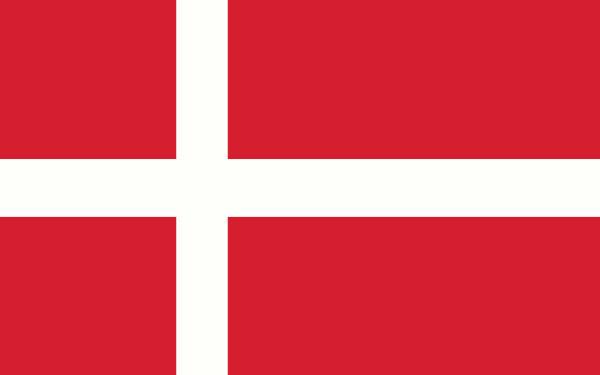
A flag of DenmarkIt is one of the symbols that represent the country. It is called the Dannebrog and is the oldest continuously used flag in the world, given that its official adoption dates back to the 14th century. There is a legend that the flag fell from the sky during the Battle of Lindanisse in 1219, in what is now the Estonia. The Danish flag is formed by a white Nordic cross, a color that represents spirituality. Christian, on a red background in allusion to the battles fought by the Danes throughout their history.
Read too: Flag of Portugal — a flag representing the transition from monarchy to republic in the country
Abstract about the flag of Denmark
The flag of Denmark is one of the symbols that represent the country.
gets the name of Dannebrog, which means “honorary cloth of the Danes”.
It consists of a white Nordic cross on a red background.
Red symbolizes battles, and white represents Christianity.
Legend has it that the flag of Denmark fell from the sky during the Battle of Lindanisse, in present-day Estonia, in 1219.
The Danish flag officially began to be used in the 14th century, but citizens were only allowed to use it in the mid-19th century.
There are two other flags in use in the country: the State Flag of Denmark and the Naval Flag, used by the Navy.
Denmark flag meaning
the flag of denmark is one of the symbols from the country. She gets the name Dannebrog, which means “honorary cloth of the Danes”. The Danish flag is rectangular in shape and consists of a red background and a superimposed white cross, called the Scandinavian cross or Nordic cross. The vertical line of the Scandinavian cross, however, is displaced to the left half of the pavilion, not centered.
The meaning of the colors of the flag of Denmark esit's on à history of the country and also of the ownbanner. A Danish legend tells that the national flag fell from the sky during a battle in the early 13th century. Therefore, the two colors present in the flag have the following meaning:
Red: symbolizes the battles fought by the Danes in the course of their history.
White: represents the wChristianity.
Flag History of Denmark
The History of the Flag of Denmark is on to a legend counted there is more of 800 years in the countrys.According to legend, a red flag with a white cross fell from the sky during a critical moment when Danish troops needed to defend themselves. Before touching the ground, the pennant was reached by the then King Valdemar II, thus giving the necessary motivation for the scenario to be reversed and Denmark to emerge victorious from the battle. The religious symbolism intrinsic to the dispute, inserted in the historical context of the Northern Crusades, also became associated with the flag.
This would have happened during the Battle of Lindanisse, in what is now Estonia, on June 15, 1219. A The date of the alleged event was adopted as Flag Day, starting to be celebrated in the year 1913.
The flag began to be officially used by Denmark in the 14th century, restricted to the monarch and members of royalty. Use by Danish citizens was authorized only in the 19th century, after Denmark's victory over the Germany in the First Slavic War.
See too: Flag of France — a flag that was adopted during the French Revolution
Other flags of Denmark
A Dannebrog, the national flag of Denmark, is not the only standard used in the country. There are two other flags that are flown by specific segments of Danish society.
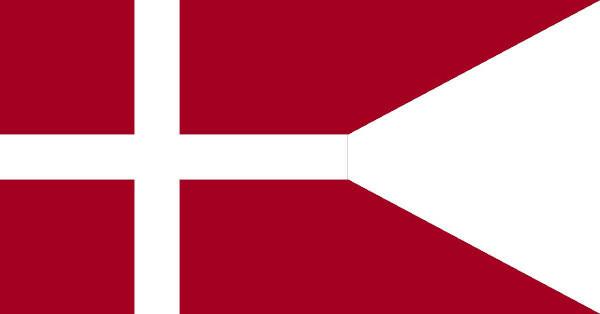
→ state flag of denmark
The state flag of Denmark is a flag with the right end divided in half (split flag). Its use is made by the authorities of the Danish monarchy.
![State flag of Denmark. [1]](/f/08b4503d7523e8b72e5897206dfd7186.jpg)
→ Danish Naval Flag
The Naval Ensign of Denmark features a darker shade of red. Call of Orlogsflag in the local language, this flag It is only used by Navy authorities.
Important: Denmark has overseas territories that use their own flags. They are: the Greenland (North America) and the Faroe Islands (Northern Europe).
Denmark's main features
Denmark is a European country located on the peninsula of Scandinavia, in the north of the continent. Its capital is the city of Copenhagen. The Danish territory is bathed by the North and Baltic seas, establishing a land border only with Germany, to the south. This is the only stretch that connects Denmark, more precisely the Jutland region, to the rest of continental Europe, given that the country is formed by a group of more than 400 islands. The three largest of these are Vendsyssel-Thy (north of Jutland), Fiôna (in the central portion between Jutland and Zealand) and Zeeland (eastern island where the city of Copenhagen is located).

Due to its maritime nature, Denmark hasclimate oceanic marked by temperatures that vary from cold to mild and by high annual rainfall, providing the development of vegetation such as that of the temperate forests.
O relief Danish is not very hilly, consisting essentially of plains and gently undulating terrain, which favors the agricultural activity in many areas, but at the same time, it makes several regions of the country susceptible to flooding, especially on the coast, during periods of high tide.
With Human Development Index (HDI) very high, Denmark has a high quality of life and stands out among the best economies in the European continent. O tertiary sector accounts for more than three quarters of revenue generation in the country, which also has a industry Modern and diverse. Denmark is still a populous country, with 5.8 million inhabitants, and urbanized.
Facts about the flag of Denmark
The flag of Denmark is one of the oldest in the world in terms of continuous use.
Like Denmark, other Nordic countries use crosses on their flags, as Norway, Sweden, Finland It is Iceland.
In the country, it is common for parties to have the Danish flag in their decoration, such as birthdays, for example.
Danish law does not prevent the country's flag from being burned. However, it is against the law to set other countries' flags on fire.
image credits
[1] Wikimedia Commons (reproduction)
[2] Wikimedia Commons (reproduction)
By Paloma Guitarrara
Geography Teacher
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/geografia/bandeira-da-dinamarca.htm

