Test your knowledge with the 10 questions next about mitosis and meiosis. Check the comments after the feedback to clear your doubts about the topic.
question 1
The cell cycle corresponds to the period between the origin of a cell until its division, being delimited in two moments: interphase and cell division.
Cell division is important because through this process eukaryotic cells are able to:
a) reproduce and multiply
b) replicate DNA and perform gene recombination
c) transcribe genetic material and produce proteins
d) produce energy and transport nutrients
Correct alternative: a) reproduce and multiply.
Single-celled cells are able to reproduce through mitosis and multicellular cells multiply through mitosis or meiosis.
question 2
Regarding the number of cells formed in divisions by mitosis and meiosis, it is correct to state that:
a) through mitosis two cells with the same number of chromosomes as the initial cell are formed, while in meiosis two cells with half the number of chromosomes are produced.
b) the same numbers of cells are formed by mitosis and meiosis, since the difference between the two types of cell division is only in the number of steps in which they occur.
c) mitosis produces two cells maintaining the number of chromosomes of the initial cell, while meiosis produces four cells with half the number of chromosomes.
d) through meiosis the four new cells formed are identical to the parent cell, while mitosis allows the two created cells to present genetic variability.
Correct alternative: c) mitosis produces two cells keeping the number of chromosomes of the initial cell, while meiosis produces four cells with half the number of chromosomes.
When diploid (2n) cells undergo mitosis, the two originating cells are also 2n because the chromosome number of the initial cell is maintained. Likewise, haploid (n) cells give rise to two more haploid (n) cells through mitosis.
In meiosis, a 2n cell produces four n cells, that is, this cell division originates cells with half the number of chromosomes of the initial cell.
question 3
Cell division is the process by which a cell produces other cells and can occur in two types in eukaryotes: mitosis and meiosis.
Human beings have somatic cells, which constitute the body, and sex cells, also called gametes, responsible for reproduction.
What type of cell division do somatic cells and gametes undergo?
a) somatic cells undergo meiosis and gametes undergo mitosis
b) somatic cells undergo mitosis and gametes undergo meiosis
c) somatic cells and gametes undergo mitosis only
d) somatic cells and gametes undergo meiosis only
Correct alternative: b) somatic cells undergo mitosis and gametes undergo meiosis.
Somatic cells in the human body have 46 chromosomes, which are 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes. When dividing by mitosis, the cells produced maintain the chromosome number of the initial cell.
Gametes or sex cells in the human body have 46 chromosomes and when they divide by meiosis, the homologous chromosomes separate. As a result, cells with half the number of chromosomes of the initial cell are produced.
question 4
Consider the following statements about mitosis and meiosis I and classify them as true (T) or false (F).
I. In the prophase of mitosis and meiosis I, the pairing of homologous chromosomes occurs.
II. Tetrads are structures formed in the equatorial region of the cell in metaphase of mitosis and meiosis I.
III. In both mitosis anaphase and meiosis I, the centromere separation occurs.
IV. At each pole of the cell in telophase of mitosis and meiosis I are n duplicated chromosomes.
The correct sequence is:
a) V, F, V, F
b) V, V, F, F
c) V, V, V, V
d) F, F, F, F
Correct alternative: d) F, F, F, F.
I. false. Pairing of chromosomes in prophase is observed only in mitosis.
II. false. Tetrads are structures formed at the equator of the cell in metaphase of meiosis I.
III. false. In anaphase of mitosis, centromere separation occurs, while in anaphase of meiosis I it does not and each component of the homologous pair migrates towards one of the poles of the cell.
IV. false. The cell poles in telophase have 2n unduplicated chromosomes in mitosis and n duplicated chromosomes in meiosis I.
question 5
Complete the comparison table with the differences between mitosis and meiosis by listing the missing information.
| Feature | Mitosis | Meiosis |
|---|---|---|
| Type of cell division | Equational | |
| Number of divisions in each process | Two cell divisions | |
| Number of cells formed | two cells | |
| Types of cells formed | Cells with genetic variability | |
| Number of chromosomes of cells formed | Same number of chromosomes as original cell | |
| Type of cells in which it occurs | germ cells | |
| Diploidy of the cell in which it occurs | diploid or haploid |
Right answer:
| Feature | Mitosis | Meiosis |
|---|---|---|
| Type of cell division | Equational | reductional |
| Number of divisions in each process | a cell division | Two cell divisions |
| Number of cells formed | two cells | four cells |
| Types of cells formed | Cells identical to the parent cell | Cells with genetic variability |
| Number of chromosomes of cells formed | Same number of chromosomes as original cell | Half the number of chromosomes of the original cell |
| Type of cells in which it occurs | somatic cells | germ cells |
| Diploidy of the cell in which it occurs | diploid or haploid | diploid |
question 6
(UDESC) Although mitosis and meiosis cell divisions are performed with different goals in some respects, both have similarities.
Analyze the propositions in relation to the information, and mark (T) for true and (F) for false.
( ) In both, DNA duplication occurs before the process of cell division begins.
Both meiosis and mitosis are characterized by a reduction in the number of chromosomes.
( ) Meiosis is characterized by two cell divisions and the number of chromosomes present at the beginning of division is not reduced in the cells originated at the end of the process.
( ) An important difference between them is that in mitosis the homologous chromosomes separate, while in meiosis only the chromatids separate.
Meiosis is a division that occurs mainly in epithelial tissues with the purpose of replacing dead cells.
