Developed countries are defined as the countries that have a high level of socioeconomic development, which is determined through several criteria, such as the Human Development Index (HDI), per capita income and Gross Domestic Product (GDP). They are characterized by the high quality of life enjoyed by their population, by the developed and consolidated industry, by the high incorporation of technology in the production processes and also by the broad investment in research and in development.
Check out our podcast: Most and least rich countries in the world
Summary on developed countries
Developed countries are those with high socioeconomic indicators.
The economy of developed countries is concentrated in the tertiary and quaternary sectors, which concern research and innovation activities.
Income distribution in developed countries is more homogeneous.
Criteria such as HDI, per capita income and GDP are used to classify developing countries.
According to the HDI, Norway is the most developed country in the world.
Taking into account the GDP, this position is occupied by the United States.
Underdeveloped countries are those with very low socioeconomic indicators, high economic and environmental vulnerability and low income levels, with a very uneven.
What are the characteristics of developed countries?
Developed countries have a common high economic development index and high level of industrialization. The first characteristic is measured by the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and also by per capita income, which corresponds to the value of the average income that is received by each of the inhabitants of these nations. In more developed economies, per capita income is high, and income distribution tends to be more homogeneous when compared to less developed countries.
Still in the economy, developed countries have an industrial sector (secondary sector) well developed and employing a high level of technology in production processes. However, corresponding to trade and services, O tertiary sector represents the predominant segment in the economic composition of these countries. In addition to tertiary activities, developed countries stand out in the fields of research and development and information technologies, which are often classified as a sector quaternary of the economy.
In addition to economic indicators, developed countries have high levels of social development that fall into this category. In general terms, they are characterized by a high quality of life, often associated with income distribution and better access to basic services (health, education, infrastructure sanitation, urban infrastructure, transport, among others) and high literacy rates.
Linked to health, it is still high Life expectancy, generally over 80 years of age, and lower death rate, and it is also possible to highlight the reduced birth rate presented by these countries.
Criteria for the classification of developed countries
There are several criteria that are used to classify developed countries. They vary considerably depending on who performs this division, as in the case of organizations such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF) it's the world Bank.
This is because they mainly take into account the per capita income and the set of goods and services produced and offered by these nations in a period of one year, which corresponds to the value of their Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
The United Nations classification (UN), however, is today one of the most used for the definition of developed countries. The criterion used is its position in the ranking based on the Human Development Index (HDI).
This index determines the pattern of socioeconomic development and the quality of life of a country taking into account three main aspects: health, education and income. Thus, nations that have a very high HDI, with values that are closer to 1, are considered developed nations.
What are the most developed countries in the world?
→ Most developed countries in the world according to the UN
Following the UN classification|1|, which takes into account the socioeconomic profile of countries and territories, we have gathered in the table below the five most developed countries in the world according to their position in the world HDI ranking.
Country |
HDI |
Norway |
0,957 |
Ireland |
0,955 |
Switzerland |
0,955 |
Iceland |
0,949 |
Hong Kong |
0,949 |
→ Most developed countries in the world according to the IMF
As we have seen, economic criteria are also used to determine the level of development of countries, one of the main indicators being GDP. The table below contains the five most developed countries in the world taking into account the value of GDP and the nations listed as developed by the IMF|2|.
Country |
GDP (in dollars) |
United States |
25.35 trillion |
Japan |
4.91 trillion |
Germany |
4.26 trillion |
UK |
3.38 trillion |
France |
2.94 trillion |
Developed countries in America
There are two developed countries in the American continent, both belonging to the North American subcontinent:
United States: have the largest national economy in the world, with a GDP that exceeds the value of 25 trillion dollars, in addition to having great influence on the international economic and financial system. Their HDI is considered very high, with a value of 0.926, placing them in the 17th position in the world ranking.
Canada: it has the second largest American economy and the eighth largest economy in the world, with a GDP of 2.2 trillion dollars. Considered one of the best countries to live in and where the population enjoys a high quality of life, Canada appears in a position above the United States in the HDI ranking. This indicator for the country is also very high, with a value of 0.929.
What are developing countries?
Countries classified as developing countries, also called countries emerging, are those that present median social and economic indicators, which denotes that the standard of living and the economy are not as advanced as in developed nations, but not at levels as low as those observed in underdeveloped countries.
The economy of developing countries is constantly evolving, but it is still quite dependent on secondary sector It's from sector primary and, having gone through a relatively recent process of industrialization, its industrial park is still in a phase of expansion and improvement.
Furthermore, exports and foreign investment play an important role in the national economies of those countries. Its GDP varies between low and medium, while Income distribution happens unevenly.
According to UN definitions, the quality of life in developing countries is low or medium, which means that the value of its HDI is in equivalent ranges, generally between 0.555 and 0.799.
→ Examples of developing countries
Below are some examples of developing countries according to the UN:
Brazil;
Russia;
China;
South Africa;
India;
Mexico;
Indonesia.
Developed countries vs underdeveloped countries
You underdeveloped countries, or least developed countries, according to the nomenclature adopted by the UN, unlike developed countries, are those that have very low rates of economic and social development.
