A carbonyl is an oxygenated functional group formed by a carbon atom of sp hybridization2, in which the double covalent bond is exerted with a oxygen atom (C=O). It is present in several organic functions, such as aldehydes, ketones, in addition to carboxylic acids and their derivatives.
Read too: Aromatic hydrocarbons — organic compounds made up exclusively of carbon and hydrogen atoms
Topics of this article
- 1 - Summary about carbonyl
- 2 - What is the formula of carbonyl?
- 3 - What are the compounds with the carbonyl group?
- 4 - Differences between carbonyl and carboxyl
- 5 - Solved exercises on carbonyl
Carbonyl summary
- A carbonyl is an oxygenated functional group in which the carbon atom forms a double covalent bond with an oxygen atom.
- Depending on the other atoms attached to the carbonyl, we have different organic functions.
- The carbonylated compounds are, basically, the aldehyde, the ketone, in addition to the carboxylic acid and its derivatives.
- The number of carboxylic acid derivatives is so large that, sometimes, some authors credit the carboxyl (junction between carbonyl and hydroxyl) as a new functional group.
Do not stop now... There's more after the publicity ;)
What is the formula for carbonyl?
The carbonyl is a oxygenated functional group consisting of a carbon atom making a covalent bond double with an oxygen atom, which can be represented by C=O. The two remaining single covalent bonds can be formed with other atoms without restriction.

What are the compounds with the carbonyl group?
Compounds that have a carbonyl group are called carbonyls. Commonly, the term covers only two organic functions, aldehydes and ketones. However, carboxylic acids and their derivatives are also considered carbonyl compounds.
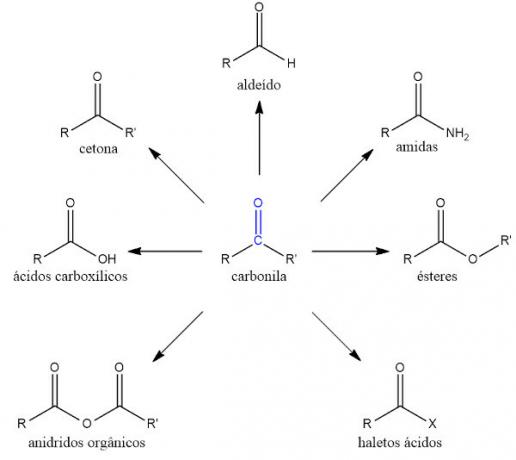
- Aldehydes: in this function, the carbonyl group always occurs at the end of the chain, with the function's carbon being number 1 in the main chain.
- Ketones: in this function, the carbonyl group always occurs between two carbons.
- carboxylic acids: in this function, one of the single bonds of the carbonyl group is made with the hydroxyl group. As with aldehydes, the carbonyl occurs at the end of the chain, with the carbonyl carbon number 1 on the main chain.
- Esters: Considered derivatives of carboxylic acids, esters have a carbonyl in which one of the single bonds are made with an oxygen atom, which is attached to another carbon chain any. Therefore, the oxygen atom acts as a heteroatom.
- Organic anhydrides: plus a group derived from carboxylic acid, in which two carbonyls are bonded to a common oxygen atom.
- Acid halides: carboxylic acid derivatives in which the carbonyl is attached directly to a halogen (element of group 17 of the Periodic table).
- Amides:nitrogen function which can also be considered a carboxylic acid derivative, in which one of the carbonyl single bonds is made with a nitrogen atom.
Important: Carbonyl compounds fall within a broader class known as oxo compounds. oxo compounds). This class encompasses all functions that have an atom connected, through a double covalent bond, with the oxygen atom, that is, not only carbonyl compounds but also carbonyl compounds. sulfur compounds, like the sulfonic acid.
See too: Isonitrils — organic compounds originating from inorganic substances
Differences between carbonyl and carboxyl
Although carboxylic acid and its derivatives are considered carbonyl compounds, it is common for some authors to distinguish between carbonyl and carboxyl.

