Haiti is a country of Central America bathed by the caribbean sea, having as capital the city of Port-au-Prince. It is located on the island of Hispaniola, which it shares with the Dominican Republic. Considered the poorest country on the American continent, Haiti has more than 11 million inhabitants and an economy concentrated in the tertiary and primary sectors. Furthermore, the island on which the Haitian territory is located is in an area of intense tectonic instability, subject to earthquakes, tidal waves and even hurricanes that form in that region.
Read too: What are the countries of America?
Topics in this article
- 1 - Summary about Haiti
- 2 - General data on Haiti
-
3 - History of Haiti
- Video lesson on Haitian independence
- 4 - Map of Haiti
-
5 - Geography of Haiti
- Haiti's climate
- relief of haiti
- vegetation of haiti
- Haiti hydrography
- 6 - Demographics of Haiti
- 7 - Haiti's Economy
- 8 - Culture of Haiti
- 9 - Infrastructure of Haiti
- 10 - Government of Haiti
- 11 - Curiosities about Haiti
Summary about Haiti
Haiti is a Caribbean country located on the island of Hispaniola. It borders the Dominican Republic and is bathed by the Caribbean Sea.
It has a humid tropical climate and mountainous relief, being located in an area of high tectonic instability and subject to the occurrence of hurricanes.
It has more than 11 million inhabitants, of which 23.7% live in its capital, Port-au-Prince.
Haiti's HDI is very low (0.510) and the country is considered the poorest in the American continent.
Its economy is concentrated in the service sector and agriculture. This accounts for a share of approximately 22% of Haiti's GDP.
Do not stop now... There's more after the ad ;)
Haiti's general data
Official name: Republic of Haiti
Gentle: Haitian
Territorial extension: 27,750 km² (UN, 2020)
Location: Central America
Capital: Port Prince
Climate: humid tropical
Government: semi-presidential republic
Administrative division: 10 departments
Language: french and creole
-
Religions:
Catholic: 35.4%
other Christian religions: 51.8%
voodoo: 1.7%
no religion: 11%
Population: 11,402,000 inhabitants (UN, 2020)
Demographic density: 413.7 inhab./km² (UN, 2020)
Human Development Index (HDI): 0,510
Coin: Gourde (HTC)
Gross Domestic Product (GDP): $22.43 billion (IMF, 2021)
per capita GDP: US$ 1940 (IMF, 2021)
Gini: 0.411 (World Bank estimate for 2014)
Timezone: GMT -4 hours
-
External relations:
UN
world Bank
OAS
Unesco
Common Market and Caribbean Community (CARICOM)
Community of Latin American and Caribbean States (CELAC)
Read too: Venezuela – South American country known for its oil reserves
Haiti's history
The territory corresponding to present-day Haiti was inhabited predominantly by the Arawak Indians until the arrival of European settlers at the end of the 15th century. The region was initially colonized by the Spaniards led by Christopher Columbus, who named the island on which they landed Hispaniola (anglicized form of “the Spanish island” in the Spanish language). The dominion of the Spaniards represented the enslavement of the local population for forced labor, mainly in agriculture, and was restricted to the eastern portion of the lands.
The incursion of French pirates, together with the weakening of the presence of the Spaniards on the island, in the 16th century, expanded the influence of other European peoples on the region, notably from the France but also from England. At the end of the 17th century, in 1697, France and Spain signed the TRyswick ratate, which guaranteed formally the French occupation of the western third of the island, which corresponds to Haiti. At the time, the French had already founded the commune of Port-de-Paix, in the northwest region of the country.
The French relocated thousands of enslaved Africans to the island. to work on plantations. The economy of Saint Dominigue, as Haiti was called at the time, was based on agricultural crops such as sugar cane, coffee and cocoa. It is estimated that the African population in Haiti during the period of French domination reached 500,000 people.
The 18th century was marked by the Haitian Revolution, led by Touissant L'Ouverture, who also came to the country as a slave. The revolution culminated in the abolition of slavery, in 1794, in the French colonies, becoming a landmark both in the history of the country and of the Americas. The movement continued after L'Ouverture's death in 1803, and Haiti declared its independence in 1804.
