THE subtropical climate occurs between latitudes 25º and 40º in both hemispheres. It is characterized by the high annual temperature range, with hot summers and cold winters, and well-distributed rainfall throughout the year. The influence of cold air masses in winter can cause frost and precipitation in the form of snow.
These characteristics are predominant, but it is possible to observe local variations. In Brazil, the subtropical climate is typical of areas below the Tropic of Capricorn, covering the entire southern region and the southern portions of the states of São Paulo and Mato Grosso do Sul.
Read too: The relationship between latitude and climate
Subtropical climate summary
It occurs between latitudes 25º and 40º, North and South.
It is characterized by high annual thermal amplitude, with hot summers and cold winters, in addition to well-distributed rainfall throughout the year.
There is not a single type of vegetation associated with this climate. It is observed, in its areas of occurrence, the presence of temperate and subtropical forests, prairies, fields and Pampas.
In Brazil, the subtropical climate comprises the entire southern region and part of São Paulo and Mato Grosso do Sul. Some of its local variations are also found in Espírito Santo, Rio de Janeiro and Minas Gerais.
Do not stop now... There's more after the ad ;)
What is subtropical?
the term subtropical designates the regions of the planet locateds in the vicinity of the tropics, that is, north of the Tropic of Cancer (23º27'N) and south of the Tropic of Capricorn (23º27'S). In these areas, there is a predominance of the subtropical climate and its local variations, covering the interval between 25º and 40º latitude in both hemispheres.
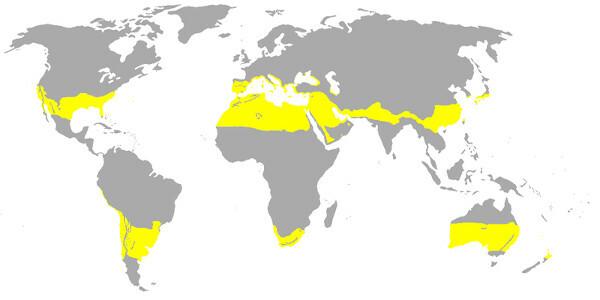
Features of the subtropical climate
The subtropical is considered a transitional climate between tropical and the tempered. In addition, it is classified as a mesothermal climate, whose main characteristics of temperature and humidity are controlled by the action of the different air masses of tropical and polar origin.
One of the main characteristics of subtropical climates is the alternation of seasons, with a better distinction between the four subdivisions than in other climatic types. Thus, one observes thermal amplitude annual rate that varies from medium to high, which will depend on latitude. This means that there is considerable variation in temperatures over the period of a year.
You summers are usually hot, with temperatures around 27 °C to 30 °C, and the cold winters, in which the thermometers show values below 10 °C, and may drop to 0 °C. The annual average is 18 ºC.
THE relative air humidity is high, and rainfall is well distributed throughout the year, which, in general, characterizes climates with the absence of a dry season. Due to the action of polar masses in winter, the phenomenon of frost and also precipitation in the form of snow in certain locations.

Subtropical climate types
The subtropical climate presents some local variations, thus conditioning its subdivision into three different types: subtropical with hot summer, subtropical with dry winter and subtropical with altitude.
Subtropical climate with hot summer: occurs in the coastal strips, in the area covered by the subtropical climate. In the Northern Hemisphere, it is also known as subtropical climate with dry summer or Mediterranean climate.|1| It is characterized by high temperatures in summer, which are lower than those recorded in tropical climates. The average temperature for this season is 22ºC or more. The volumes of rain in summer are considerably low (in Brazil, around 30 mm), while, in autumn and winter, rainfall is high.
Subtropical dry winter climate: its main characteristic is the low rainfall in the months corresponding to the Winter, that is, there is less rainfall in this period. Winter temperatures are mild, averaging 18°C, while summers are hot. In Brazil, it is typical of the states of Southeast region (parts of São Paulo, Minas Gerais, Espírito Santo and Rio de Janeiro), also covering the south of Mato Grosso do Sul.
High altitude subtropical climate: its most striking aspect is the mild temperature that prevails throughout the year, which is due to the influence of the altitude factor. Winters are cold, and summers register values that do not exceed 22 ºC.
Read too: Influence of altitude on climate
Formation of the subtropical climate
the subtropical climate formed in the temperate zones of the planet Earth, which are distributed in mid-latitudes, both in the Northern Hemisphere and in the Southern Hemisphere. In both areas, the rays of sunlight fall at an angle on the surface, with angles lower than those observed in tropical zones, but higher than in polar zones. This phenomenon conditions a different heat distribution from the other areas described, resulting in the occurrence of mild average temperatures.
The air masses that circulate through the atmosphere are also responsible for the characteristics of the climate. subtropical, notably associated with the water regime, humidity and annual variations of temperature. THE performance of the tropical masses is stronger in the summer months, when higher temperatures are recorded. When originating in the oceans, they provide high moisture content wherever they go.
Already the polar masses are responsible for the drop in temperatures, its performance being more accentuated in winter, also causing precipitation in the form of rain due to the formation of cold fronts, in addition to the occurrence of frost and snow.
Others Climatic factors are equally important in the characterization of the subtropical climate, as the altitude and the general circulation of the oceans, which originates the sea currents.
Subtropical climate vegetation
Due to the accentuated local variation, the vegetation of the areas of occurrence of the subtropical climate is not homogeneous. The different plant covers, which sometimes include more than one biome, are mainly the result of different water regimes, that is, the alternation between periods of greater and lesser availability of moisture.
Forest formations are found in subtropical climates, such as temperate forests that form in the Northern Hemisphere, subtropical forests and the araucaria forest, typical of regions with a humid subtropical climate, as well as forests and grasslands, such as prairies and pampas.
Read too: Brazil's morphoclimatic domains — areas defined based on their landscape composition
Subtropical climate in Brazil
The subtropical climate is characteristic of the entire South region (Paraná, Santa Catarina and Rio Grande do Sul), part of the Southeast region of Brazil and the southern portion of Mato Grosso do Sul. More specifically, the subtropical climate is giftnothose parts of the territory that are in the Zonea Temperada sul, below the Tropic of Capricorn. The variation of this climate that comprises larger areas is the humid subtropical climate.
In Brazil, the subtropical climate is characterized by high annual temperature range, with cold winters, with temperatures below 18ºC, and hot summers, which can reach 30ºC in some areas. The annual volume of rainfall varies between 1250 mm and 1500 mm, evenly distributed throughout the year. There are, of course, local variations, with the occurrence of areas with summers or winters with low rainfall.
Another important characteristic of the Brazilian subtropical climate is the strong performance of mroast of Ther Plook, which causes frontal rains and a drop in temperatures, notably in the south of the country. The occurrence of frosts in winter is not uncommon, and in some areas, such as municipalities of Santa Catarina and not Rio Grande do Sul, it may snow.
Subtropical climate zones
The subtropical climate is present between latitudes 25º and 40º, in both hemispheres of the planet. It is characteristic of the following areas:
eastern Australia and South Africa;
southern South America, covering the southern lands of Brazil and part of Uruguay, Paraguay and Argentina;
Southeast Asia, which encompasses southeastern China and northern India;
Arabian peninsula, in southwest Asia;
North Africa;
Southern Europe and part of Central Europe (Mediterranean climate areas);
southeastern United States.
Grades
|1| AYOADE, J. THE. Introduction to çlimatology for the tropics. Rio de Janeiro: Bertrand Brazil, 1996. 332 p. 4th ed. Translation by Maria Juraci Zani dos Santos.
image credits
[1] Wikimedia Commons (reproduction)
By Paloma Guitarrara
Geography teacher


