Friedel-Crafts acylation reactions are organic substitution reactions, in which a hydrogen bonded to an aromatic ring is exchanged for a acyl group, shown below:

Usually the acylation reaction occurs between the aromatic compound it is a acyl chloride, as the acetyl chloride shown above, in the presence of a catalyst (Lewis acid), such as aluminum chloride.
The product formed in this type of reaction is a aryl ketone.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
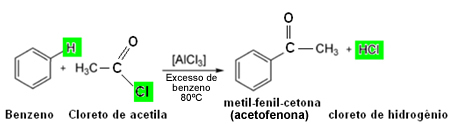
Below is an example of acylation of benzene:
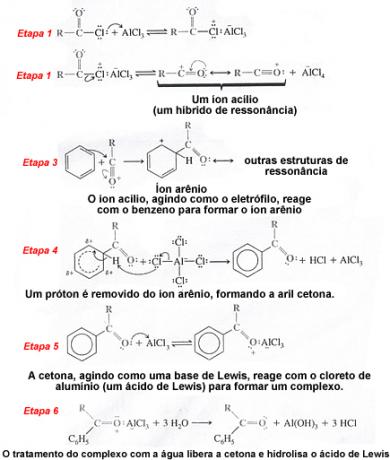
Now let's look at the mechanism of this reaction in detail. Note in the first and second steps that the acyl halide forms the acyl ion, which acts as the electrophile of this reaction:
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Acylation Reaction"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/reacao-acilacao.htm. Accessed on July 27, 2021.