From our first contacts with geometry, we learned how to calculate the area of a triangle using its general formula (base x height, and the result divided by two). However, as we advance in the study of mathematical concepts, we learn various expressions and relationships that can be established in this gigantic world of mathematics. Today we will see that it is possible to calculate the area of a triangle without knowing the value of its height, requiring only the measurements of two sides and the angle of these sides.
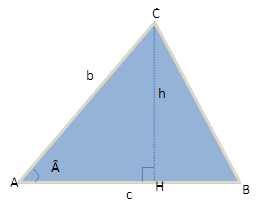
For this, let's draw any triangle (?ABC), whose sides are worth (B and ç) and the angle between them is equal to Â.
We know that the area of this triangle must be calculated by the expression:

We can note that the triangle formed by the ACH vertices is a right triangle, with that we can use the trigonometric concepts of a right triangle.
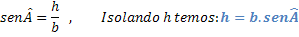
Since we have this expression for the height in relation to the hypotenuse and the sine of the angle, we can substitute it in our first formula for the area.
With that, we will have,
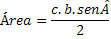
As you can see, the area is then given as a function of the measure of the sides we know and the sine of the angle between these sides. Remember that the coefficients (B and ç) represent the measure you know.
This expression is called the Area Theorem: “The area of the triangle is equal to the semi-product of the measurements of two sides by the sine of the angle formed by these sides”.
With that, you already know: if it is difficult to find the height value to calculate the area, and you have the enough information to use this formula we've learned today, don't waste time as it will facilitate the calculation.
By Gabriel Alessandro de Oliveira
Graduated in Mathematics
Brazil School Team
plane geometry - Math - Brazil School
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/matematica/calculando-area-triangulo-utilizando-angulos.htm

