Alkylation reactions are those that occur with the objective of obtaining alkylbenzene, that is, compounds whose structure has a benzene with a substituent group. Usually occur between aromatics and organic halides(R─ X).
Simply put, in this type of reaction one or more hydrogen atoms of the aromatic ring is replaced by an alkyl radical (R─).
A general equation representing the alkylation reaction is shown below:
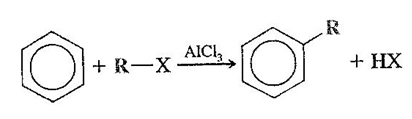
Note the presence of anhydrous aluminum chloride as a catalyst, you can also use other catalysts such as FeCl3.
This type of reaction is also called Friedel-Crafts alkylation, because in 1877 a French chemist, Charles Friedel, and his North American collaborator, James Mason Crafts, discovered this method with the aim of preparing alkylbenzenes.
Consider as an example the alkylation reaction of benzene with isopropyl chloride, whose mechanism is shown below:

See two more examples of alkylation:
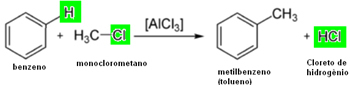
1. Benzene methylation:
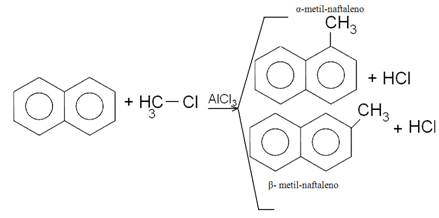
2. Naphthalene methylation: Two products are formed, with the substituted α being the product obtained in greater percentage.
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/reacoes-alquilacao-friedel-crafts.htm
