When we hear the word “silicone” we immediately think of breast implants placed through plastic surgery. However, silicone is a material that has several purposes, including its use in products that we commonly consume in our daily lives.
But before looking at these applications, see what the chemical makeup of silicone is and how it is produced.
O silicone it is a condensation polymer, that is, their long molecular chains are formed through condensation polymerization reactions, in which the monomers, when united, release water or another simple substance.
THE structure silicone fundamental is shown below. Note that instead of carbon (C) we have silicon (Si) as the central element, as the main chain of silicon is made up of silicon atoms alternating with oxygen atom. This is possible because silicon belongs to the same family, in the Periodic Table, as carbon, coming in the period right after carbon. Therefore, silicon has properties similar to those of carbon and, therefore, it can bind to organic groups (R).
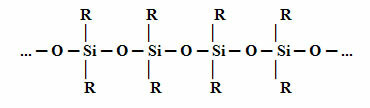
In the case of silicone, the most commonly used monomers in its production are dichlo-dimethyl-silane or dichloro-diphenyl-silane. These monomers are obtained through the reaction between silica, present mainly in sand, with coke coal, to first obtain silicon:
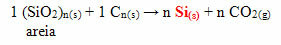
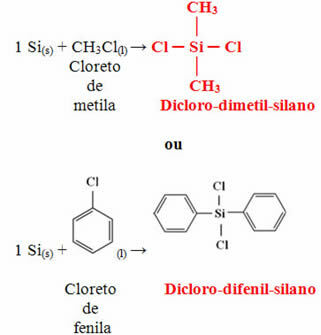
The next step is to react this silicon obtained with methyl chloride or with phenyl chloride to form one of the two monomers mentioned above:
The monomer obtained will eventually react with water to form the polymer (silicone) and release hydrochloric acid as a by-product:
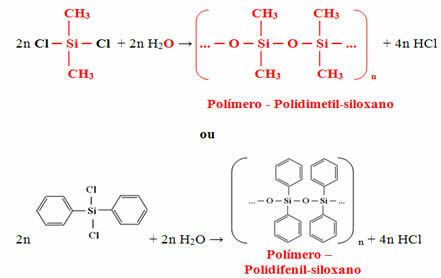
Silicone is a very stable polymer and has great resistance to heat, as only the organic compounds bound to the silicone start to combust in contact with heat. However, when these radicals have finished reacting, only silica (sand) remains, which prevents combustion from continuing.
Because it has these characteristics, it is non-toxic, has great chemical inertness and presents itself in ways that vary from the extremely fluid liquid to rubber-like solid, these polymers are used in the most diverse areas. Below are some of these applications:

By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/silicone-constituicao-aplicacoes.htm