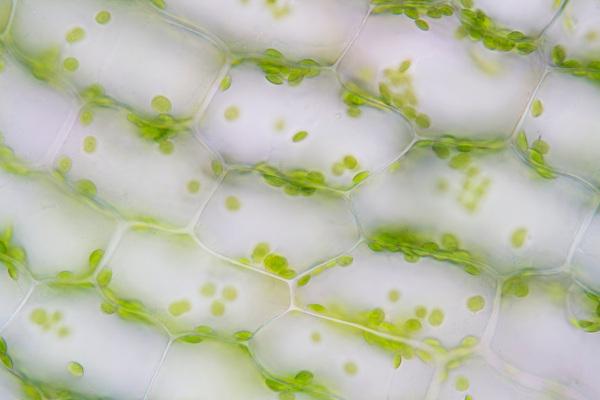
You chloroplasts are organelles that occur only in the cells of vegetable and seaweed and are rich in chlorophyll, a green colored pigment. They are related to the process of photosynthesis, in plants, and are found mainly in leaves.
We can find about half a million chloroplasts per square millimeter of leaf surface and about 40 to 50 chloroplasts in leaf mesophyll cells. In the angiosperms, chloroplasts are from 3 to 10 µm in diameter and have a discoid shape. Chloroplasts have a double membrane and a complex system of membranes inside.
Read too: What are the differences between animal cells and plant cells?
What is a chloroplast?
Chloroplast is a cellular organelle found in plant and algae cells. Chloroplasts are a type of plastid or plastid which together with the presence of vacuoles and cellulosic cell wall characterize a plant cell. The chloroplast is rich in chlorophyll, a green pigment that acts in the photosynthesis process and is responsible for ensuring the green color of green plants and algae. In addition to chlorophyll, chloroplasts also have carotenoids, which are yellow and orange colored pigments. These pigments are normally masked by chlorophyll.
other plastids
As stated earlier, chloroplasts are a type of plastid or plastid. In addition to chloroplasts, we also have two other important plastids:
- chromoplasts,
- leukoplasts.
You chromoplasts have carotenoid pigments, not containing chlorophyll in its structure. The presence of carotenoids makes these organelles responsible, for example, for the coloring of flowers, fruits and even roots, as is the case with the carrot.
You leukoplasts, in turn, do not have pigments, nor do they have an elaborate system of membranes. These organelles are related to the storage of some substances. Some leukoplasts are called amyloplasts because of the accumulation of starch.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Chloroplast structure
Chloroplasts are cell organelles that have a complex structure. They have a discoid format and, as well as the mitochondria, two membranes covering them. Between these two membranes, there is the intermembrane space. Inside the chloroplasts, there is a dense fluid called the stroma, in which there is a system of membranes that form species of bags called thylakoids. The space within the thylakoids is called the thylakoid fire, and chlorophylls and carotenoids are contained in the thylakoid membrane.
The thylakoids can be piled up forming columns that resemble piles of coins, called granule or grain. The thylakoids present in the piles are called granule thylakoids, and those that interconnect the stacks are called intergranule thylakoids or stromal thylakoids.
Chloroplasts can show starch grains, with the appearance of these grains being linked to the photosynthesis process. These grains only appear when the organism is actively carrying out photosynthesis. This starch is temporarily stored, tending to disappear in situations of prolonged dark. In addition to starch, small oil bodies can occur in these organelles.

Like mitochondria, chloroplasts have their own circular DNA, similar to organisms prokaryotes, and ribosomes. Due to the presence of DNA and ribosomes, we say that chloroplasts are semi-autonomous organelles, featuring the ability to synthesize some proteins, but not all necessary. Another important feature of chloroplasts is their ability to form another by division. The characteristics of chloroplasts and mitochondria suggest that these organelles arose through a symbiotic association with another organism. The theory that explains the emergence of these organelles is called endosymbiotic theory.
Read too: What are the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
Chloroplast function
Chloroplasts are cell organelles that participate in the process ofphotosynthesis, which consists of the process of formation of carbohydrates using carbon dioxide and water in the presence of light. In addition to its role in photosynthesis, we must highlight the role of chloroplasts in other processes such as temporary storage of starch and synthesis of amino acids and fatty acids.
By Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos
Biology teacher
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SANTOS, Vanessa Sardinha dos. "Chloroplasts"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/cloroplastos.htm. Accessed on July 27, 2021.

