You greenhouse gases (GHG) are molecules capable of absorbing heat. These gases retain energy from the Sun and increase the temperature of the planet, causing the natural phenomenon called the greenhouse effect.
carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), ozone (O3), chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and water vapor are examples of greenhouse gases.
In the atmosphere, a “barrier” is then formed that prevents heat from returning to space and diffuses it into the environment. Consequently, the greenhouse effect makes the Earth's average temperature, around 15 ºC, favorable for the maintenance of life.
However, the increase in emissions by human actions has caused a greater concentration of these specific gaseous substances and, consequently, global warming.
Main greenhouse gases
Carbon dioxide (CO2): it is the main component of the greenhouse effect released in human activities, such as the burning of fossil fuels (gasoline, diesel, coal, etc.) and burning in solid waste and forests.
Methane
(CH4): is the second main component of the greenhouse effect. It is produced in the digestion of ruminants and in the decomposition of organic waste. Its heat retention capacity is greater than that of carbon dioxide.Nitrous oxide (N2O): is one of the main components of the phenomenon and is generated in biological reactions by microorganisms in soil and water. It is also released into the environment that uses chemical fertilizers.
Ozone (O3): from atmospheric pollution, ozone is produced in reactions involving carbon monoxide (CO) and participates in the greenhouse effect in the lower layers of the atmosphere.
water vapor (H2O): the higher the temperature on the earth's surface, the greater the evaporation of water. Due to its high radiative capacity, water molecules found in suspension in the atmosphere contribute 2/3 of the heat absorption in the natural greenhouse effect.
Fluoride compounds: Industrial processes can release many synthetic chemicals that enhance the greenhouse effect, such as hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (HFCs), sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) and nitrogen trifluoride (NF3).
You chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), for example, are fluoride gases used primarily in refrigeration systems.
How do greenhouse gases work?
In the operation of a greenhouse we see that transparent structures on the roof allow the passage of sunlight. A part of the energy is reflected and the other absorbed fraction is trapped allowing its interior to be heated.
Likewise, the Earth's atmosphere has gases in its composition that are capable of retaining energy from the Sun, as in the following image.
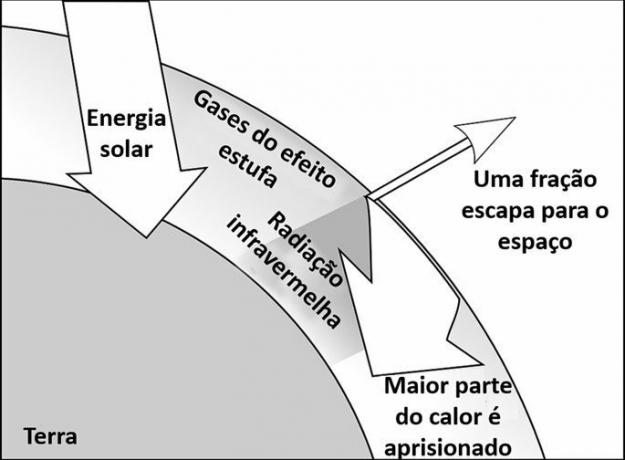
- The Earth receives a set of radiations coming from the Sun;
- 70% of the solar energy is absorbed by the planet and 30% is returned to space;
- Energy exchanges between the atmosphere and the earth's surface radiate invisible infrared radiation;
- The greenhouse gas layer traps about 90% infrared radiation and traps heat in the atmosphere.
Learn more about greenhouse effect.
Greenhouse effect vs global warming
The gaseous elements of the greenhouse effect trap heat in the atmosphere. Therefore, more gas molecules with this capacity will modify the amount of heat trapped.
The burning of fossil fuels such as coal, gasoline, diesel, natural gas, among others, releases a large amount of gases into the atmosphere.
Other activities such as burning, farming, industrial processes, electricity generation increase the emission of GHG gases into the environment.
Although the greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon, global warming is a phenomenon caused by the intensification of the greenhouse effect.
Some of the estimated consequences for the increase in the Earth's average temperature are:
- Climate changes;
- Food insecurity;
- Melting of polar ice caps;
- Rising sea levels and flooding of coastal regions.
know more about greenhouse effect and global warming.
