O Simple Present Tense, also called Present Simple (simple present), is one of the verb tenses of English.
It is equivalent to present tense in the Portuguese language.
When to use Simple Present?
O Simple Present is a tense used to indicate usual actions that occur in the present.
Also, it is used to express universal truths, feelings, wishes, opinions and preferences.
Sometimes the sentences in the Simple Present present expressions of time (adverbs).
The most common are:
| Adverb | Translation |
|---|---|
now |
now |
| always | ever |
| never | Never |
| today | today |
| every day | every day |
| daily | daily |
| often | often |
| sometimes | sometimes |
| generally | usually |
| usually | usually |
See some example sentences in the Simple Present:
- he plays soccer very well. (He plays football very well.)
- she loves chocolate. (She loves chocolate.)
- they go to school in the afternoon. (They go to school in the afternoon.)
- I alwaysread the newspaper in the morning. (I always read the paper in the morning.)
- we generally travel to Brazil in December. (We usually travel to Brazil in December.)
Simple Present Rules
the conjugation of Simple Present varies according to the verbal person, the ending of the verb and the type of sentence (affirmative, negative and interrogative.)
Check below the explanation of the formation of the Simpish Present in the forms affirmative, negative and interrogative.
Affirmative Form
As a general rule, it can be said that to conjugate a verb in the Simpish Present, just use it in the infinitive without the I'm in the case of pronouns I, you, we and they, and add -s, -are you or -yes in the case of pronouns he, she and it.
See below for an example with the conjugation of the verb I work (work; work):

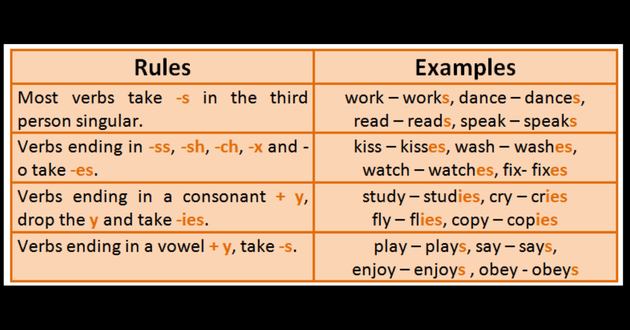
However, there are some specific rules for third person singular inflection (hey,she and it) which are related to the ending of verbs.
Verbs ending in -o, -z, -ss, -ch, -sh, -x
It is necessary to add -are you at the end of the verb.
Examples:
- to teach (teach) - Teaches
- to watch (to attend) - watches
- to push (push) - pushes
- I'm kissing (kiss) - kisses
- I go (go) - goes
- I'm fix (to repair) - cool
Verbs ending in -y preceded by consonant
Remove the -y and add up -yes
Examples:
- I'm fry (fry) - fries
- to fly (fly) - flies
- to study (to study) - studies
- to worry (worry) - worries
Verbs ending in -y preceded by vowel
Add only the -s.
Examples:
- to say (to say) - says
- to play (to play; to play) - plays
Verb position in affirmative sentences
See below for the structure of affirmative sentence formation in Simple Present:
Subject + main verb + complement
Examples:
- I live in Brazil. (I live in Brazil). - verb I'm live (to live, to live).
- he Teaches spanish at the university. (He teaches Spanish at university.) - verb I'm teatea (teach).
- they prefer Italian food. (They prefer Italian food.) - verb I prefer (to prefer).
- she watches TV every day. (She watches TV every day.) - verb to wattea (to attend).
- we like to go to the beach during the week. (We like to go to the beach during the week.) - verb I like (like).
- It pushes the door when it wants to get in. (he/she pushes the door when he wants to enter)-verb I'm poosh (push).
- you always arrive bark. (You are always late.) - verb to arrive (to arrive).
- she always kisses her grandma before leaving. (She always kisses her grandmother before she leaves.) - verb I'm kiss (kiss).
- he goes to the gym on weekends. (He goes to the gym on weekends.) - verb I'm gO (go).
- she cool her car by herself. (She fixes her car herself.) - verb I'm fix (to repair).
Negative Form
The negative form of the Simple Present is formed using auxiliary verbs of and does.
Of is used with the pronouns I, you, we and they. The assistant does is used with he, she, it.
See below the conjugation of the negative form of the verb I work (work; work) in the Simple Present.

Note that in the negative form of the simple Present, the verb is always used in the infinitive without the I'm, even when it comes to the third person singular (he, she and it).
Negative sentences can be written in full (do not or does not) or contracted (don't or doesn't):
- Of + not = don’t
- Does + not = doesn’t
Verb position in negative sentences
See below for the structure of negative sentence formation in Simple Present:
Subject + auxiliary verb + not + main verb + complement
Examples:
- I do not live in Brazil. (I don't live in Brazil). - verb I'm live (to live, to live).
- he does not teach spanish at the university. (He does not teach Spanish at university.) - verb to teach (teach).
- they don'tprefer Italian food. (They don't prefer Italian food.) - verb I prefer (to prefer).
- she doesn'twatch TV every day. (She doesn't watch TV every day.) - verb to watch (to attend).
- we do not like to go to the beach during the week. (We don't like going to the beach during the week.) - verb I like (like).
- It does not push the door when it wants to get in. (He/she doesn't push the door when he wants to get in.) -Verb to push (push).
- you don't arrive bark. (You are not late.) - verb to arrive (to arrive).
- she don't kiss her grandma before leaving. (She doesn't kiss her grandmother before she leaves.) - verb I'm kissing (kiss).
- he does not go to the gym on weekends. (He doesn't go to the gym on weekends.) - verb I go (go).
- she doesn't fix her car by herself. (She doesn't fix her car herself.) - verb I'm fix (to repair).

Interrogative Form
As with negative sentences, auxiliaries of and does are used to form interrogative sentences in the Simple Present.
Of is used with I, you, we and they, and does is used with he, she and it.
See below the conjugation of the interrogative form of the verb I work (work; work) in the Simple Present:

note that the verb is always used in the infinitive without the I'm, even when it comes to the third person singular (he, she and it).
Verb position in interrogative sentences
See below for the structure of interrogative sentence formation in Simple Present.
Auxiliary verb + subject + main verb + complement
Examples:
- Do I own you money? (Do I owe you money?). - verb to own (to owe).
- does he teach Spanish at the university? (Does he teach Spanish at university?) - verb to teach (teach).
- do they prefer Italian food? (Do they prefer Italian food?) - verb I prefer (to prefer).
- does she watchTV every day? (Does she watch TV every day?) - verb to watch (to attend).
- do we have classes on Saturdays? (Do we have classes on Saturdays?) - verb I have (to have).
- does it push the door when it wants to get in? (Does he/she push the door all the way in?) - verb to push (push).
- do you arrive bark? (Are you late?) - verb to arrive (to arrive).
- does she kissher grandma before leaving? (Does she kiss her grandmother before she leaves?) - verb I'm kissing (kiss).
- does he go to the gym on weekends? (Does he go to the gym on weekends?) - verb I go (go).
- does she fix her car by herself? (She fixes her car herself?) - verb I'm fix (to repair).
IMPORTANT
The verb I do means to do. However, in the Simple Present it is used as an auxiliary verb that complements the formation of negative and interrogative sentences.
As assistants, of and does have no meaning.
The do and does helpers are also used in short answers.
Note the examples below:

Conjugated verb tables
Now that you've learned the rules of Simple Present, see some examples of conjugated verbs.
Verb to love
| Affirmative | negative | Interrogative |
|---|---|---|
| i love | I do not/don't love | Do I love? |
| you love | you do not/don't love | Do you love? |
| he loves | he does not/doesn't love | Does he love? |
| she she loves | she does not/does n't love | Does she love? |
| it loves | It does not/doesn't love | Does it love? |
| we love | we do not/don't love | Do we love? |
| you love | you do not/don't love | Do you love? |
| they love | They do not/don't love | Do they love? |
Verb to be (to be/be)
| Affirmative | negative | Interrogative |
|---|---|---|
| I am/I'm | I'm not/I'm not | Am I? |
| you are/you are | You are not | Are you? |
| He is/He's | He is not/isn't | Is he? |
| she she is / she she's | She she is not / she is not | Is she? |
| It is/It's | It is not/isn't | Is it? |
| we are/we are | We are not | Are we? |
| you are/you are | You are not | Are you? |
| they are/they are | They are not | Are they? |
NOTE: As with the modal verbs (modal verbs), the negative form and the interrogative form of the verb to be are not formed using auxiliaries of and does.
verb to have
| Affirmative | negative | Interrogative |
|---|---|---|
| I have | I do not/don't have | Do I have? |
| you have | You do not/don't have | Do you have? |
| he has | He doesn't/doesn't have | Does he have? |
| she has | She she does not / she does not have | Does she have? |
| It has | It doesn't have | Does it have? |
| we have | We do not/don't have | Do we have? |
| you have | You do not/don't have | Do you have? |
| they have | They do not/don't have | Do they have? |
Simple Present x Present Continuous
both the Simple Present (simple gift) as the Present Continuous (continuous present) are English tenses that indicate present tense.
However, it is common for both to cause doubts for those who want to practice and build sentences in English.
