Steppe is a type of vegetation cover very common in areas of semi-arid and continental climates, marked by long periods of drought. The vegetation of the steppes is equivalent to the prairies, however it occurs in different climatic conditions, being formed by extensive open fields of grasses (or grass) and shrubs. The steppes, however, are often described as transitional strips between deserts and other plant formations. A well-known example is the Sahel, immediately south of the Saara's desert, in Africa.
Know more: Brazilian biomes — what are they?
Topics of this article
- 1 - What is a steppe?
-
2 - Characteristics of the steppes
- → Location of steppes
- → Climate of the steppes
- → Vegetation of the steppes
- → Fauna of the steppes
- 3 - What is the difference between prairie and steppe?
What is steppe?
Steppe is a type of small vegetation cover that covers flat and gently undulating lands in regions of climates continental semiarid and temperate. Steppes are commonly described as transitional formations situated between two completely different natural landscapes, such as forests and deserts.
Features of the steppes
the steppes are often calledThes of grasslands or prairies per possessionírin close features of these vegetations. However, there are aspects, such as climatic occurrence and floristic composition, that make these landscapes unique. We draw attention to these points in the description below.
→ Location of steppes
In both hemispheres of the planet, both North and South, it is possible to identify the presence of vegetation characteristic of the steppes. She is present in low and mid latitude areas and is commonmin the close lanesThe The deserts.
An example is the steppes located immediately north and south (Sahel region) of the great Sahara desert on the African continent. Like the desert surface, the African steppes stretch from the east to the west of the continent. In this context, the steppes separate the Sahara from the savannas.
Do not stop now... There's more after the ad ;)
The steppes are still present in the central region of North America, covering the territories of the United States and Canada, parts of the Southeast and East of Europe, as in Ukraine, and to a greater extent in the region of Central Asia. In this area, it extends to countries such as Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan.
Still in the north, steppes are observed in the Middle East and in East Asian countries, especially Mongolia, southern Russia, eastern China and parts of India. In the south, the steppes are located in the southwest of South America, especially in the region of Patagonia, in the south of Africa and in parts of Australia.
Also know:Savanna — the biome that occurs predominantly in the tropical zone of the planet
→ Climate of the steppes
the steppes grow in dry climates such as tempered continental and the semiarid. Mainly in the second type, temperatures are high during most of the year, reaching above 35 °C, and the dry periods, that is, without the occurrence of rain, are very long.
In some areas, the average annual rainfall is around 300 mm. In others, the accumulated total is doubled. These conditions make it impossible to maintain perennial rivers and extensive drainage systems.
In steppes located at higher latitudes, there can be a great contrast between the summer it's the Winter, with negative temperatures recorded during the coldest months of the year.
→ Vegetation of the steppes
The vegetation present in the steppes is open and small, formed by different types of grasses (grass) and shrub plants, as well as in the prairies. Some of the species that are part of the steppe flora are adapted to the extreme conditions of many of the regions where the steppe develops. It is the plants and fauna of the steppes that constantly provide organic material for the soils, which makes them chemically fertile and prone to the development of agricultural activities.
→ Fauna of the steppes
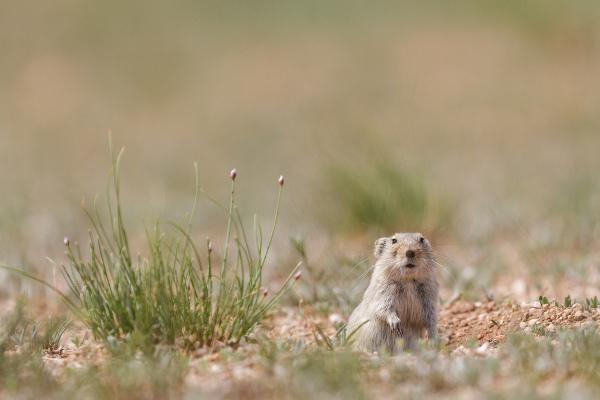

The fauna of the steppes it's very differentada and depends on where this training takes place., with many endemic species. At Australia, for example, there are animals like kangaroos living in savannas and steppes. taking into account the biodiversity present in the steppes around the world, the fauna is composed of animals such as:
◦ bison;
◦ wolves;
◦ antelopes;
◦ badgers;
◦ marmots;
◦ steppe voles;
◦ steppe eagles;
◦ Lesser kestrel (a species of falcon);
◦ European Roller;
◦ jackals;
◦ horses;
◦ camels;
◦ rabbits;
◦ reptiles;
◦ insects.
What is the difference between prairie and steppe?
Grasslands and steppes consist of the same form of vegetation cover, which are open fields covered by grasses and shrubs. It is not uncommon to find materials referring to steppes and prairies as being the same natural landscape, with different names according to the location. Taking into account the plant aspects, in this case, TheThe steppes would correspond to the Central Asian and European prairies.
It is important to note, however, that the vegetation corresponding to the steppes develops in areas with semi-arid climates or with a seasonal prominent drought, representing a transitional band between deserts (arid) and other vegetation cover, such as savannas and forests.
By Paloma Guitarrara
Geography teacher