The main difference between tuber, tuberous root and bulb is in which part of the plant develops to store energy.
While tubers accumulate in the stem, as in the case of potatoes and yams, tuberous roots store nutrients in their roots, as in carrots and beets. The bulb also accumulates nutrients in the stem, but it has a different and flattened shape.
| Tuber | Source | Bulb | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Developed part | In tubers, the part developed to store energy is the stem. | In tuberous roots, nutrients are accumulated within the root itself. | The bulb also develops and stores energy in its stem, but it has a different shape. |
| Stalk | The tubers have an underground stem, generally rounded in shape. |
The stem is partially out of the ground. | It has an underground stem, in the shape of a disk, which is known as a "plate". |
| Source | The roots of the tuber are responsible for fixing it to the soil. They don't accumulate nutrients, they just absorb and conduct. | Accumulates energy. | The roots of bulbs do not accumulate nutrients. |
| Examples | Potato, yam. | Radish, beet, sweet potato, carrot, cassava | Onion garlic. |
Tuber

Tubers are vegetables where the stem is the developed part, to accumulate nutrients. It is this developed part that serves us as food.
Generally, its stem has a rounded and hypertrophied shape, which accumulate starch. Its roots have the function of fixing the plant to the soil and conducting nutrients and water, but without storing them.
The best known tubers are the potato, the yam and the yam.
Tuberous root

Tuberous roots are those that grow underground. Its nutrients accumulate inside the root, and its stem stays above the surface.
The best known tuberous roots are beets, carrots, cassava and sweet potatoes.
Bulb
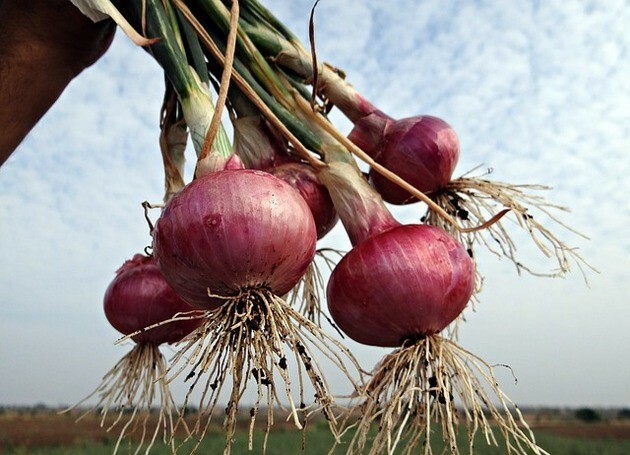

Bulbs also accumulate nutrients in their stems, however, unlike tubers, they have a flattened shape, called a plate.
The best-known examples of bulbs are onions and garlic.
See also the difference between:
- vegetables and greens
- types of carbohydrates