Vegetation is the set of plants that covers the soil of a certain area, and its development depends on the characteristics of that soil, the relief and the predominant type of climate. Thus, we find a wide variety of plant formations all over the world and also in Brazil.
Vegetation is fundamental to a series of processes in nature, like biogeochemical cycles and climate regulation. In addition, its presence is important for the biodiversity of planet Earth, for human beings and for carrying out economic activities in society, such as agriculture.
Read too:What are the forms of Brazilian relief?
Topics of this article
- 1 - Summary on vegetation
- 2 - What is vegetation?
- 3 - What is the use of vegetation?
- 4 - What are the types of vegetation?
-
5 - What are the types of vegetation in Brazil?
- → Forest vegetation
- → Savanna vegetation
- → prairie
- → Complex vegetation
- → Video lesson on types of vegetation in Brazil
- 6 - What is the importance of vegetation?
- 7 - What is the relationship between vegetation, climate and soil?
- 8 - What is the relationship between vegetation and agriculture?
Abstract about vegetation
Vegetation is the name given to the set of plants that cover a certain area.
Vegetation development depends mainly on climate, soil and relief.
It has numerous functions, ranging from maintaining biodiversity and soil integrity to participating in biogeochemical cycles.
Vegetation types are: desert, taiga, tundra, steppe, forests (temperate, tropical, equatorial, monsoon, and Mediterranean), prairie (or grassland), savanna, and complex vegetation.
Brazil has a wide variety of plant formations. The typical vegetation of the country are: Amazon forest, Atlantic forest, Araucaria forest, coconut forest, Cerrado, Caatinga, Pampas, Pantanal and mangrove.
Vegetation is fundamental for the balance of the environment and climate regulation, in addition to playing an important role for society.
The maintenance of native vegetation has many benefits for economic activities, especially for agriculture.
What is vegetation?
Vegetation can be defined as the set of plants and vegetables that covers a certain surface, forming different types of natural landscape. The type of vegetation that characterizes an area depends on three main factors:
type of weather, which determines the availability of humidity and solar radiation.
soil type, which is related to the nutrients and support structure of the plant.
Relief of the land where they develop, which can affect the elements mentioned above, such as the depth of the soil, the leaching of nutrients from the substrate, etc.
Do not stop now... There's more after the publicity ;)
What is vegetation for?
Vegetation has several important functions. for the maintenance of biodiversity, for soil maintenance and for the regulation of processes and cycles that take place in the environment. Taking this into account, we can say that the vegetation serves for:
Protect the soil structure from the impact of rainwater.
Ensuring the stability of the substrate structure on steep slopes, preventing erosion and landslides.
Provide organic matter for the soil and ensure its nutrient recharge.
Regulate local temperatures and provide moisture to the atmosphere.
Supply oxygen to the atmosphere, regulating the cycle of this and other elements (like carbon and nitrogen).
Habitat for different species of animals.
Obtaining natural resources by human beings.
Assist in the maintenance of water bodies.
See too: Forests — what they are, how they form and main types
What are the types of vegetation?
Deserts: have soils that are very poor in nutrients and lack of moisture, which results in a very sparse and almost non-existent vegetation. In hot deserts, it is possible to observe the presence of adapted bushes to adverse weather conditions, as well as flowers that grow in the midst of rocks and dunes. In the frozen deserts, one finds undergrowth, moss and lichens in regions protected from extreme cold.
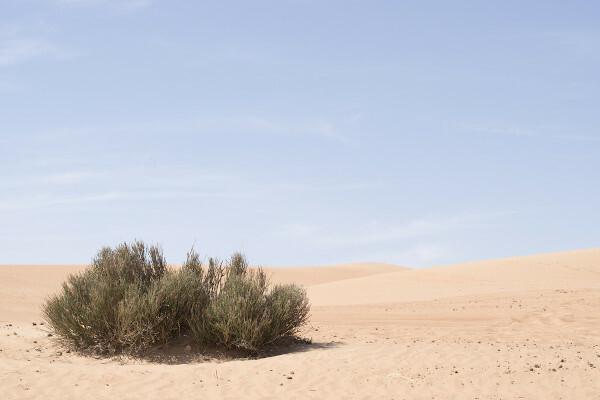

