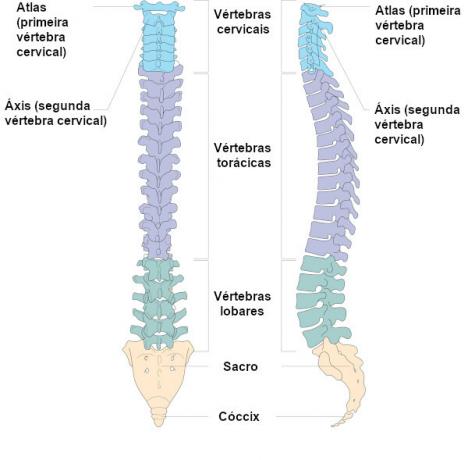
THE spine is one of the parts that make up our locomotive system. It is the central axis of our body, ensuring the support of the body and playing an essential role in our locomotion and balance. The spine is formed by a series of articulated bones called vertebrae. In total, we have 33 vertebrae forming this structure, 7 of which are cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral and 4 coccygeal.
Read too: How poor posture can harm students
spine summary
The spine is formed by 33 vertebrae, 7 of which are cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral and 4 coccygeal.
Between the vertebrae, the intervertebral discs are present.
The spine is the central axis of our body.
The spine protects the spinal cord.
The spine is not a completely straight structure, having natural curvatures.
Some problems that can affect the spine are herniated disc, parrot beak and postural deviations.
THE good posture can help prevent back pain.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
spinal anatomy
the spine is a structure of the skeleton axial formed by bones called vertebrae, which
they are joined together through joints. The length of the spine corresponds to approximately two-fifths of the total height of our body. Between each vertebra are the so-called intervertebral discs, cartilaginous structures that prevent friction between these bones and also cushion impacts.The spine is formed by 33 vertebrae, as follows:
7 cervical vertebrae;
12 thoracic vertebrae;
5 lumbar vertebrae;
5 fused vertebrae, which form the sacrum;
4 fused vertebrae, which form the coccyx.
An typical vertebra has a body, an arch, and the vertebral processes. The body is the anterior region of the vertebra and is composed of a cylindrical mass of cancellous bone with upper and lower edges formed by compact bone.
The body of one vertebra is separated from the body of the other vertebra by the intervertebral disc. In the posterior region of the body is the bow. The arch is formed by the right and left pedicles and by the right and left blades. It is responsible for forming the walls of the vertebral foramen, where the spinal cord.
Finally, we have the vertebral processes, which are bone tips that come from the blades. Vertebral processes vary in shape, direction and size, depending on the region of the spine where the vertebra is located.
Spinal curvatures
In the embryo, the vertebral column has only one curve, having the shape of a C. After birth, with increasing head and the adoption of an erect posture, the spine acquires its normal curvatures.
In an adult individual, there are four sagittal curvatures: cervical curvature, thoracic curvature, lumbar curvature and curvature sacrococcygeal. The cervical curvature is forward convex, the thoracic curvature is forward concave, the lumbar curvature is forward convex, and the sacrococcygeal curvature is forward concave.
The column also has lateral curvatures and these, generally, are presented in number of three: curvatures cervical, dorsal and lumbar. The cervical curvature is convex to the left, the dorsal curve is convex to the right, and the lumbar curve is convex to the left. Improper posture, or even an accident, can accentuate the normal curves of the spine.
Read too: Column Functions — protection of the spinal cord and other organs
spinal function
the spine is the central axis of our body. It guarantees the necessary rigidity to support our organism and also offers the necessary flexibility for we are able to move our trunk, being essential to maintain our balance, posture and allow our locomotion. In addition, the spine provides protection to the spinal cord, a component of the central nervous system.
Spinal Diseases
Different problems can affect our spine. One of the most known problems is the call. herniated disc, which occurs when an intervertebral disc moves out of its normal position. When this happens, the disc can compress the nerve roots, causing pains intense and even disabling. It is common, in these cases, to feel tingling, pain in the leg and even paralysis of movements.
Another problem observed in the column is called parrot beak or osteophytosis. In this case, there is an abnormal growth of a bony protrusion in the vertebrae, which may arise as a result, among other factors, of the wear of the intervertebral disc. This bulge can compress nerves and blood vessels.
When we talk about the spinal column, we must also mention the changes in the curvature of the spine. When there are changes in the curvature of the spine in the frontal plane, we speak of scoliosis, while in the sagittal plane there is kyphosis, or hyperkyphosis, and lordosis, or hyperlordosis.
Scoliosis: It is usually associated with a rotational deformity. In this case, the column is shifted to the side.
Kyphosis or hyperkyphosis: In this type of curvature change, we notice an accentuation of curvature in the thoracic area. People who have this postural change have an arched back and shoulders that are projected forward.
Lordosis or hyperlordosis: Occurs when the anterior curvature is accentuated in the lumbar area.
It is important to highlight that many back problems could be avoided if simple measures were adopted, such as not using pillows very thin that change the curvature of the spine, lean properly against chairs when sitting, do not carry backpacks or bags with the weight in on one side of the body, avoid performing domestic activities with the trunk fully bent and bending down by bending the knees instead of the back. To learn more, read: Spine care.
By Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos
Biology teacher