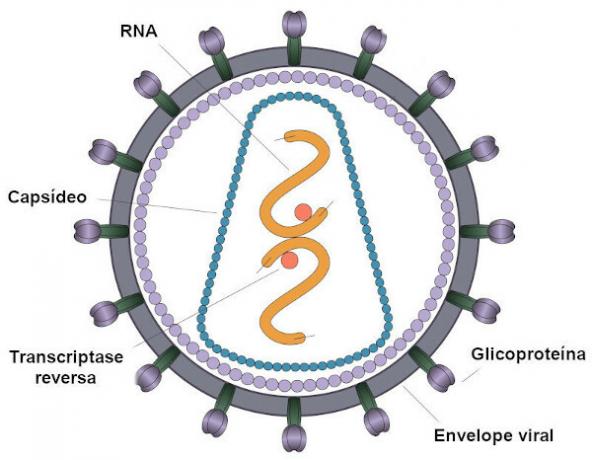
retrovirus they are virus that have RNA as genetic material and have an enzyme called reverse transcriptase, which is capable of transcribing an RNA template into DNA. In addition, retroviruses stand out for being enveloped viruses. The best-known example of a retrovirus is HIV, responsible for causing ssyndrome of Imunodeficiency Aacquired.
Read too: What are adenoviruses and what can they cause?
Abstract about retroviruses
Retroviruses are viruses that have reverse transcriptase.
The genetic material of retroviruses is RNA.
Reverse transcriptase transcribes an RNA template into DNA.
The enzyme is called reverse transcriptase because the flow of information occurs in the opposite direction to normal.
HIV is the best known retrovirus.
What is retrovirus?
retrovirus are virusesthat have a genetic material consisting of RNA and the presence of the enzyme reverse transcriptase. This enzyme is capable of transforming the RNA of the virus into complementary DNA, which will be incorporated into the DNA of the virus. cell hostess.
It is important to note that reverse transcriptase establishes a flow of information from RNA to DNA, which is the opposite of the normal direction that occurs in DNA. transcription. Hence the reason for the enzyme present in these viruses will be called reverse.
Another characteristic observed in the so-called retroviruses is the fact dIt is they be enveloped. The envelope is an outer membrane derived from the plasma membrane of the host cell, however most of the molecules present in this membrane are encoded by genes of the virus.
How do retroviruses replicate?
Next, we will describe the replication of the HIV virus to explain a typical retrovirus reproductive cycle. Initially, the virus fuses with the host cell membrane. The retrovirus then releases into the cytoplasm RNA and proteins viruses, in addition to reverse transcriptase. The enzyme will be responsible for catalyzing the synthesis of a complementary DNA strand (cDNA) to the viral RNA.

The newly synthesized viral DNA will enter the host cell nucleus and bind to the cell's chromosomal DNA. The integrated viral DNA, which is called a provirus, will remain in the genome of the host. The provirus genes will be transcribed into RNA molecules, which may act as mRNA in the synthesis of viral proteins and also as a genome for the new viruses that will be formed.
See too: How to prevent viral diseases?
Retroviruses and HIV
HIV, the human immunodeficiency virus, is one of the most well-known retroviruses worldwide. This virus affects specific cells in our immune system, the so-called T-CD4+ lymphocytes, and is responsible for triggering a syndrome known as AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome).
Aids stands out for being a disease that causes the weakening of our immune system, making the individual more susceptible to opportunistic diseases. It is worth mentioning that Being HIV positive is not the same as having AIDS.. An individual can live for many years with the virus without developing the syndrome. We say that a person has AIDS only when he reaches the most advanced stage of the disease. infection by HIV.
People with HIV can currently rely on medications that improve their quality of life and even reduce the risk of virus transmission for other people. O treatment is commonly called antiretroviral therapy and can be obtained free of charge by United Health System (SUS).
It is important to highlight that the HIV virus is transmitted through the exchange of fluiof the corporealsuch as semen, vaginal secretions, blood It is milk maternal. One of the main forms of prevention is the use of condoms in all sexual intercourse. It is also essential to emphasize that hugging and kissing people with HIV are not considered forms of transmission.
By Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos
Biology teacher