The word “carboxyl” originates from the contraction of two words: carbonyl and hydroxyl. This is easy to understand, since carboxyl is a functional group in which the carbonyl is directly attached to the hydroxyl group.
chemically, The carboxyl carbon is generally more positive than the carbonyl carbon., after all, is bonded to two oxygen atoms, both of which are very electronegative. This makes this carbon more susceptible to nucleophilic attack by nucleophiles.
Solved exercises on carbonyl
question 1
(Uniube) Organic compounds are classified according to the organic functions present in their chemical structures. They represent a large family of compounds, many of them with important biological activities. Of the compounds listed below, which one contains the carbonyl group in its chemical structure is:
A) butane
B) ethylamine
C) propan-1-ol
D) ethanal
E) benzene
Resolution:
Alternative D
Ethanal, being an aldehyde, has the carbonyl group in its chemical structure. The other compounds do not belong to any carbonyl function, being butane It is benzene belonging to Hydrocarbons; ethylamine, at amines; and propan-1-ol, to alcohols.
question 2
(UFRN) Benzocaine (ethyl para-aminobenzoate) is generally used as a local anesthetic for endoscopy. This compound is obtained by the reaction of paraaminobenzoic acid with ethanol, in an acid medium, according to the reaction:
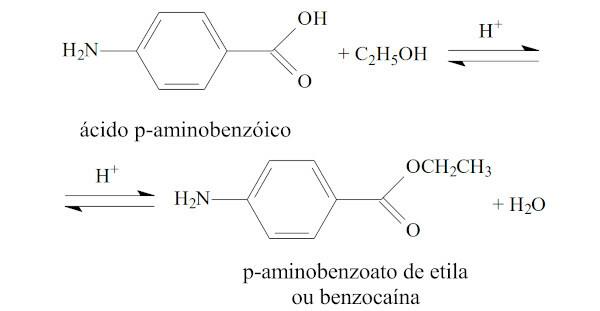
Regarding benzocaine, it can be stated that
A) has a carbonyl.
B) does not form hydrogen bonds.
C) forms an ionic bond between nitrogen and carbon atoms.
D) has no resonance but has double bonds.
Resolution:
Alternative A
The carbonyl is present in benzocaine, directly attached to the benzene ring.
Option B is wrong because there is a possibility of formation of hydrogen bonds by the amine group (–NH2).
Choice C is wrong because the bond between nitrogen and carbon is covalent.
Alternative D is wrong because the aromatic (benzene) ring does have resonance, an essential effect for its stability.
By Stefano Araujo Novais
Chemistry teacher
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
NOVAIS, Stefano Araujo. "Carbonyl"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/carbonila.htm. Accessed on July 4, 2023.
Aldehydes, carbonyl compounds, carbonyl group, Main aldehydes, Ethanal, raw material in the pesticide and medicine industry, Methanal, formaldehyde, plastics and resins industry.
Learn more about amide classifications according to their substituents. Learn how the nomenclature of the compound is made and its main applications.
Organic anhydrides are products originating from the elimination of water from carboxylic acid molecules.
Ketones, organic substances, carbonyl functional group, obtaining nail polish solvent, propanone, ketone bodies in the bloodstream, extraction of oils and fats from plant seeds, solvents organic.
Click to learn about the main characteristics and the IUPAC nomenclature of organic substances called acid chlorides.
Learn about carboxylic acids. Learn what their characteristics are, how they are named and which of them are present in everyday life.
Esters, food flavoring, flavorings, esterification reaction, Methyl anthranilate, Pentyl acetate, Butyl ethanoate, Ethyl butanoate, Propanetriol, Glycerin, Stearin.
Cringe
The slang adapted from English is used to designate someone who is seen as tacky, shameful, outdated and out of fashion.
Neurodiversity
A term coined by Judy Singer, it is used to describe the wide variety of ways the human mind behaves.
PL of Fake News
Also known as PL2660, it is a bill that establishes mechanisms for the regulation of social networks in Brazil.


