Vector is the representation that determines the magnitude, direction and direction of a vector quantity. Vectors are straight segments oriented by an arrow at one end.
We name the vectors with a letter and a small arrow.
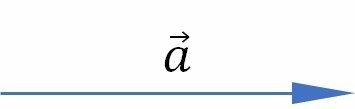
Vectors characterize vector quantities, which are quantities that need orientation, that is, direction and direction. Some examples are: force, velocity, acceleration and displacement. The numerical value is not enough, it is necessary to describe where these quantities act.
modulus of a vector
The vector's modulus, or intensity, is its numerical value, followed by the unit of measure of the magnitude it represents, for example:
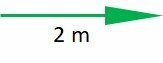
We indicate the module between bars keeping the arrow or, just the letter, without bars and without arrow.
The length of the vector is proportional to the modulus. A larger vector represents a larger modulus.
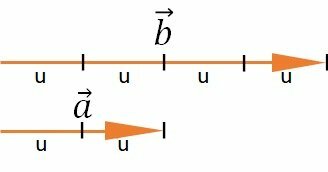
the vector module is 4 units, while vector
is 2 units.
Direction of a Vector
The direction of the vector is the slope of the support line on which it is determined. There is only one direction for each vector.
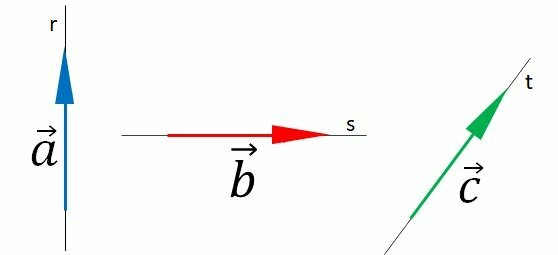
sense of a vector
The direction of the vector is shown by the arrow. The same direction can contain two directions, such as up or down and left or right.
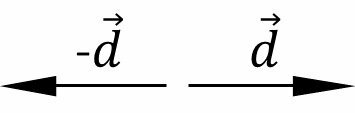
Adopting a direction as positive, the opposite direction, negative, is represented with a minus sign before the vector symbol.
Resulting Vector
The resulting vector is the result of vector operations and is equivalent to a set of vectors. It is convenient to know the vector that represents the effect produced by more than one vector.
For example, a body can be subject to a set of forces and we want to know the result they will produce, all together, on this body. Each force is represented by a vector, but the result can be represented by only one vector: the resultant vector.

The resulting vector, , of horizontal direction and direction to the right, is the result of additions and subtractions of the vectors.
,
,
and
. The resulting vector shows a tendency for the body to move in this orientation.
The vectors with vertical direction have the same size, that is, the same module. As they have opposite meanings, they cancel each other out. This shows that there will be no movement of the crate in the vertical direction.
When analyzing the vectors and
, which have the same direction and opposite directions, we realize that a part of the force "remains" to the right, as the vector
is bigger than the
, that is, the module of
it's bigger.
To determine the resulting vector, we perform vector addition and subtraction operations.
Addition and subtraction of vectors with the same direction
With equal senses, we add the modules and keep the direction and direction.
Example:
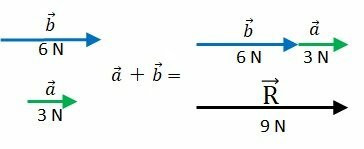
Graphically we place the vectors in sequence, without changing their modules. The beginning of one must coincide with the end of the other.
The commutative property of addition is valid, as the order does not change the result.
With opposite senses, we subtract the modules and keep the direction. The direction of the resulting vector is that of the vector with the largest modulus.
Example: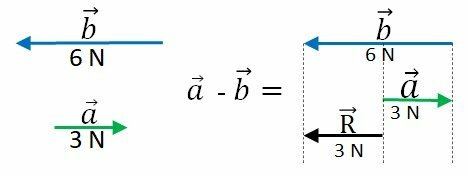
the vector is the leftover part of
, after withdrawing
.
Subtracting one vector is equivalent to adding with the opposite of the other.
Addition and Subtraction of Perpendicular Vectors
To add two vectors with perpendicular directions, we move the vectors without changing their modulus, so that the beginning of one coincides with the end of the other.
The resulting vector links the beginning of the first to the end of the second.
