The capacity that the connections have to attract electrical charges is defined as Polarity, which takes on a different character depending on the connection where it is present.
The most frequent bonds involving organic compounds happen between carbon atoms or between carbon and hydrogen atoms: C ─ C and C ─ H (hydrocarbons). We classify this type of bond as covalent, it is present in all bonds of organic compounds formed only by carbon and hydrogen.
When in the molecule of an organic compound there is another chemical element besides carbon and hydrogen, its molecules will have a certain polarity. We call this element a heteroatom and it can be: nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), among others.
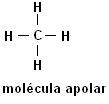
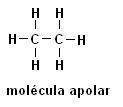
Methane (CH4) Ethane (C2H6)
Note that in both structures there is no presence of heteroatoms, in this case the molecules are classified as non-polar.


The presence of Oxygen as a heteroatom makes the molecules show polarity. The first molecule is the compound Ethanol (CH3CH2oh), the presence of hydroxyl – OH gives this compound a polar character, even if in its structure it contains a non-polar part.
By Líria Alves
Graduated in Chemistry
Brazil School Team
See more! flat isomer
Organic chemistry - Chemistry - Brazil School
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/moleculas-organicas-polares-apolares.htm