Steppes: are wide fields of grasses and some species of shrubby plants that grow in regions with a dry climate, most commonly in the transition between deserts and other types of denser vegetation. To learn more about this type of vegetation, click here.
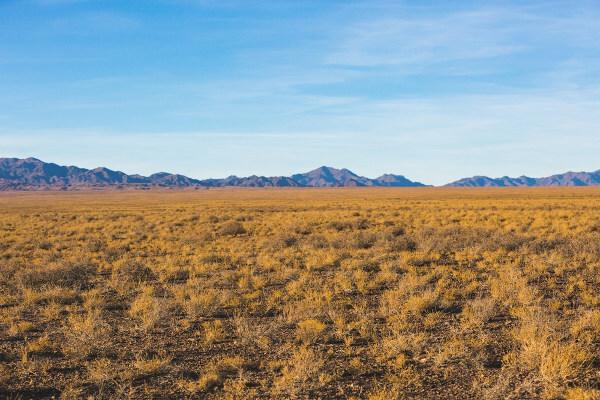

Prairie: it is often confused with the steppes. However, this vegetation is composed of herbaceous plants and grasses which can reach up to two meters in height (high prairie), and develop in climates with greater availability of moisture, such as in the subtropics. Prairies are also called fields. Also, in Brazil, this type of vegetation is called pampas. To learn more about prairies, click here.

Tundra: develops in areas of high altitude (alpine tundra) or high latitude (arctic tundra), and is consisting mainly of small plants, such as grasses and shrubs, and creeping species. The soils in which this vegetation develops are poor in nutrients, and spend most of the time frozen. To learn more about this type of vegetation, click here.

Taiga: it is located in areas with a cold climate, with severe winters and mild summers, which develop in mid-latitudes. It presents tall trees, predominantly conifers. These trees share space with smaller plants, such as shrubs, grasses and creeping species. They are also known as boreal forest. To learn more about this vegetation, click here.

Savannah: It develops in areas with a tropical and semi-arid climate, with alternating dry and rainy seasons and high average temperatures. the savanna is made up of deciduous trees (which lose their leaves in the dry season) of medium and small size, shrubs and grasses. The woody and shrubby species present in the savannas present twisted stem and adaptation to dry weather and fire. The roots tend to be deep and the leaves narrower. To learn more about this type of vegetation, click here.

temperate forest: also called temperate deciduous forest, it is a denser vegetation formation that occurs in regions of medium latitude and mild climate. É formed by medium and large trees, with broad leaves that are renewed throughout the year. This means that trees in temperate forests lose their leaves in the dry period, being characterized as deciduous or semi-deciduous (the period of leaf loss is shorter).

Mediterranean forest: Also called Mediterranean vegetation, this type of vegetation is made up of bushy plants adapted to hot and dry periods, such as summers in the Mediterranean climate. The Mediterranean forest is formed by the coverage of maquis (higher bush density) or garrigue (lower bush density).

Tropical forest: this vegetal formation, classified as dense rain forest, presents great complexity and is quite heterogeneous in terms of biodiversity. It grows in areas that receive a lot of sunlight throughout the year and that have tropical climates that may or may not have a dry season. Tropical forests have a high and dense canopy, derived from the large trees with broad leaves that are present in this type of vegetation. In addition to tall trees,species of different heights can be found. that form the different plant strata found in this type of forest.

equatorial forest: can be described as a type of tropical forest that occurs exclusively in the equatorial climate, or humid tropical climate, which has very high air humidity and no dry season. The world's existing equatorial forests, such as the Amazon and the Congo Forest, are home to a significant portion of our planet's biodiversity. To learn more about this type of vegetation, click here.
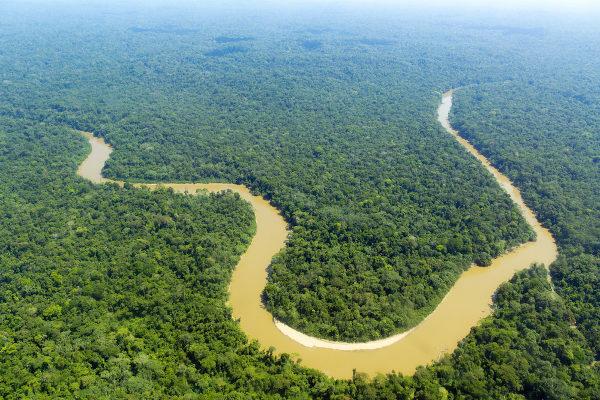