Tick the alternative that indicates the correct sequence, from top to bottom.
a) V – F – F – F – F
b) V – F – F – V – F
c) F – F – F – V – V
d) F – F – V – V – F
e) V – F – V – F – V
Correct alternative: a) V – F – F – F – F
true. DNA duplication occurs before cell division, in the S phase of interphase.
false. The reduction in the number of chromosomes occurs only in meiosis.
false. The number of chromosomes in the initial cell is reduced by half in cells formed in meiosis.
false. Homologous pairs separate in the first division, which is meiosis I, and sister chromatids in meiosis II.
false. Epithelial tissues are formed by somatic cells and undergo mitosis. Meiosis occurs in sex cells.
question 7
(Fuvest-SP) Consider the following events, which can occur in mitosis or meiosis:
I. Pairing of duplicated homologous chromosomes.
II. Alignment of chromosomes in the equatorial plane of the cell.
III. Permutation of segments between homologous chromosomes.
IV. Division of centromeres resulting in separation of sister chromatids.
In the process of cell multiplication for tissue repair, events related to the equitable distribution of genetic material among the resulting cells are indicated in
a) I and III only.
b) II and IV, only.
c) II and III only.
d) I and IV only.
e) I, II, III and IV.
Correct alternative: b) II and IV, only.
Since tissues are made up of somatic cells, the type of division that occurs in these types of cells is mitosis, a process of equational division that generates cell multiplication to repair fabrics.
I. wrong. Homologous chromosomes do not pair up in mitosis.
II. correct. Alignment of homologous chromosomes in the equatorial region occurs in metaphase of mitosis.
III. wrong. Permutation occurs only in meiosis and produces genetic variability.
IV. correct. Centromere separation occurs in anaphase of mitosis.
question 8
(Unesp) The figure represents an anaphase of an animal diploid cell. Is this cell in mitosis or meiosis? Justify, informing the diploid number of chromosomes in a somatic cell of this animal.
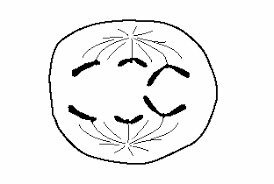
Correct answer: The cell is in meiosis, as the process described in the image corresponds to the anaphase stage II.
Anaphase II is characterized by the separation of sister chromatids and migration to the poles of the cell, directed by the spindle fibers.
The diploid number of chromosomes in a somatic cell of this animal is 2n = 6.
question 9
(PUC-SP) Considering a cell with 6 chromosomes (2n = 6) and which is undergoing division, the diagram below represents a:

a) anaphase I of meiosis.
b) metaphase I of meiosis.
c) metaphase II to meiosis.
d) mitotic anaphase.
e) mitotic metaphase.
Correct alternative: a) anaphase I of meiosis.
In anaphase I of meiosis there is no division of the centromeres. The homologous pair of chromosomes separates and each component of the homologous pair migrates toward one of the poles of the cell.
question 10
(Enem/2009) Living beings have different life cycles, characterized by the phases in which gametes are produced and by the reproductive processes that result in the generation of new individuals.
Considering a standard simplified model for generating viable individuals, the alternative that corresponds to what is observed in humans is:
The) 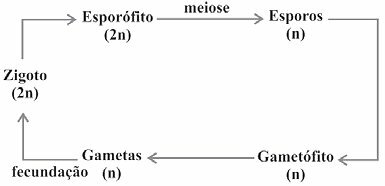
B) 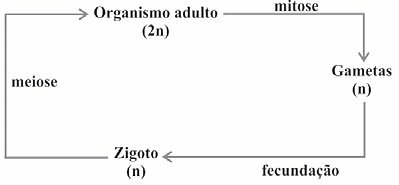
ç) 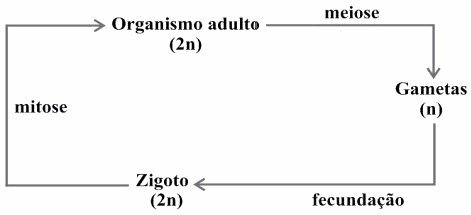
d) 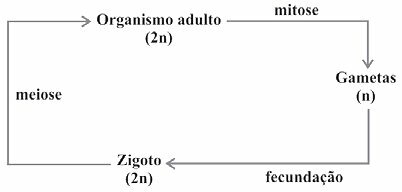
and) 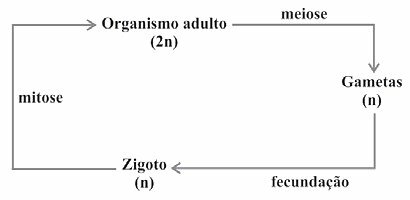
Correct alternative: c).
Gametes are sex cells that divide by meiosis. An initial diploid cell (2n) undergoes meiosis and the number of chromosomes is reduced by half, generating haploid (n) cells. At fertilization, the gametes unite, that is, an egg and a sperm, and the diploid number (2n) is restored.
In the formation of gametes (or sex cells), an initial diploid cell with 46 chromosomes undergoes meiosis and the homologous chromosomes separate. Thus, each cell gives rise to four with half the number of chromosomes of the initial cell, that is, 23 chromosomes each. When fertilization occurs, an egg and a sperm unite, recomposing the diploid number of the species: 46 chromosomes or 23 pairs of homologs.
Gain more knowledge with the contents:
- mitosis and meiosis
- Mitosis exercises