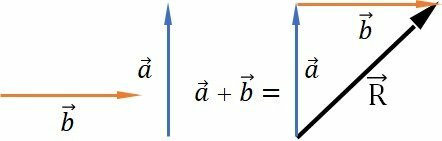
To determine the magnitude of the resulting vector between two perpendicular vectors, we match the start of the two vectors.
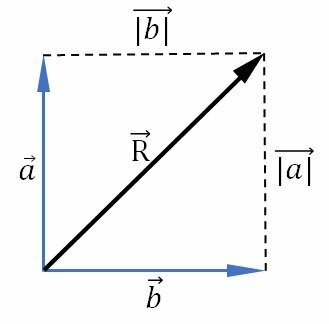
The modulus of the resulting vector is determined by the Pythagorean theorem.
Addition and subtraction of oblique vectors
Two vectors are oblique when they form an angle between their directions other than 0°, 90° and 180°. To add or subtract oblique vectors, the parallelogram and polygonal line methods are used.
parallelogram method
To perform the method, or rule, of the parallelogram between two vectors and draw the resulting vector, we follow these steps:
The first step is to position their origins at the same point and draw lines parallel to the vectors to form a parallelogram.
The second is to draw a diagonal vector on the parallelogram, between the union of vectors and the union of parallel lines.

The dotted lines are parallel to the vectors and the geometric figure formed is a parallelogram.
The resulting vector is the line connecting the origin of the vectors to the parallels.
O modulus of the resulting vector is obtained by the Cosine Law.
Where:
R is the magnitude of the resulting vector;
a is the vector module ;
b is the modulus of the vector ;
is the angle formed between the directions of the vectors.
The parallelogram method is used to add a pair of vectors. If you want to add more than two vectors, you must add them two by two. To the vector resulting from the sum of the first two, we add the third and so on.
Another way to add more than two vectors is to use the polygon line method.
polygonal line method
The polygonal line method is used to find the vector resulting from adding vectors. This method is especially useful when adding more than two vectors, such as the following vectors ,
,
and
.
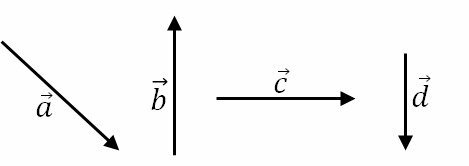
To use this method we must order the vectors so that the end of one (arrow) coincides with the beginning of another. It is important to conserve the module, direction and direction.
After arranging all the vectors in the form of a polygonal line, we must draw the resulting vector that goes from the beginning of the first to the end of the last.
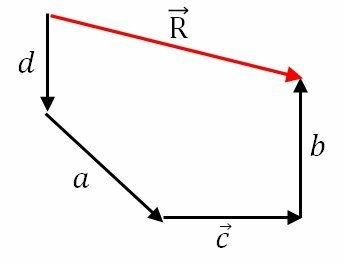
It is important that the resulting vector closes the polygon, with its arrow coinciding with the arrow in the last vector.
The commutative property is valid, since the order in which we place the plot-vectors does not change the resulting vector.
vector decomposition
To decompose a vector is to write the components that make up this vector. These components are other vectors.
Every vector can be written as a composition of other vectors, through a vector sum. In other words, we can write a vector as being the sum of two vectors, which we call components.
Using a Cartesian coordinate system, with perpendicular x and y axes, we determine the components of the vector.
the vector is the result of the vector sum between the component vectors.
and
.
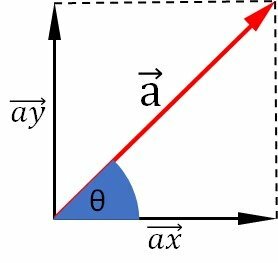
the vector tilt
forms a right triangle with the x axis. Thus, we determine the modules of the component vectors using trigonometry.
Component module ax.
Component module ay.
the vector module is obtained from the Pythagorean Theorem.
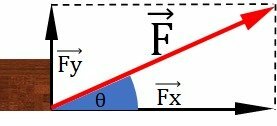
Example
A force is performed by pulling a block from the ground. The 50 N modulus force is tilted 30° from the horizontal. Determine the horizontal and vertical components of this force.