O Simple Present indicates usual actions occurred in the present and also universal truths, feelings, wishes, opinions and preferences.
already the Present Continuous indicates actions that are taking place in the present, that is, at the moment of speaking. Equivalent to the gerund of the Portuguese language. As a general rule, to combine the Present Continuous, it is necessary to add -ing at the end of the verb...
Examples:
- they are watching the movie. (They are watching a movie.) - verb to watch (to attend).
- I am making the phone call. (I'm making a phone call.) - verb to make (to do).
See below some sentences in the Simple Present and in the Present Continuous that illustrate the difference between the two verb tenses.
Examples:
- he is playing baseball. (He is playing baseball.) - PRESENT CONTINUOUS
- He plays baseball. (He plays baseball.) - SIMPLE PRESENT
- They study German. (They study German.) - SIMPLE PRESENT
- they are studying German. (They are studying German.) - PRESENT CONTINUOUS
How about knowing more about the English language? See too:
- The 10 most used conjunctions in English
- Simple Past
- English tenses
- Regular and Irregular English Verbs
- Passive voice (exercises with commented feedback)
- Present Continuous Exercises
- Past Continuous exercises with commented feedback
Video about Simple Present
Now that you've seen everything you need to know about Simple Present, watch the video below to consolidate your learning.
Simple Present Summary
Check out the infographic that Toda Matéria prepared for you below, with a summary of the use of Simple Present tense.

If you want more information on how to study English, it is worth checking the articles below:
- How to learn English on your own
- English in Enem: how to study
Exercises on Simple Present
question 1
(Unifor-CE/2001)
In the age-old battle between independence-seeking teenagers and worried parents, the older generation is packing some new weapons. Caller tells ID parents who is calling their kids. Cell-phone bills detail every local number the kid has called. New computer programs track just about everything − every website visited, every email felt − that a teenager does online.
Parental reconnaissance is going to get worse − or good, depending on your perspective.
(Wall Street Journal, Nov. 6, 2000)
The verbs that are in Simple Present, in the text, are:
a) detail - track - get
b) worried - visited - sat
c) is packing - is calling - is going
d) tells - detail - track
e) worried - has called - does
Correct alternative: d) tells - detail - track
The alternative d) is the only one where all the verbs are inflected in the Simple Present.
- tells is the bending of Simple Present of the verb to tell (to say), in the third person singular (he/she/it).
- detail is the bending of Simple Present of the verb to detail (detail), used with the pronouns I, you, we, they.
- track is the bending of Simple Present of the verb to track (track), used with the pronouns I, you, we, they.
See what the tenses of the other alternatives are:
The) detail - track - get: detail and track they are in Simple Present, however, in the text, the verb get is part of the future structure of Simple Future, going to get.
B) worried - visited - sit: all verbs are in the Simple Past.
ç) is packing - is calling - is going: is packing and is calling they are in Present Continuous. Ois going is part of the future structure of Simple Future, is going to get.
and) worried - has called - does: worried it's in the Simple Past, has called it's in the Present Perfect and does is the only verb in the Simple Present.
question 2
(Ufac/2010) Choose the alternative that best completes the sentence:
Charles normally ________ water, but now he ________ Coke.
a) drinks; is drinking.
b) is drinking; drinks.
c) was drinking; drinks.
d) drink; is drinking.
e) drinks, was drinking.
Correct alternative: a) drinks; is drinking.
Note that the adverb was used in the sentence normally (usually), which indicates a habitual action. Therefore, the verb to be used to fill the gap must be conjugated in the Simple Present.
Of the available alternatives, only letters a), d) and e) are suitable. The letter b) starts with a flexion conjugated in the Present Continuous (is drinking) and letter c) has its first option conjugated in the Past Continuous (was drinking).
In the second part of the prayer, the word now (now), which requires the use of a conjugated verb in the Present Continuous (continuous present) to indicate an action in progress in the present.
Options a) and d) remain. The correct option was the letter a) because the subject of the sentence is Charles, which corresponds to the pronoun he (he). For he, she and it must add the -s at the end of the verb.
question 3
Check the correct alternative to complete with the Simple Present:
She doesnt ________ anymore.
a) to work out
b) work out
c) working out
d) works out
e) worked out
Alternative b: She doesn't work out anymore.
The sentence presents a third person singular inflection (he, she and it) in the negative form of the Simple Present, indicated by the use of doesn't.
When the does or the does not are used, you must use the main verb in the infinitive without the I'm.
