Solve the list of exercises on Bhaskara's formula and clear your doubts with solved and commented exercises.
Bhaskara's Formula
Where:
The is the coefficient next to ,
B is the coefficient next to ,
ç is the independent coefficient.
Exercise 1
Using Bhaskara's formula, find the roots of the equation .
Determining the delta
Determining the roots of the equation
Exercise 2
The solution set that makes the equation true is
a) S={1.7}
b) S={3,4}
c) S={2, -7}.
d) S={4.5}
e) S={8,3}
Correct answer: c) S={2, -7}.
The coefficients are:
a = 1
b = 5
c = -14
Determining the delta
Using Bhaskara's formula
The solution set of the equation is S={2, -7}.
Exercise 3
Determine The Values Of X That Satisfy The Equation .
Using the distributive property of multiplication, we have:
The terms of the quadratic equation are:
a = -1
b = 1
c = 12
Calculating the delta
Using Bhaskara's formula to find the roots of the equation:
The values of x that satisfy the equation are x = -3 and x = 4.
Exercise 4
Since the following equation of the second degree, , find the product of the roots.
Correct answer: -8/3
Determining the roots of the equation using Bhaskara's formula.
The coefficients are:
a = 3
b = 2
c = -8
Delta
Calculation of roots
Determining the product between the roots.
Exercise 5
Classify equations that have real roots.
Correct answers: II and IV.
There are no real roots in equations with negative because in Bhaskara's formula it is the radicand of a square root, and there is no square root of negative numbers in real numbers.
Negative delta, so I has no real solution.
Positive delta, therefore II has a real solution.
Negative delta, so III has no real resolution.
Positive delta, therefore IV has a real solution.
Exercise 6
The following graph is determined by the function of the second degree . The parameter c indicates the point of intersection of the curve with the y axis. The roots x1 and x2 are the real numbers that, when substituted into the equation, make it true, that is, both sides of the equality will be equal to zero. Based on the information and graph, determine parameter c.
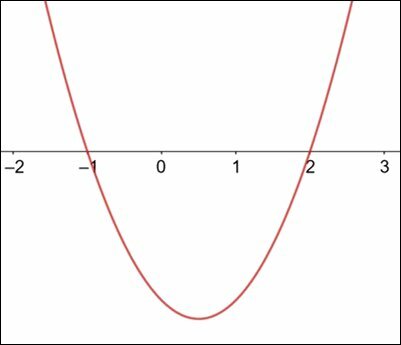
Correct answer: c = -2.
objective
determine c.
Resolution
The roots are the points where the curve cuts the x-axis of the abscissa. So the roots are:
The parameters are:
Bhaskara's formula is an equality that relates all these parameters.
To determine the value of c, just isolate it in the formula and, for this, we will arbitrate one of the roots, using the one with the highest value, therefore the positive value of the delta.
At this point, we square both sides of the equation to take the root of the delta.
Substituting the numeric values:
Thus, the parameter c is -2.
Exercise 7
(São José dos Pinhais City Hall - PR 2021) Tick the alternative that brings a correct statement of the largest of the solutions of the equation:
a) It is unique.
b) It is negative.
c) It is a multiple of 4.
d) It is a perfect square.
e) It is equal to zero.
Correct Answer: a) It is odd.
Equation parameters:
a = 1
b = 2
c = -15
Since the greatest solution of the equation, 3, is an odd number.
Exercise 8
(PUC - 2016)
Consider a right triangle of hypotenuse a and legs b and c, with b > c, whose sides obey this rule. If a + b + c = 90, the value of a. c, yeah
a) 327
b) 345
c) 369
d) 381
Correct answer: c) 369.
The terms in parentheses are equivalent to the sides a, b, and c of the right triangle.
The statement also provides that a + b + c = 90, thus replacing the terms of the Pythagorean triad. In the case of a sum, the order does not matter.
Solving the quadratic equation to find m:
The coefficients are,
a = 1
b = 1
c = -90
As it is a measure, we will disregard m2, as there is no negative measure.
Substituting the value 9 in the terms:
In a right triangle, the hypotenuse is the longest side, so a = 41. The smallest side is c, according to the statement, so c = 9.
In this way, the product is:
Exercise 9
Bhaskara formula and spreadsheet
(CRF-SP - 2018) Bhaskara's formula is a method to find the real roots of a quadratic equation using only its coefficients. It is worth remembering that coefficient is the number that multiplies an unknown in an equation. In its original form, Bhaskara's formula is given by the following expression:
Discriminant is the expression present within the root in Bhaskara's formula. It is commonly represented by the Greek letter Δ (Delta) and gets its name from the fact that it discriminates the results of a equation as follows: Mark the alternative that correctly transcribes the formula Δ = b2 – 4.a.c in the cell E2.

a) =C2*(C2-4)*B2*D2.
b) =(B2^B2)-4*A2*C2.
c) =POWER(C2;2)-4*B2*D2.
d) =POWER(C2;C2)-4*B2*D2.
Correct answer: c) =POWER(C2;2)-4*B2*D2.
The delta equation must be entered in cell E2 (column E and row 2). Therefore, the parameters are all from line 2.
In a spreadsheet every formula starts with the equal symbol =.
Since the delta equation starts with , in the worksheet, the formula of having a power, thus, we discard options a) and b).
In the worksheet, the parameter b is in cell C2, and it is the value that is in this cell that must be squared.
The construction of the power function in a spreadsheet looks like this:
1) To call the power function, type: =POWER
2) The base and the exponent follow immediately, in parentheses, separated with a semicolon ;
3) First the base, then the exponent.
So the function is:
Study more with:
- 2nd degree equations exercises
- Quadratic Function - Exercises
- 27 Basic Math exercises
Read too:
- Bhaskara's Formula
- Quadratic Function
- Vertex of the Parabola
