The different types of carbohydrates differ according to the amount of carbon in their formation. The main types of carbohydrates are: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Carbohydrates are the main source of energy obtained through food, they release important sugars for the development of various functions of the human body. They are basically composed of carbon, oxygen and hydrogen ([C(H2O)]n).
| monosaccharides | disaccharides | polysaccharides | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | Simple carbohydrates, reduced in size and quickly absorbed by the body. | Simple carbohydrates, formed by the union of two monosaccharides. | Complex carbohydrates, formed by linking several monosaccharides, have large molecules and are slowly absorbed by the body. |
| Shapes |
|
|
|
| Foods |
|
|
|
Foods can be composed of one or more types of carbohydrates, which when digested release sugar and feed the body's cells.
Simple carbohydrates have a high glycemic index, are quickly digested and absorbed by the body. Complex carbohydrates, on the other hand, require a greater effort from the body for their digestion and release of energy, thus having a lower glycemic index.
monosaccharides
Monosaccharides are simple carbohydrates that do not undergo hydrolysis, such as glucose, fructose and galactose. They are mainly found in fruits, honey and milk.
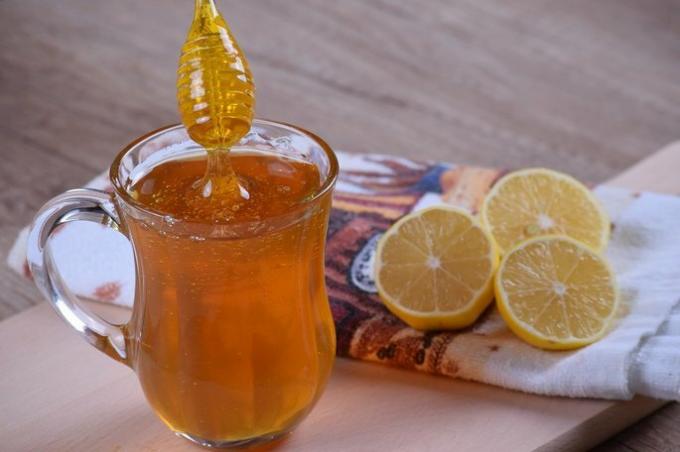

Monosaccharides are primarily responsible for the sweet taste of food. Some rich in this type of carbohydrate are:
- Honey;
- Banana, apple and pineapple;
- Milk (galactose is not found isolated in nature, but associated with lactose in milk).
disaccharides
Disaccharides, also called oligosaccharides, are simple carbohydrates, resulting from the link between two monosaccharides.

The main ones are:
- sucrose: union of glucose with fructose, present in table sugar and some sweeteners;
- Maltose: union of its glucose molecules, extracted from cereals, such as barley, germinated;
- Lactose: union of glucose with galactose, found in milk sugar.
polysaccharides
Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates, have large molecules and are therefore digested more slowly by the body. This type of carbohydrate is found in foods with a low glycemic index.
In general, they are formed by linking smaller carbohydrates. And they play a very important role in food because they gradually release the energy the body needs.
Unlike monosaccharides and disaccharides, polysaccharides act as an energy reservoir that is released over a longer period of time.
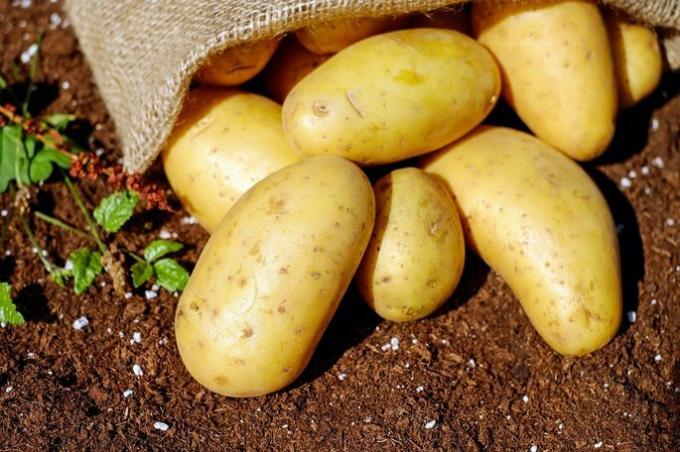

The starch present in foods such as potatoes, cassava and their derivatives are macromolecules that take time to be digested and absorbed by the body.
Carbohydrate-rich foods
Carbohydrate-rich foods release a lot of energy for the body. However, if this energy is not spent through some activity in the body, it tends to be stored in the form of fat.
For this reason, carbohydrates are often seen as villains in diets. For a healthy diet it is necessary to regulate the consumption of carbohydrates.
Breads, cereals, some fruits and vegetables are rich in simple and complex carbohydrates. A moderate consumption related to the activity to be developed is recommended.
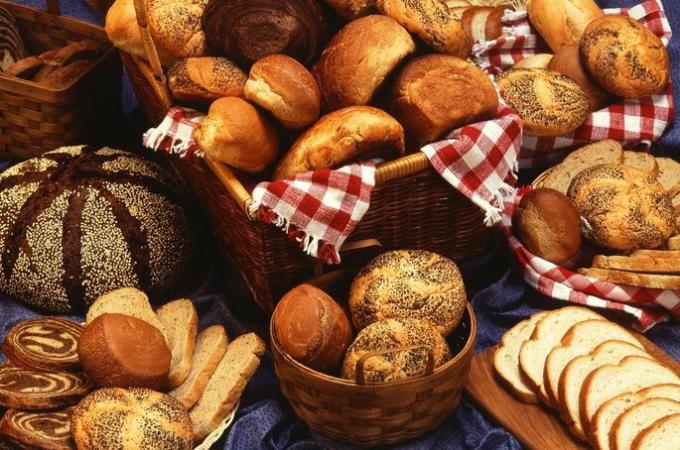

Foods with a high fiber content make it difficult for the body to absorb carbohydrates and can be a good alternative to accompany a healthy diet.
Here are some examples of carbohydrate-rich foods:
- french bread: 57,3%
- Rice: 28,0%
- Noodle: 19,9%
- boiled potato: 18,5%
- Bean: 14,0%
so called diets low carb aim to reduce carbohydrate intake so that the body has to draw on fat reserves as a source of energy.
See also the difference between:
- types of noodles
- types of fat
- Light and Diet
- vegan and vegetarian
- greens and vegetables