In the history of its social and political constitution, Haiti has gone through several periods of institutional crisis and dictatorships, as happened between 1957 and 1986, with the dictatorial governments of François Duvalier (“Papa Doc”) and his son, who succeeded him, Jean Claude Duvalier (“Baby Doc”). With 11 million inhabitants, Haiti is now considered the poorest country on the American continent.
Video lesson on Haitian independence
Haiti map
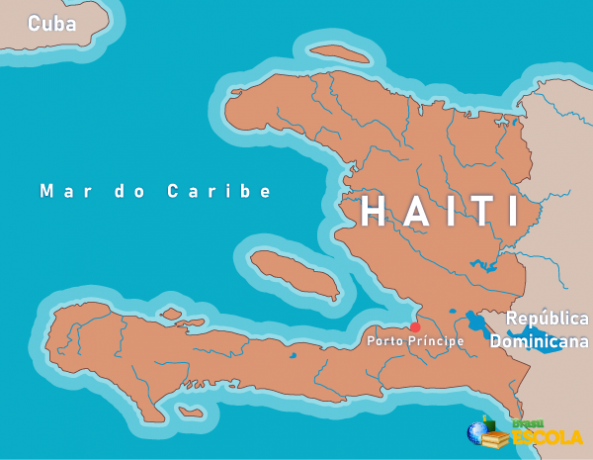
Haiti's geography
Haiti is an American country of 27 thousand km² located in the Central American subcontinent, with the capital city of Port-au-Prince. It is located on the island of São Domingos, also called Hispaniola, bordering, to the east, with the Dominican Republic. To the northwest, it is located Cuba, which is separated from the Haitian territory by the Barlavento channel, while, to the west, the Jamaica channel extends, which separates the island of Santo Domingo from the Jamaican territory.
The country is bathed by the Caribbean Sea, which also involves a small group of islands that integratesm your territory, which are: the island of Tortuga, Gonâve, the Cayemites and Île-à-Vache. Below we will analyze some more physiographic characteristics of Haiti.

Haiti's climate
The predominant climate in Haiti is Ttropical damp, with local variations determined by the relief. One of its main characteristics is the high daily temperature range and, on the other hand, the low annual variation.
Average annual temperatures are between 25°C and 30°C, and in higher places the conditions are milder, with minimums of up to 16 ºC. The volume of rainfall varies greatly and reaches 700 mm on mountain slopes. The areas to the east are drier, which is due to the presence of mountain ranges, which prevent the arrival of winds humid to the region.
Read too: What is the influence of altitude on climate?
relief of haiti
Haiti is located in an area of youth relief, with rather mountainous and rugged terrain and with at least four mountain ranges crossing the country. The highest point in Haiti is in the La Selle massif, in the southern region. This is the La Selle peak, located at 2680 meters above sea level.
vegetation of haiti
The natural vegetation of Haiti is formed by tropical forests. However, the largest remaining areas of this formation are found in the higher areas, especially in the southern and central-south massifs. Fields and woods are found in plains or areas of less rugged relief, while on the coast the presence of mangroves is observed.
The Artibonite River is the main and longest river in Haiti and also the entire island of São Domingos, with an extension of 253 km. Most of the waterways that bathe the country flow into the Gulf of Gonâve, a triangular gulf that forms the entire west coast of Haiti, and is also the largest gulf in the Caribbean Sea.
Haiti's Demographics
Haiti is a populous country, bringing together 11,402,000 inhabitants, according to United Nations data for 2020. Haitian territory is also densely populated, with a distribution of around 413.7 inhab./km² (UN, 2020).
Coastal regions are those that concentrate the largest number of people, although there is a relatively homogeneous distribution throughout the territory. Haiti is an urbanized country, with about 58% of its population living in cities. The capital, Port-au-Prince, concentrates 23.7% of all the country's inhabitants, with a population of 2,704,200 people (UN, 2020). As such, it is the largest and main urban area in Haiti.
The country has a quite young population, whose median age is 24.1 years, while having a low life expectancy when compared to other countries, which reached 65.61 years, according to an estimate for 2021. Annually, the Haitian population grows by about 1.22%, which is mainly due to the high birth rate.
According to the UNDP (United Nations Development Programme) Human Development Report released in 2020, Haiti has one of the smallest Human Development Indexes (HDI) of the world, although there has been some growth in recent years. The most recent value, according to the UNDP, is 0.510, ranking 170th among the countries of the UN.
