THE titration is a laboratory procedure used to determine the concentration in quantity of matter (or concentration in mol/L) of a solution containing an acid or a base.
During the titration, there is always a mixture of solutions containing different solutes with occurrence of chemical reaction. As mixed solutions always have an acid and a base, therefore, the chemical reaction that takes place is a neutralization.
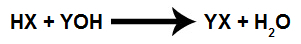
Chemical equation representing a titration.
The process for determining the molar concentration of an unknown solution during titration depends on the following factors:
• Know the molar concentration of the solution that will be mixed with the unknown;
• Know the volume of the solution of unknown concentration;
• Know the volume of solution of known concentration.
Formula used in a titration
And in titration a neutralization occurs (equal number of moles of acid and base), we can use the following formula to determine the molar concentration of the unknown solution:
noThe = nB
MThe.VThe = MB.VB
Note: The number of moles is the product between the molar concentration (M) and the volume of a solution (V).
Equipment needed to perform a degree
• Burette: equipment used to measure the volume of solution of known concentration;

• Erlenmeyer: equipment used to receive the solution of unknown concentration;
• Universal support: equipment to which the claw is fixed;

• Claw: equipment used to hold the burette;

• Magnetic stirrer: equipment used to stir the solution present in the Erlenmeyer flask.

Steps of a degree
-
1st Stage: fix the burette to the universal support using the claw;
-
2nd Stage: position the Erlenmeyer flask on the magnetic stirrer;
-
3rd Stage: add a certain volume, inside the Erlenmeyer flask, of the solution of unknown concentration. For example: add 10 mL of the solution to the Erlenmeyer flask;
- 4th Stage: add phenolphthalein to the solution present in the Erlenmeyer flask.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Note: If the solution in the Erlenmeyer flask is acidic, when adding the phenolphthalein, the solution will remain unaltered in color, however, if the solution is basic, it will be pink reddish.

Phenolphthalein added to a basic characteristic solution.
-
5th Stage: add a magnetic bar inside the Erlenmeyer flask. Then, turn on the magnetic stirrer so that the liquid inside the Erlenmeyer is stirred;
-
6th Stage: add inside the burette, up to its maximum capacity, a volume of a solution of known concentration, that is, if the burette is 50 mL, add 50 mL of this solution.
- 7th Step: open the burette valve and allow the liquid from its interior to fall into the Erlenmeyer flask.
Observations made during the titration
As soon as the burette is opened on the Erlenmeyer flask, the neutralization reaction begins, that is, the acid reacts with the base, gradually forming salt and water.
As the neutralization reaction occurs with the mixture, the color of the solution present in the erlenmeyer also changes gradually, what we call the turning point, as follows:
- If it was colorless, it starts to look pinkreddish,
- if it waspinkreddish, starts to turn colorless.
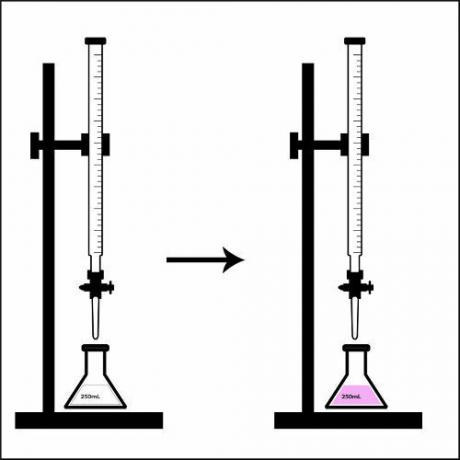
Representation of the turning point in a titration.
When the solution present in the erlenmeyer flask completely changes color, that is, it has reached the turning point, we say that the titration is over. At that moment, just check the used volume of the solution of known concentration that was there on the burette.
From the sum between the volume of the solution of known concentration, which was determined in the burette, and volume of the unknown solution, which was the erlenmeyer flask, we are in a position to determine its concentration molar.
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
DAYS, Diogo Lopes. "What is titration?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/quimica/o-que-titulacao.htm. Accessed on July 27, 2021.