monsoon forest: this type of vegetation is quite specific to the tropical monsoon climate that occurs on the Asian continent. It can be described as a type of rainforest that features both deciduous and evergreen trees, due to the distinct rainfall regime of this climate, in addition to a less closed canopy than in the traditional tropical forests, thus allowing the greatest passage of light to the most down.|1|

Complex vegetation: commonly covers areas with a tropical climate. The complex vegetation is composed of different types of plant species, ranging from shrubs to medium-sized trees, some of which can adapt to dry weather and extreme heat, or even to the humid conditions of coastal areas. The Brazilian Pantanal is an example of complex vegetation, because it presents elements of more than one type of vegetation. Coastal vegetation, such as mangroves, may also be included in this category.
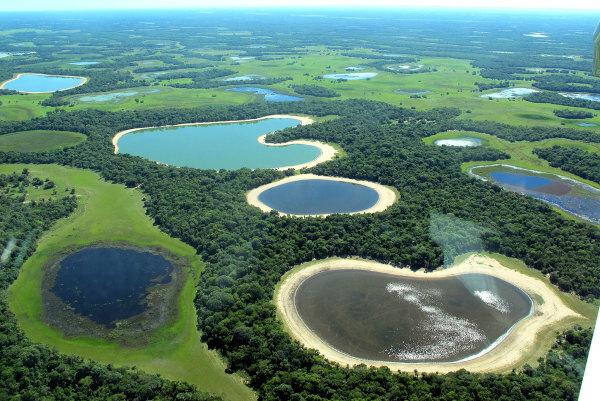

