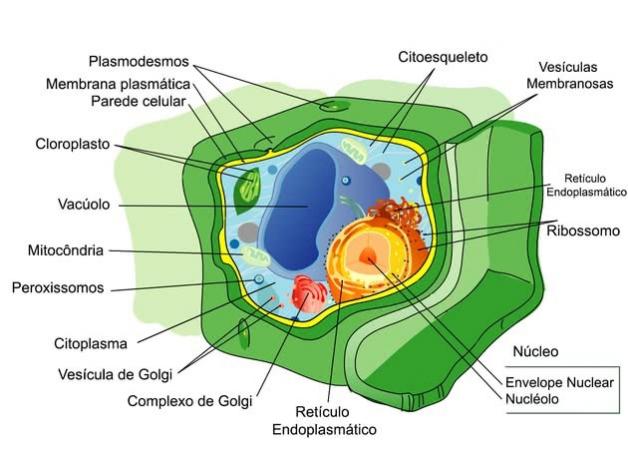
Plant and animal cells have many differences and similarities in their structure.
Animal cells lack cell walls or chloroplasts, which plant cells do. Their shape is also different because animal cells are round and have an irregular shape, while plant cells have fixed and rectangular shapes.
Both plant and animal cells are eukaryotic. That is why they have several characteristics in common, such as the presence of a cell membrane and organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum.
| animal cell | plant cell | |
|---|---|---|
| What is it | These are the cells that make up the tissues of animals. | These are the cells that make up the tissues of plants. |
| cell type | eukaryote | eukaryote |
| cell wall | does not have | Formed by cellulose |
| Format | Circular, irregularly shaped | Rectangular, fixed shape |
| Size | Animal cells are generally smaller than plant cells, ranging from 10 to 30 micrometers in length. | They range from 10 to 100 micrometers in length |
| energy storage | Store energy in the form of glycogen | Store energy as starch |
Growth |
Animal cells increase in size by multiplying the number of their cells | Plant cells get bigger by increasing the size of their cells |
| chloroplast | Animal cells do not have chloroplasts | Plant cells have chloroplasts because they make their own food |
| Centrioles | Present in all animal cells | Only lower forms of plants have centrioles. |
| vacuole | One or more small vacuoles (much smaller than plant cells). | A large central vacuole occupying 90% of the cell volume |
| Cytoplasm | It has | It has |
| ribosome | It has | It has |
| mitochondria | It has | It has |
| plastids | does not have | It has |
| Glyoxysomes | does not have | It has |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | It has | It has |
| Golgi complex | It has | It has |
| peroxisomes | It has | It has |
| Plasma membrane | It has | It has |
| lysosomes | Lysosomes occur in the cytoplasm | Rarely have lysosomes |
Structure of plant cells and animal cells
All eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane, which separates the intracellular and extracellular environment.
However, plant cells also have a cell wall that lines the outside. This wall is formed mainly by cellulose and ensures more resistance to this cell, in addition to giving it its rectangular shape.
Organelles that are different between plant and animal cells:
- Lysosomes: only present in animal cells;
- Centriole: is present in most animal cells. In plants they are found in only a few groups, such as bryophytes and pteridophytes;
- Plastids: present only in plant cells. There are the chromoplasts, leucoplasts and the chloroplast;
- Glyoxysome: present only in plant cells.
Organelles that are common among plant and animal cells:
- Ribosomes;
- Endoplasmic reticulum;
- Golgi complex;
- Peroxisomes;
- Mitochondria;
- Plasma membrane;
- Cytoplasm.
animal eukaryotic cell

plant eukaryotic cell
How do plant and animal cells produce energy?
Plants are autotrophs, they produce energy from sunlight through the process of photosynthesis, using cellular organelles called chloroplasts.
Animal cells do not have chloroplasts, and they produce energy from glucose through the process of cellular respiration.
Cellular respiration in animal cells takes place in the mitochondria, which are analogous to chloroplasts, and also perform the function of producing energy.
See also the difference between:
- Mitosis and Meiosis
- Simple and easy distribution
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
- Viruses, bacteria and fungi