazil School
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/matematica/raiz-uma-equacao-2-grau.htm