THE flat isomerism or constitutional is one in which two or more compounds have the same molecular formula, but differ in some aspect of their structural formula.
An isomer of this type is the function isomerism or functional, in which the isomers differ by belonging to different functions.
See below the most common cases of functional isomerism:
1. Isomerism between aldehyde and ketone:Note below that the two compounds have the same molecular formula, which is C4H8O, however one of them belongs to the group of aldehydes (butanal) and the other to the group of ketones (butanone):
O O
║ ║
H3C CH2 CH2 ─ CH H3C C ─ CH2 CH3
Butanone Butanone
(Aldehyde) (Ketone)
2. Isomerism between carboxylic acid and ester: Below we have two compounds with the same molecular formula (C3H6O2), but propanoic acid belongs to the carboxylic acid functional group and methyl ethanoate belongs to the ether group:
O O
║ ║
H3C CH2 ─ C ─ OH H3C─C─O─CH3
Propanic Acid Methyl Ethanoate
(Carboxylic Acid) (Ester)
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
3. Isomerism between an alcohol and an ether: Butanol and ethoxyethane are functional isomers, as both molecular formulas of these compounds are C4H10O, but one is alcohol and the other is an ether:
H3C CH2 CH2 CH2 ─ OH H3C CH2 O CH2 CH3
Butanol Ethoxyethane
(Alcohol) (Ether)
4. Isomerism between an aromatic alcohol and a phenol: This can be seen below, where the compounds shown have the molecular formula C7H8O, but the first is a phenol and the other is an aromatic alcohol:

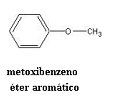
This isomerism can also occur with an aromatic ether. The compound below, for example, has the same molecular formula as the previous alcohol and phenol:
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Function Isomerism"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/isomeria-funcao.htm. Accessed on July 27, 2021.