Brazilian energy matrix is the set of energy sources used in the national territory. Just over half of Brazil's energy matrix (55%) is made up of non-renewable sources of energy generation, with emphasis on fossil fuels. Despite this, attention is drawn to the large share of sources considered clean, such as biofuels and hydraulic energy. For this reason, the Brazilian energy matrix is considered one of the most renewable in the world.
Check out our podcast:What are the main impacts generated by the use of energy sources?
Topics of this article
- 1 - Summary of the Brazilian energy matrix
- 2 - What is the energy matrix?
- 3 - What is the Brazilian energy matrix?
- 4 - Graph of the Brazilian energy matrix
-
5 - What are the advantages and disadvantages of the Brazilian energy matrix?
- → Advantages of the Brazilian energy matrix
- → Disadvantages of the Brazilian energy matrix
- 6 - World energy matrix
- 7 - What is the Brazilian electrical matrix?
- 8 - Solved exercises on the Brazilian energy matrix
Summary on the Brazilian energy matrix
The Brazilian energy matrix is the set of sources used to generate all the energy that is consumed in the national territory.
It is formed by 55.2% of non-renewable sources and 44.8% of renewable sources.
Oil, natural gas, sugarcane biomass and hydropower are the main sources of energy in the Brazilian energy matrix.
One advantage of the Brazilian energy matrix is the large share of renewable sources in its composition. As a result, it is considered one of the cleanest in the world.
However, non-renewable sources, such as fossil fuels, still represent more than half of the matrix. This is one of its downsides.
The world energy matrix is dominated by fossil fuels (natural gas, oil and mineral coal). Renewable sources represent only 15% of global energy.
The Brazilian electrical matrix is formed by the energy sources used in the generation of electricity.
Renewable sources make up 78.1% of the electricity matrix in Brazil, with emphasis on hydropower, which represents a slice of 56.8% of the electricity produced in the country.
What is an energy matrix?
Energy matrix is the given nameThethe set of fonts used for the generation dThe energy consumed in a certain locality. The composition of the energy matrix therefore takes into account the relationship between energy consumption by different users (industry, agriculture, commerce, residences, etc.) and supply from both renewable and non-renewable sources renewable. It is important to briefly resume what each of these types of energy sources is:
Renewable sources power generation: elements that have rapid replacement capacity in nature, which is why they are characterized as inexhaustible. Examples: water, solar radiation, winds, biomass, tides, and Earth's internal heat.
non-renewable sources power generation: elements that do not regenerate quickly in nature and whose reserves could be depleted in the near future. Examples: petroleum, mineral coal, natural gas, and radioactive substances such as uranium.
Do not stop now... There's more after the publicity ;)
What is the Brazilian energy matrix?
The Brazilian energy matrix is made up of 44,8% of renewable energy sources, according to the Energy Research Company (EPE), which makes it one of the cleanest in the world.
One of these renewable sources is water, used in the generation of hydroelectric energy. While The hydraulic energy represents 11% of the energy matrix Brazilian, water accounts for 56.8% of the electricity generated in Brazil, making it the main source of electricity in the country.
Despite the drop observed between 2020 and 2021 (explained by factors such as the water scarcity in the country), The biomass and other elements derived from sugarcane represent the main source of renewable energy in Brazil, accounting for 16.4% of the national energy matrix. In the case of ethanol, one of the elements derived from sugarcane, its main use is as fuel in the transport sector.
Firewood, charcoal and other sources complete the picture of renewable resources in the Brazilian energy matrix. The set described as “other renewable sources” by EPE includes energy sources that have grown in recent years in Brazil, such as wind energy and solar energy. This group also includes lye (or black liquor) — the liquid resulting from pulp and paper processing —, biodiesel and biogas.
Despite the increasing use of renewable energy, Non-renewable sources are predominant in the Brazilian energy matrix. The most recent EPE report indicates that this type of source represents 55.2% of the country's energy matrix, with a greater share of fossil fuels. Oil alone accounts for 34.4% of the energy consumed in Brazil, followed by natural gas (13.3%) and mineral coal (5.6%). In addition to these, uranium is also part of the Brazilian matrix, being used in the generation of nuclear energy.
Graph of the Brazilian energy matrix
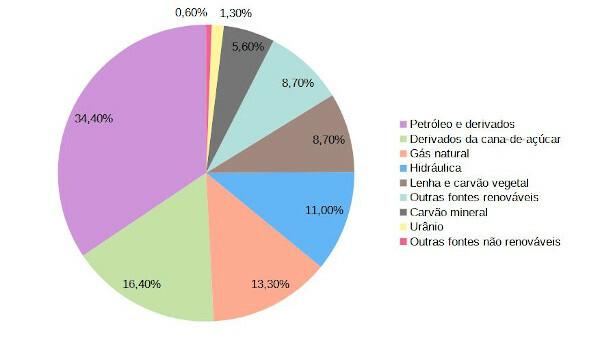
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the Brazilian energy matrix?
→ Advantages of the Brazilian energy matrix
The Brazilian energy matrix is quite diverse and it is considered one of the cleanest in the world, which configures its main advantages.
Based on this picture, we can say that the consumption and generation of energy in Brazil become less aggressive to the environment and emit less polluting gases in the atmosphere compared to other countries that rely on fossil fuels, such as natural gas, which is widely used to heat homes in colder regions of the world.
→ Disadvantages of the Brazilian energy matrix
A predominance of non-renewable sources is the biggest disadvantage of the Brazilian energy matrix, since these sources represent more than half of the country's energy generation.
There has been a recent increase in the use of clean energy in Brazil, with emphasis on solar and wind energy. However, the infrastructure for its installation demands a high investment, in addition to its use and their use depend on atmospheric and climatic factors, which becomes an impediment to their use in some areas of the country.