The classification carried out by the United Nations describes this group of countries as having a low level of human resources and with restricted availability of infrastructure, being dependent on the primary sector of the economy and highly vulnerable economically and environmentally.
Contrary to what we have identified for developed countries, the per capita income of underdeveloped countries is at a very low level, which is commonly below one thousand dollars.
For this reason, a large proportion of the population of underdeveloped nations lives in poverty and vulnerability, with a huge discrepancy between the income of the richest and the poorest part of its inhabitants. According to the HDI, countries with indices further away from 1, generally below 0.555, are considered underdeveloped.
→ Examples of underdeveloped countries
The UN list counts 46 underdeveloped countries, some of which are listed below.
Somalia;
Ethiopia;
Afghanistan;
East Timor;
Yemen;
Haiti;
Bangladesh;
Nepal;
Uganda;
Mozambique.
Know more: African underdevelopment and its roots — why are most underdeveloped countries African?
Human Development Index (HDI)
We present in the table below the ten countries and territories with the best development index in the world and also those which have the lowest rates, according to data from the UN Human Development Report (HDR) published in 2020.
high HDI |
low HDI |
Norway (0.957) |
Niger (0,394) |
Ireland (0.955) |
Central African Republic (0,397) |
Switzerland (0.955) |
Chad (0,398) |
Hong Kong (0.949) |
South Sudan (0.433) |
Iceland (0.949) |
mali (0,434) |
Germany (0,947) |
Sierra Leone (0,452) |
Sweden (0,945) |
Burkina Faso (0,452) |
Australia (0,944) |
Mozambique (0.456) |
Netherlands (0,944) |
eritrea (0,459) |
Denmark (0,940) |
Yemen (0.470) |
Exercises solved on developed countries
question 1
(Fatec 2013) The Human Development Index (HDI) is a comparative measure used to classify quality of life offered by a country to its inhabitants, taking into account three basic dimensions of human development: income, education and health. The HDI ranges from 0 to 1. The closer to 1, the more developed the country.
Review the following table:
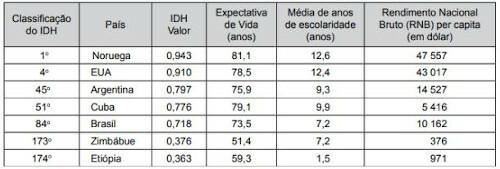
(www.hdrundp.org/en/media/HDR_2011_PT_Tables.pdf. Accessed on: 24.09.2012. Adapted)
It can be correctly concluded that:
A) Ethiopia, due to the quality of its health and environmental sanitation services, has increased the life expectancy of its inhabitants.
B) Zimbabwe has an average number of years of schooling equal to that of Brazil and has a Gross National Income higher than that of Ethiopia.
C) Cuba, despite having a high Gross National Income, does not invest in the education sector and in the health of its population.
D) Argentina, due to its economic crisis, has lower levels of income, education and health than Brazil.
E) Norway ranks highest in the HDI for, among other factors, ensuring several years of schooling for its inhabitants.
Resolution:
Alternative E
The HDI calculation takes into account factors such as education, which includes years of schooling, health and income. Thus, the education of the population is one of the aspects that condition Norway's status as a developed country in the HDI ranking.
question 2
(Enem PPL 2009)
Among the promises contained in the ideology of the economic globalization process was the dispersion of knowledge production in the global sphere, an expectation that has not been materialized. In this scenario, the technopoles appear as a high-tech research and development center that has a highly qualified workforce. The impacts of this process on the insertion of countries in the global economy were hierarchical and asymmetrical. Even in the group in which the productive restructuring was engendered, there was an uneven diffusion of the technological and organizational paradigm shift. The weight of asymmetry was projected more strongly between the more developed countries and the developing ones.
BARROS, F. THE. F. Technical-scientific concentration: an expanding trend in the contemporary world: Campinas: Inovação Uniemp, v. 3, No. 1 Jan./Feb. 2007
In view of the changes that have taken place, it is recognized that:
A) Technological innovation has reached the city and the countryside, incorporating agriculture, industry and services, especially in developed countries.
B) The flows of information, capital, goods and people have slowed down, following the new model based on technological capacity.
C) New technologies spread with equity in the geographic space and among the populations that incorporate them in their daily lives.
D) Technopoles, in times of globalization, occupy the old centers of industrialization, concentrated in some emerging countries.
E) The economic growth of developing countries, resulting from the dispersion of knowledge production in the global sphere, is on a par with that of developed countries.
Resolution:
Alternative A
Technological innovations, which have helped to expand the flows of information, capital and goods, were incorporated on a larger scale in developed countries. These countries are also home to the main global technopoles.
Grades
|1| UNPD. Human Development Reports: Human Development Insights, 2020. Available here.
|2| MFI Data mapper: GDP, current prices. IMF, 2022. Available here.
By Paloma Guitarrara
Geography teacher
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/geografia/paises-desenvolvidos.htm