Data:
Multiplication of a real number by a vector
By multiplying a real number by a vector, the result will be a new vector, which has the following characteristics:
- Same direction if real number is non-zero;
- Same direction, if the real number is positive, and in the opposite direction if it is negative;
- The modulus will be the product of the modulus of the real number and the modulus of the multiplied vector.
Product between a real number and a vector
Where: is the vector resulting from the multiplication;
is the real number;
is the vector being multiplied.
Example
Let the real number n = 3 and the vector of modulo 2, the product between them is equal to:
Module calculation
The direction and direction will be the same.
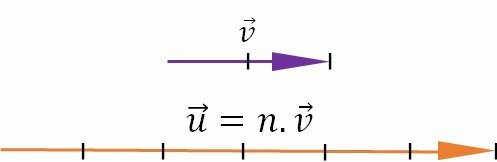
Exercise 1
(Enem 2011) The friction force is a force that depends on the contact between bodies. It can be defined as an opposing force to the displacement tendency of bodies and is generated due to irregularities between two surfaces in contact. In the figure, the arrows represent forces acting on the body and the enlarged dot represents the irregularities that exist between the two surfaces.

In the figure, the vectors that represent the forces that cause displacement and friction are, respectively:
The) 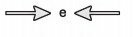
B) 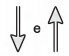
ç) 
d) 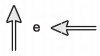
and) 
Correct answer: letter a) 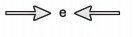
The arrows represent the vectors of forces that act in the movement in the horizontal direction, being an action-reaction pair, they have opposite directions.
The vertical arrows represent the actions of the Weight force and the Normal force and, as they are equal, they cancel each other out, with no movement in the vertical direction.
Exercise 2
(UEFS 2011) The vector diagram in the figure outlines the forces exerted by two rubber bands on a tooth of a person undergoing orthodontic treatment.
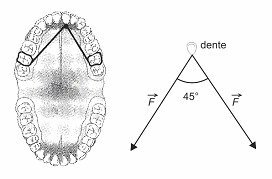
Assuming F = 10.0N, sen45° = 0.7 and cos45° = 0.7, the intensity of the force applied by the elastics on the tooth, in N, is equal to
a) 3√10
b) 2√30
c) 2√85
d) 3√35
e) 2√45
Correct answer: c) 2√85
The intensity of the force applied to the tooth is obtained by the Law of Cosines.
a and b are equal to 10 N.
Factoring the square root gives us:
Therefore, the intensity of the resultant force applied by the rubber bands on the tooth is .
Exercise 3
(PUC RJ 2016) Forces F1, F2, F3 and F4, in the Figure, make right angles to each other and their modules are, respectively, 1 N, 2 N, 3 N and 4 N.
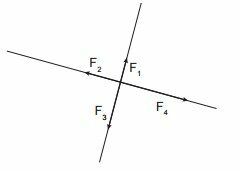
Calculate the modulus of the net force, in N.
a) 0
b) √2
c) 2
d) 2√ 2
e) 10
Correct answer: d) 2√ 2
We use the polygonal line method to determine the resulting vector. To do this, we rearrange the vectors so that the end of one coincides with the beginning of the other, like this:
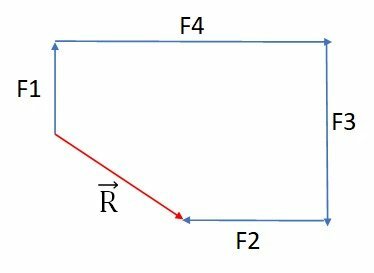
Using a coordinate system with origin at the beginning of the resulting vector, we can determine the modules of its components, as follows:
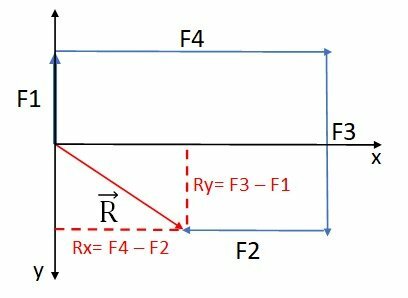
Thus, we have to:
Ry = 3 - 1 = 2 N
Rx = 4 - 2 = 2 N
The magnitude of the resulting vector is determined by the Pythagorean Theorem.
Therefore, modulus of the net force is equal to .
learn more about
- Vectors: addition, subtraction and decomposition.
- Vector Quantities
✖