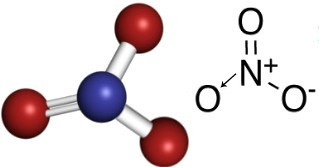
Nitrates are inorganic compounds that contain the anion NO3-.
Nitrogen is family 15, has 5 electrons in the valence shell and needs to make three covalent bonds (with sharing electrons) to have eight electrons in the valence shell and thus to have stable. However, each oxygen has 6 electrons in the last shell and therefore each of its atoms needs to make two bonds to be stable.
So, in the nitrate anion, nitrogen is the central element, which makes a double bond with one of the oxygens, which is stable, a single bond with one of the other two oxygens, and with the other a covalent bond dative. This means that one of the oxygens is not stable, needing to receive 1 more electron, giving a total charge equal to -1. With the dative nitrogen makes a bond more than it could do, donating one of its electrons, getting a charge equal to +1. See below the structure of this anion:
This anion can receive an electron and form an electrically neutral compound, an inorganic salt. These compounds are all soluble in water.
The main applications of nitrates are in medicines, such as vasodilators in the treatment of angina pectoris (pain in the caused by low oxygen supply by blood flow to the heart muscle) and erectile dysfunction male. They are also used in fertilizers and explosives, as will be mentioned later.
Nitrates can be produced through a nitric acid (HNO) neutralization reaction.3) with some basis. See the example below, where magnesium nitrate was formed:
HNO3 + Mg(OH)2 → Mg (NO3)2+ H2O
Three main examples of this type of compound are the sodium nitrate (NaNO3), potassium nitrate (KNO3) and ammonium nitrate (NH4AT THE3). In all these cases, the cations (Na+,K+ and NH4+) provide 1 electron to a nitrate anion. But in reality, these opposite charges attract each other and form well-defined ionic clusters, which are the crystalline lattices. Thus, nitrates are usually crystalline solids, as shown below in the case of sodium nitrate:
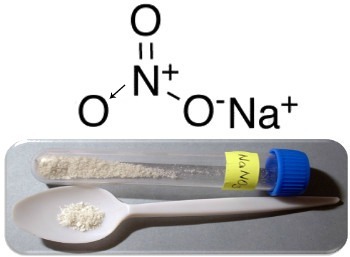
This compound is used in the manufacture of fertilizers, but it is mainly known as Chilean saltpeter, as there are large deposits of it in the Chilean deserts. It is transformed into potassium nitrate, which is used to make the black powder used in various weapons and explosives.

Both sodium nitrate and potassium nitrate are called "saltpetre", being widely used as preservatives of the color of canned and smoked meats, as well as in some foods for giving a greater sensation of satiety. However, its consumption brings serious damage to health, as these nitrates can be transformed by bacteria from the organism into nitrites and, later, into nitrosamines, which are carcinogenic, mainly causing cancers in the stomach. Nitrites also convert the hemoglobins in the blood, making them unable to carry oxygen.
The main causes of excess intake of nitrates are the use of nitrogen fertilizers in the cultivation of vegetables.
Saltpeter is also dangerous because it increases the concentration of sodium ions in the body, which can cause heart problems such as high blood pressure.
O ammonium nitrate it is also used as a fertilizer and explosive, and was even used with fuel oil in the terrorist attack on World Trade Center buildings on September 11, 2001.

The attack on the World Trade Center used ammonium nitrate*
* Image copyright: Dan Howell and Shutterstock.com
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry