Dominance and recessivity are two important concepts when we talk about expression of a feature. Next, we'll understand what dominance is and what recessiveness is, and we'll find out how to interpret and solve exercises that address this topic.
Heads up: To understand the subject, it is essential to know some basic concepts of genetics. You can get to know some of these terms by reading the text: Basic concepts in genetics.
What are alleles?
Before we understand what dominance and recessivity are, we must understand what alleles are. We know that the geneis a specific nucleotide sequence in the DNA which determines a hereditary character. The genes that determine the same characteristic are located in the same place (locus) in chromosomes counterparts. You alleles would then be alternative forms of a gene that occupies the same locus on homologous chromosomes.
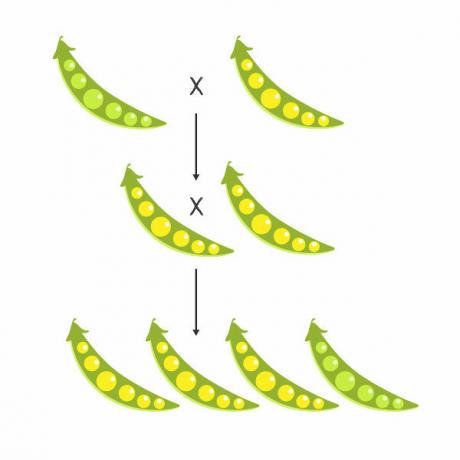
For a better understanding, we can think about the color of the flowers of the peas studied by Gregor Mendel. He noticed that there were purple flowers and white flowers. So there is the gene that determines the color of flowers, and there are two versions (the one that determines the color purple and the one that determines the white color) for this gene, which are the alleles.
For each feature, a organism inherits two alleles of a gene, one from the mother and the other from the father. In an individual, the alleles of a given locus on homologous chromosomes can be identical or different.

Read too:Genotype and phenotype: two concepts of genetics that are interconnected
What is dominance?
We say that an allele is dominant when it gets determine a phenotype, even if it occurs in a single dose. This means that the dominant allele will express itself so much in homozygous how much in heterozygosis.
Dominant allele is expressed in phenotype, even in single dose. |
To better understand this issue, let us recall one of the characteristics studied by Mendel in his work with peas. He noted that there were plants that generated yellow seeds and the ones that generated green seeds. After performing several crosses, Mendel came to the conclusion that the yellow trait was dominant, while the green was recessive.
Using the letter v to indicate the recessive allele and V to indicate the dominant allele, we have that plants that have the Vv and VV alleles are yellow. This is due to the fact that the V allele is dominant and, even if it occurs in a single dose, the characteristic it determines is expressed, which, in this case, is the yellowish color of the seed.
Read too:Mendel's First Law
What is recessiveness?
We say that a allele is recessive when he only expresses his phenotype in pairs. Thus, heterozygous individuals do not express the phenotype determined by the recessive allele.
Recessive allele is expressed in the phenotype only in double dose. |
Going back to the example given when we talk about dominance, we have that pea seeds can be yellow or green. The v allele indicates the recessive allele, which determines the color green, while the V allele indicates the dominant allele, which is responsible for the yellow color. As the recessive allele determines the color green, the individual will only present seeds of this color if he inherits two v alleles, that is, if the individual is vv.
Read too: What is codominance?
Dominance and Recessivity Exercises
See some questions that address the topic of dominance and recessivity:
|
Question 1- (UFLA) The allele that manifests its phenotype in both homozygous and heterozygous individuals is called: a) lethal b) Epistatic c) recessive d) Dominant e) On |
Answer to question 1: As we have seen throughout the text, alleles can be dominant or recessive. The dominant alleles are those that express their phenotype even in a single dose, that is, in homozygotes and heterozygotes. Thus, the correct answer to this question is letter d.
|
question 2 - (Urca) In guinea pigs, the Andes rodent is widely bred in captivity all over the world, the short hair is conditioned by a dominant gene, and the long hair is conditioned by a pair of recessive alleles. Smooth hair is conditioned by a dominant gene, and curly hair by a pair of recessive genes. If a pair of guinea pigs heterozygous for the two traits involving the type of hair is crossed, what percentage of guinea pigs with the same phenotype as the parents can we expect? a) 6% b) 12% c) 25% d) 50% e) 56% |
Answer to question 2: According to the statement, short hair is determined by a dominant gene (L), while long hair is determined by a recessive (l) allele. On the other hand, smooth hair is conditioned by a dominant allele (C), while curly hair is conditioned by a recessive allele (c). If the pair of guinea pigs is heterozygous for both characteristics, we have that each individual is LlCc and presents the phenotype of short and smooth hair. These individuals will form gametes: LC, Lc, lC and lc. By crossing the two guinea pigs, we have:
LC |
lc |
lC |
lc |
|
LC |
LLCC |
LLCc |
LlCC |
LlCc |
lc |
LLCc |
LLcc |
LlCc |
Llcc |
lC |
LlCC |
LlCc |
llCC |
llCc |
lc |
LlCc |
Llcc |
llCc |
llcc |
Individuals who have a short, straight hair phenotype, similar to their parents, are those who have at least one L allele and one C allele. These individuals were highlighted in green color and correspond to 9/16, or 56%. Therefore, the correct alternative is the letter e.
By Ma. Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/domonancia-recessividade.htm