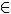O African continent It is recognized for its vast territorial area, in addition to a geographic position that makes this continent the only one to be located in all terrestrial hemispheres. The Equator Line, Earth's main parallel, passes through Africa practically at its center, bringing deep natural differences in terms of climate and vegetation.
Africa's Climate
The climatic diversity of the African continent is greatly influenced by differences in latitude and, to a lesser extent, by maritimity and continentality, besides, in some points, the altitude also determines some climatic types, such as the Cold one of Mountain. In the map below, we have a generic classification of African climates.
Map of climate types in the African continent *
Many authors state that the African climate is apparently "mirrored", that is, with a repetition of a good part of the climatic ranges during north and south of the equator, although there are differences, such as the lower proportion of occupation of the desert climate, in addition to a lower performance of the semiarid. O
Saara's desert, in the north, occupies a large area, characterizing the climate of the so-called North Africa, while the Kalahari Desert occupies a smaller area in the extreme south.
Landscape of the Kalahari Desert at a point in northern South Africa.
Although Sahara is the biggest hot desert in the world and bring a wide influence to the continental atmosphere, most of the African continent is occupied by the tropical climate (similar to what occurs in Brazil), with a dry and cold climate in winter and hot and rainy in the summer. This climatic range is interrupted in some stretches of the equatorial climate, which is hotter and more humid due to the presence of the Congo forest in the central portion of Africa.
The Vegetation of Africa
If we look at the map below, where there is a generic indication of the main African biomes, we can see that there is a balanced relationship between the climate and vegetation of Africa, with the large desert strips already mentioned, in addition to the presence of Steppes in most regions semiarid.
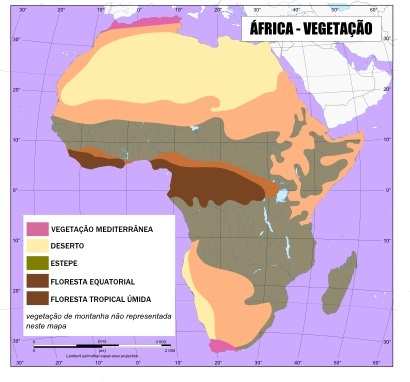
Map of Vegetation Types in Africa *
At savannas, a type of vegetation very similar to thick Brazil and occupying most of the continent, are found almost entirely in the tropical climate ranges. The equatorial forest, responsible for the highest humidity on the continent, is found in low latitudes and it remains surrounded by a humid tropical forest, while in the extreme north and south it inhabits the Mediterranean vegetation.

African savanna landscape
It is important to highlight, however, that the boundaries between one natural type and another are not completely clear and well defined, with areas of transition between one type and another. An example is the steppe vegetation, which becomes thinner, with areas of field, as its geographical position approaches the desert zones.
______________________
* Map base: Eric Gaba / Wikimedia Commons. Maps created by the author of the text.
By Rodolfo Alves Pena
Graduated in Geography
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/geografia/aspectos-naturais-Africa-clima-vegetacao.htm