What are the types of vegetation in Brazil?
Brazil has one of the greatest landscape and biological diversity in the world. In its more than 8.5 million square kilometers of territory, the variety of climates and soils, in addition to the different forms of relief, conditions the development of forests, savannas, prairies and vegetation complex. Check below what are the main Brazilian plant formations.
→ forest vegetation
- Amazon rainforest: it is considered the largest equatorial forest in the world. The Amazon predominantly covers the northern region of the country, and is characterized by dense vegetation adapted to the climate hot and very humid, being still constituted by three strata: forest of igapó, forest of várzea and forest of land firm.
- Atlantic forest: It is a type of tropical forest that extends along the east coast of Brazil, occurring under a humid tropical climate. It covers some of the areas with the highest population density in the country, which is why it registers a high rate of degradation.
- Araucaria forest: it is a type of rainforest that covers areas of subtropical climate, most found in the states of the southern region of Brazil, with emphasis on Paraná. This formation receives the name of araucaria forest due to the presence of Paraná pine or araucaria.
- Coconut forest: It is a type of rainforest that can be classified as an ecotone, which is nothing more than a transitional cover between different types of vegetation. In the case of the cocais forest, it is located between the Amazon Forest, the caatinga and the cerrado. It extends through the North and Northeast regions of the country.
→ savanna vegetation
- Thick: is commonly described as a type of Brazilian savannah, being predominantly present in the regions with an alternately dry and rainy tropical climate, such as part of the Southeast and throughout the Midwest of the country.
Caatinga: can be described as a type of Brazilian savanna and as a complex vegetation, as we saw earlier. Unlike the cerrado, the caatinga is present in the semi-arid climate, marked by a long season without rain. For this reason, xerophytic species, adapted to heat and drought, can be identified in this vegetation formation.
→ Prairie
- Pampas: the pampas vegetation is present only in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, being characterized by broad fields of grasses of varying sizes that cover the plains of this part of the territory Brazilian.
→ complex vegetation
- Pantanal: it covers plain areas in the states of Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul, close to the Amazon rainforest and the cerrado. The swamp is formed by riparian forests, shrubs, grass fields and aquatic plants that are located in the floodplains — areas that are filled with water during the flooding of the rivers.
Mangrove: It is a type of coastal vegetation composed of plants adapted to both fresh and salt water from the sea. The mangrove can be found along the entire Brazilian coast, from the coast of Amapá, in the North of the country, to the South region, in the state of Santa Catarina.
→ Video lesson on types of vegetation in Brazil
What is the importance of vegetation?
The vegetation that covers an area is of great importance for the soil, for the regulation of the elements and processes of the environment and for human beings.
The vegetation cover protect the soildirect action of water and sunlight, in addition to being essential for supporting the substrate on a slope or slope. The removal of vegetation from very steep terrain can cause landslides and the fall of blocks of rock and soil. With the deposition of leaves, branches and other materials from the vegetation, an important layer of organic material is formed, called litter, which provides nutrients to the soil. This burlap also offers a new layer of protection to the substrate.
The microclimate (local atmospheric conditions) is regulated by the presence or absence of vegetation, which provides an important moisture load to the air through the process of transpiration and controls temperatures. When we consider large formations, such as tropical forests, their presence can influence the distribution of moisture in wider areas, in addition to assist in recharging springs and maintaining water quality.|3|
The biological functions of plants make vegetation an important place for the proper functioning of biogeochemical cycles, such as water, carbon and oxygen, which benefit local biodiversity and human beings. In addition, the vegetation serves as a habitat for many species of animals and can be used as a resource by society.
Know more: Deforestation in the Amazon — main causes and consequences
What is the relationship between vegetation, climate and soil?
Vegetation, climate and soil are aspects and components of nature that are directly related, with a view to dependency on one another. The soil development process, called pedogenesis, happens according to the speed and type of weathering that affects an area, which directly depends on the elements of the climate.
These climatic elements, such as solar radiation, humidity and temperature, influence the development of plants. It is also noted that the vegetation that develops in specific types of climate and soil supplies elements to the atmosphere and renews soil nutrients. To learn more about this topic, click here.
What is the relationship between vegetation and agriculture?
The ever-increasing demand for raw materials of agricultural origin, and also for food, means that new areas are opened every day for the development of this activity. This process removes the original vegetation coverand directly impacts the balance of the environment, which has been observed in several areas of the world, notably in Brazilian biomes such as the Amazon and the Cerrado. The removal of native vegetation, however, does not imply benefits for agriculture.
As we saw earlier, vegetation is important for microclimate and humidity regulation, for water bodies (aquifers and rivers) and for soil nutritional and structural maintenance. For that reason, she becomes an ally of agricultural activity in guaranteeing adequate environmental conditions for production, and it is important to ensure the crop productivity.
Grades
|1| IBGE. School atlas. Rio de Janeiro: IBGE, 2018. 8. ed.
|2| IBGE. School atlas. Rio de Janeiro: IBGE, 2018. 8. ed.
|3| STATE GOVERNMENT PORTAL. Vegetation maintains water quality and preserves soil. Government of the State of São Paulo, 16 Aug. 2015. Available in: https://www.saopaulo.sp.gov.br/ultimas-noticias/vegetacao-mantem-qualidade-da-agua-e-preserva-solo/
By Paloma Guitarrara
Geography Teacher
See the characteristics of the six Brazilian biomes: Cerrado, Amazon, Atlantic Forest, Pantanal, Pampa and Caatinga.
Do you know which are the main biomes in the world? Click here to know its features!
Learn a little more about the carbon cycle, the cycle of an element found in various materials that make up the planet and in organic molecules.
Understand what biogeochemical cycles are, the factors that influence them and their importance for the maintenance of ecosystems.
Learn what deforestation is and how this practice has caused numerous environmental problems. See how deforestation is doing in the world and in Brazilian biomes.
Click here, understand what forests are and how they are formed. See data on forests in Brazil and around the world.
Get to know the main types of vegetation in Brazil and their specific characteristics.
Access the link to read a little more about the vegetation of Brazil. Find out what are the main types of vegetation that cover the country and their main aspects.