There are still many socio-environmental impacts caused by power generation through renewable and non-renewable sources. Fossil fuels, as we know, are highly polluting and cause numerous environmental problems, in addition to contributing to the worsening of global warming.
In the case of clean sources, the opening of areas for the construction of power plants and power generation centers and their own infrastructure can cause an imbalance environmental impact with deforestation, diversion of watercourses and changes in soils, which damages biodiversity and can result in inconvenience for the population local.
Read too: How is electricity distributed in Brazil?
world energy matrix
The world energy matrix is against the Brazilian energy matrix. According to data from the International Energy Agency (IEA), Thes non-renewable energy sources account for 85% of the world's energy matrix, and, of these, only fossil fuels (oil, coal and natural gas) represent almost 80%. Of the renewable sources, biofuels and biomass are the most used worldwide, representing 9.8% of the energy matrix.
Check the composition of the world energy matrix in the following table |1|:
world energy matrix | |
Power supply |
Participation |
Petroleum |
29,5% |
Mineral coal |
26,8% |
Natural gas |
23,7% |
Biofuels and biomass |
9,8% |
Nuclear |
5% |
Hydraulics |
2,7% |
Other sources (solar, wind, thermal, etc.) |
2,5% |
What is the Brazilian electrical matrix?
The Brazilian electrical matrix is nothing more than the set of sources used to generate electricity in the country. More than half of the electricity in Brazil corresponds to Hydro-electric energy, from hydroelectric plants. Considering all renewable sources, they correspond to 78.1% of electricity generation in the national territory. As a result, we can say that Brazil has a clean (or renewable) electrical matrix.
Check how the Brazilian electrical matrix is composed in the following table |2|:
Brazilian electrical matrix | |
Power supply |
Participation |
Hydraulics |
56,8% |
Natural gas |
12,8% |
Wind |
10,6% |
Biomass |
8,2% |
Coal and derivatives |
3,9% |
Oil derivates |
3% |
Solar |
2,5% |
Nuclear |
2,2% |
Solved exercises on the Brazilian energy matrix
question 1
(Unicamp) Energy matrix is the set of available energy sources. The following graphs represent the energy matrix in the world and in Brazil, showing renewable and non-renewable energy sources.
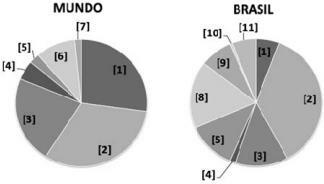
[1] Charcoal.
[2] Oil and derivatives.
[3] Natural gas.
[4] Nuclear.
[5] Hydraulic energy.
[6] Biomass.
[7] Solar, wind and geothermal energy.
[8] Sugarcane derivatives.
[9] Firewood and charcoal.
[10] Other non-renewable sources.
[11] Bleach (liquid resulting from wood processing for pulp extraction) and other renewable sources.
(Source: http://www.epe.gov.br/pt/abcdenergia/matriz-energetica-e-eletrica. Accessed 5/2/2019.)
Considering your knowledge about the environment and the information provided, mark the correct alternative.
A) The Brazilian energy matrix uses a smaller percentage of renewable energy than the world's, with the predominant use of fossil fuels.
B) Natural gas, biomass, hydropower, solar, wind and geothermal energy are the renewable energy sources used in the world matrix.
C) The Brazilian energy matrix is more dependent on renewable energy sources than the world matrix, as an alternative to the use of fossil fuels.
D) Biofuels derived from sugarcane and natural gas are the main renewable sources in the Brazilian and world matrices, respectively.
Resolution:
Alternative C
The Brazilian energy matrix uses more renewable sources than the world matrix. More than 44% of energy sources in Brazil are considered clean, while in the rest of the world this share drops to just 15%.
question 2
(Unesp) Oil leads and will continue to lead the ranking of energy sources in the coming decades, followed by coal and natural gas. Other energy sources are also pointed out as alternatives for the 21st century. Check the alternative that highlights Brazil's contribution to this global scenario.
A) Brazil emerges with technologies for the production of nuclear energy as a more economical alternative than the others.
B) Brazil has, in recent years, exported knowledge and technologies in the wind energy sector, leading the ranking in this sector.
C) In Brazil, small industries are responsible for production and for international agreements relating to biofuel.
D) Studies on solar energy used in southern Brazil have attracted the attention of countries such as England and Italy, which have invested heavily in the sector.
E) Brazil has great advantages (physical and territorial) for the production of biofuel, which enhance the production of renewable energy.
Resolution:
Alternative E
The biofuel produced from sugarcane is one of the means of contribution of Brazil in this global scenario, considering the conditions climatic conditions conducive to the development of this crop and the wide extensions of planted land, made possible by the territorial extension of the country.
Grades
|1| IEA. Energy Statistics Data Browser: Energy supply. IEA, 2021. Available here.
|2| EPE. National Energy Balance 2022: Base year 2021. Rio de Janeiro: Energy Research Company (EPE), 2022. Available here.
By Paloma Guitarrara
Geography Teacher
Do you know what's behind the energy crisis experienced by Brazil in 2021? Read our text and understand its causes and consequences. Know if there are risks of blackout.
Click here, learn what geothermal energy is, understand how this type of energy works and learn about its advantages and disadvantages.
Learn more about energy sources, resources capable of generating energy, which can be renewable or non-renewable. The following text will address some renewable and non-renewable energy sources, in addition to the advantages and disadvantages of using some energy sources.
Do you know what non-renewable energy sources are? Click here, see examples and understand what are their advantages and disadvantages.
Check out an explanatory summary about each of the main renewable energy sources, their importance and their respective properties.
Understand here the definitions and formalizations of the matrix structure. See also how to operate its elements and the different types of matrices.