Haiti's economy
Haiti is considered the poorest country on the American continent, which is due to a series of historical socioeconomic factors, perpetuated over time, and also political, of the which highlights the periods of political and institutional instability and coups d'état, followed by long dictatorships in the country.
Also noteworthy is the unequal income distribution and intense concentration in the hands of a very small portion of the population. According to the World Bank, 20% of the population detêm 64% of the country's wealth. Furthermore, relatively frequent natural disasters such as hurricanes and earthquakes, further weaken the situation of the Haitian population.
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) data for 2021 shows that the country's GDP per capita is 1904 dollars. O Poverty rate reached 60% of the population in 2020, as indicated by the World Bank, which was aggravated by the health crisis caused by the pandemic of Covid-19.
the haiti it's a Pthere non-industrialized, with an economy centered on tertiary sector and in agriculture. This represents a share of approximately 22% of the country's GDP, which is currently US$ 22.43 billion. Haitian agricultural production includes sugarcane, corn, cassava, mango, banana, guava and vegetables in general. Industry is responsible for 20% of GDP, with emphasis on the textile, sugar refining, flour milling, assembly and cement sectors.

Haitian culture
Haiti is a country with a black majority, with only 5% of its inhabitants considered white or from other ethnicities. Its cultural framework is quite rich and diverse, being formed based on the predominant influence of Africans and also of French and Spanishhello. This is reflected in various aspects and forms of cultural manifestation, especially in music, the arts in general, language and religiosity.
Haitian Creole and French are considered the official spoken languages dthe country, the second being used mainly for political and administrative purposes, in addition to being the main language used for writing. The Creole language is spoken by the vast majority of Haitians, and has regional variations.
Religiosity is another interesting aspect of Haitian culture. Religious syncretism is widely present in Haiti, with the predominance of Christian religions of European origin and African religions, especially voodoo, which has its origins in West African traditions. Voodoo was formalized as a religion in Haiti in 2003, and many of its elements are used in various religious practices in the country.
Check it out on our podcast: Material and immaterial culture
Haiti's Infrastructure
Haiti is a country facing serious infrastructural problems that are deepened with each new natural disaster that affects the island of Hispaniola, such as the three earthquakes of great magnitude that hit the region between 2010 and 2021.
Recent data indicate that 75% of the Haitian population have access to sources of drinking water, with the largest portion located in urban centers. Adequate sanitation networks, however, reach a smaller share of the population, which is around 60%. Only 39% of the Haitian population have access to electricity, of which 60% live in cities and 12% in rural areas. The country's energy comes mainly from fossil fuels, and only 18% of it is generated by hydroelectric plants.
Travel is carried out via national highways., departmental or managed by counties. In urban areas, in addition to private transport, tap-tap is used, a type of public transport that can be bus or other adapted vehicle that draws attention for its intense colors and external decoration ornate. In addition to the sea ports, the main airports that provide access to the country are in the cities of Port-au-Prince and Cap-Haïtien.
![Tap-tap, a form of collective public transport in Haiti.[2]](/f/a0b89fba02f2a8fb938a022511b4578e.jpg)
Government of Haiti
O system of government adopted in Haiti is the semi-presidential republican. The country has a president, who exercises the function of head of state, being chosen by the Haitians through the vote. The duration of his term is five years. The head of government is the prime minister, appointed by the president-elect to fill the position in the National Assembly.
Facts about Haiti
Haiti is located in an area prone to the formation of tropical storms or hurricanes. The south of the country is generally the most affected portion of the territory, but, being a small country, the entire country is subject to the devastating effects of this meteorological phenomenon.
In addition to hurricanes, the Haitian territory is subject to the occurrence of earthquakes and tidal waves. This is due to its location in an area of intense tectonic instability due to the meeting of plates.
The island of La Gonâve is one of the most biologically diverse places in Haiti, with the presence of many endogenous species. In total, Haiti has more than 25,000 species among animals, plants and other microbial and kingdom organisms. fungi.
The name of the country is derived from the Arahuaca language, and means “land of high mountains”. The original denomination had been assigned to the entire island of Hispaniola.
Image credits
[1] Michelle D. Milliman / shutterstock
[2] naTsumi / shutterstock
By Paloma Guitarrara
Geography teacher



