O Pacific Ring of Fire – also called Pacific Fire Circle or simply from Fire ring – is an area with high geological instability located in the Pacific Ocean, covering the West of the Americas and East Asia and Oceania. With a length of 40,000 km, this belt has a shape that resembles a horseshoe or a semicircle. It basically consists of mountain ranges or mountain ranges, ocean trenches (deep valleys) and volcanic island arches.
This zone of instability is responsible for most earthquakes that occur over the Earth's surface. It exists by virtue of friction and movement between various tectonic plates. While the plates move away in the region of the Atlantic Ocean, on the coast of the American continents and Asian, they collide, modifying the relief and providing earthquakes and the proliferation of volcanoes. Look at the map below:
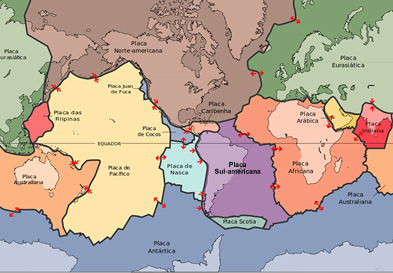
Compare with the previous map and note the location of the ring of fire and the encounter between the plates.
The tectonic processes that give rise to the Pacific Ring of Fire are responsible for about 90% of earthquakes recorded on the planet throughout history. The largest of them occurred in Chile, in the 1960s, with 9th on the Richter Scale (which varies from 1 to 10).
Another phenomenon associated with the Ring of Fire is the tsunamis, including the largest recently recorded, which occurred in 2004, which gained great repercussion when killed thousands of people on the coast of Indonesia, Sri Lanka, India, Thailand and many others countries. Not to mention, of course, what happened in Japan in 2011 and hit the Fukushima nuclear power plant.
It is interesting to note that the existence of the Pacific Fire Circle even influences climatic phenomena, as volcanoes existing in the portion of the Pacific to the west of the American continent, added to other factors, cause the warming of the waters of this ocean in the Peru, which are responsible for cyclical climatic anomalies, both short-term (such as El Niño and La Niña) and long term (like the Pacific Decadal Oscillation).
Understanding the formative processes and constitutive characteristics of the Pacific Ring of Fire is very important for help reduce the unpredictability of earthquakes and tsunamis, which can mitigate their effects on geographic space Social.
By Rodolfo Alves Pena
Graduated in Geography
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/geografia/anel-fogo-pacifico.htm

