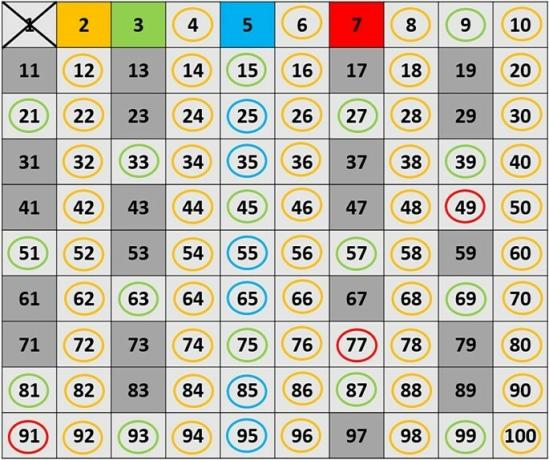
Even numbers are those ending in 0, 2, 4, 6 or 8, while odd numbers end in 1, 3, 5, 7 or 9. Every natural number is either even or odd, there being no other possibility. In mathematics, this concept is called parity.

Pair numbers
Formally, there is another criterion for saying that a number is even, that of division by 2. Every even number is divisible by 2, and being divisible means that the division is exact, or the remainder is zero.
Examples
As the division is exact, we can say that 12 is an even number.
It is possible to write an algebraic expression for the pairs:
Where,
p is an even number,
n is any natural number.
This is equivalent to saying that every integer multiplied by 2 is, therefore, even. That is, every multiple of 2 is even.
Then p is even if and only if p is a multiple of 2.
Odd numbers
Since every non-even integer is odd, it can be said that every number not divisible by 2 is odd. Also, when dividing an odd number by 2, the remainder is 1.
Example
The number 4.5 is not an integer, which means that the division is not exact, so we say that 9 is odd. Notice that the number 9 can be written as a multiplication and an addition.
Likewise, every odd number can too.
15 = 2x7+1
23 = 2 x 11 + 1
57 = 2x28+1
109 = 2 x 54 + 1
We can generalize an expression to every odd number.
Where,
i is an odd number,
n is any natural.
Then i is odd if and only if i no is a multiple of 2. Another test is to divide by 2, if the remainder is 1, the number is odd.
Set of even and odd numbers
Even and odd numbers are grouped into sets. These sets are infinite, as there is always a successor.
The set of pairs can be represented as:
PAIRS = {0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, …}
The set of odds:
ODD = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, …}
Both are contained in a larger numerical set, the set of natural numbers. Its representation is:
properties and curiosities
- The sum of two even numbers results in an even number.
- The sum of two odd numbers is a number pair.
- Multiplying two odd numbers results in an odd number.
- Multiplying two even numbers, that is, one even and one odd, results in an even number.
- An integer can only be classified as even or odd.
- Even is any whole number divisible by 2.
- Odd is any whole number not divisible by 2.
- Even and odd are always consecutive.
- Between two even numbers there is always an odd number.
- Between two odd numbers there is always an even.
You may be interested in:
- Natural Numbers
- Numerical sets
ASTH, Rafael. Even and odd numbers: what they are and how to define them.All Matter, [n.d.]. Available in: https://www.todamateria.com.br/numeros-pares-e-impares/. Access at:
See too
- What are Prime Numbers?
- Numerical Set Exercises
- multiples and divisors
- What are prime and composite numbers?
- multiples
- Whole number exercises with answer
- division exercises
- GCD - Greatest Common Divisor