Exercises on greenhouse gases
question 1
(UFPR/2016) A study by the Federal University of Minas Gerais shows that it is possible to greatly reduce belching 211 of the millions of heads of the Brazilian herd. With better pasture and feed supplementation, cattle would get fatter and faster and spend less time burping.
Source: Folha de S. Paul, August 29, 2015.
Reducing the amount of burping can help control global warming because it reduces the emission of:
a) sulfur dioxide (SO2)
b) methane (CH4)
c) carbon monoxide (CO)
d) nitrite (NO2)
e) ozone (O3)
Correct alternative: b) methane (CH4).
Ruminants are herbivorous animals. When they feed on plants, the digestive process generates methane, a greenhouse gas with a high capacity to absorb infrared radiation.
question 2
(ACAFE/2016) Countries sign pact to fight climate change in New York.
In New York, the United Nations (UN) begins the process of ratifying the goals assumed by 195 countries and the European Union in the Paris Agreement, which aims to combat the effects of climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions stove.
With the objective of entering into force in 2020, the agreement, however, will only materialize when it is ratified by 55 States responsible for at least 55% of greenhouse gas emissions. This is the first binding universal pact to fight climate change and determines that its 195 signatory countries act to ensure that the average temperature of the planet rises “well below 2ºC.”
Source: Zero Hora newspaper, 04/22/2016
Available in: http://zh.clicrbs.com.br/rs/noticias
Consider the information above and the knowledge related to the topic and mark the correct alternative.
a) carbon dioxide (CO2) present in the atmosphere is emitted as a result of numerous human activities, for example, through the use of fossil fuels. It also comes from the breathing and decomposition processes of living beings. During photosynthesis, the carbon atoms present in carbon dioxide are used to form organic molecules, essentially consisting of glucose. Part of these molecules is degraded during cellular respiration, and the carbon is returned to the atmosphere in the form of CO2 indicating that, from the point of view of the chemical reaction, photosynthesis is complementary to respiration.
b) The emission of so-called greenhouse gases (GHG) is one of the causes of global warming. There are four main GHG gases, carbon dioxide (CO2) methane gas (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), in addition to two families of gases, regulated by the Kyoto Protocol, hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and perfluorocarbons.
c) The concern to reduce the emission of the so-called greenhouse gases (GHG), with emphasis on CO2, is due to the fact that these intensify the dispersion of solar rays before they reach the surface, resulting in an increase in the temperature of the planet.
d) The significant increase in the temperature of the earth's surface is exclusively due to anthropogenic action, such as fires, deforestation, the burning of fossil fuels, in addition to the release of gases generated in livestock, in sanitary landfills and those produced by factories.
Correct alternative: b) The emission of the so-called greenhouse gases (GHG) is one of the causes of global warming. There are four main GHG gases, carbon dioxide (CO2) methane gas (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), in addition to two families of gases, regulated by the Kyoto Protocol, hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and perfluorocarbons.
question 3
(PUC-RIO/2010) The greenhouse effect is a natural and fundamental phenomenon for the maintenance of life on planet Earth, however, excessive amounts of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere can raise the planet's temperature to levels unwanted. The Kyoto Protocol (1997) proposes a timetable by which signatory countries have the obligation to reduce the emission of greenhouse gases by at least 5.2% by 2012, in relation to the levels from 1990.
Regarding global warming and greenhouse gases, it is INCORRECT to state that:
a) The CO2 It is a greenhouse gas that retains part of the solar radiation reflected by the Earth's surface.
b) CO2 is absorbed by the oceans, decreasing the pH value of its waters.
c) NO2 can react with water in the atmosphere, forming HNO3, one of the components of acid rain.
d) The process of photosynthesis in plants contributes to global warming.
e) The Kyoto Protocol does not aim to totally eliminate the greenhouse effect.
Correct alternative: d) The process of photosynthesis in plants contributes to global warming.
In fact, photosynthesis contributes to capturing atmospheric carbon in the form of CO2, a greenhouse gas, and fixing it in the form of carbohydrate.
Test your knowledge with questions about the greenhouse effect.