The infinitive in question is to work out (exercise), soon, work out without I'm. Therefore, letter b) is the correct alternative.
question 4
Fill in the spaces with the conjugation of the verbs in the Simple Present:
a) Do you ______ in America? (to live)
Correct answer: a) live
As the phrase is a question, the verb must be used in the infinitive without the I'm. In this case, as the infinitive is I'mlive (live), just use the live.
b) Jane ______ your friend. (to love)
Correct answer: b) loves
jane is the subject of the sentence. As it is a female name, it is equivalent to the pronoun she (Is it over there).
the bending of simple Present in he, she and it must be done by adding -s to the end of the infinitive verb without the I'm.
the infinitive is I love (love). Without I'm, we only have love. So, just add the -s: loves
c) Juan and Carla ______ on the beach every morning. (to run)
Correct answer: c) run
Juan and Carla equate to the pronoun they (they).
to inflect the verb to run (run) in the third person plural (they), just use the infinitive verb without the I'm. how the infinitive is to run, without I'm we just have run. Soon, Juan and Carla run.
d) she She _______ English every day. (to teach)
Correct answer: d) teaches
When a verb ends in -O, -z, -ss, -tea, -sh or -x, the bending of simple Present in he, she and it must be done with the addition of -are you at the end of the infinitive verb without the I'm.
the infinitive is to teach (teach). Without I'm, we only have teach. So, just add the -es: teaches.
e) Thomas ______ his car weekly. (to wash)
Correct answer: washes
When a verb ends in -O, -z, -ss, -tea, -sh or -x, the bending of simple Present in he, she and it must be done with the addition of -are you at the end of the infinitive verb without the I'm.
the infinitive is to wash (to wash). Without I'm, we only have wash. So, just add the -es: washes.
question 5
Write the following sentence in negative and interrogative forms:
We go to school every day.
Negative form:
Correct answer: We don't go to school every day or We don't go to school every day.
The main verb of the sentence is I go (go).
To form negative sentences in the Simple Present, you must use the helper of or the helper does, and add the not. Contracted shapes can also be used. don't or doesn't.
does not and doesn't are used with the pronouns he, she and it. With the other pronouns (I, you,we and they) use up do not or don't.
After the auxiliary, you must use the main verb in the infinitive without the I'm. As the main verb of the infinitive sentence is I go, without I'm we have go.
Position of the verb in negative sentences: subject + auxiliary verb + not + main verb + complement
Bearing in mind that the pronoun used in the sentence is the we (we) can choose to use do not or don't:
- We don't go to school every day.
- We do not go to school every day.
Interrogative form:
Correct answer: Do we go to school every day?
The main verb of the sentence is I go (go).
To form interrogative sentences in the Simple Present, you must use the helper of or the helper does.
Does is used with the pronouns he, she and it. With the other pronouns (I, you,we and they) use up of.
After the auxiliary, you must use the main verb in the infinitive without the I'm. As the main verb of the infinitive sentence is I go, without I'm we have go.
Verb position in interrogative sentences: auxiliary verb + subject + main verb + complement
Bearing in mind that the pronoun used in the sentence is the we (us), the correct answer is Do we go to school every day?
question 6
According to the formation of sentences in the Simple Present, the sentence in which the words appear in the correct order is:
a) My girlfriend visits her parents on Sundays.
b) On Sundays my girlfriend her parents visits.
c) Visits her parents on Sundays my girlfriend.
d) My girlfriend parents her visits her on Sundays.
e) Her parents my girlfriend visits on Sundays.
Correct alternative: a) My girlfriend visits her parents on Sundays.
At the Simple Present, the formation of affirmative sentences follows the following structure:
Subject + main verb + complement
- Subject: My girlfriend
- Main verb: visits
- Complement: her parents on Sundays
question 7
Complete with the correct form of the verb in parentheses.
a) They ______ their email every day. (check-checks)
b) The sun ______ in the east. (rise-rises)
c) We ______ shopping on Saturdays. (go-goes)
d) Water ______ at 100°C. (boil-boils)
e) Daniel ______ for a big hotel in the city center. (work-works)
To conjugate a verb in Simple Present, just use it in the infinitive without the I'm in the case of pronouns I, you, we and they, and add -s, -are you or -yes in the case of pronouns he, she and it. So, the correct answers are:
a) check - They check their email every day. (They check their email every day.)
b) rises - The sun rises in the east. (The sun rises in the east.)
c) go - We go shopping on Saturdays. (We go shopping on Saturdays.)
d) boils - Water boils at 100 °C. (The water boils at 100 °C.)
e) works - Daniel works for a big hotel in the city center. (Daniel works for a large hotel downtown.)
question 8
Fill in the blanks with the correct auxiliary verb: I do or I'mwell.
a) ______ are you married?
Yes, my husband's name is Frank.
b) ______ do you have any children?
Yes, I have three sounds.
c) Where ______ do you work?
I’m a doctor at the local hospital.
d) What ______ their names?
Lucy and Tomas.
e) What ______ do you do?
I work in a club.
both the verb I do how much the verb to be can be used in English as auxiliary verbs.
The verb I do, as an auxiliary, it does not have a translation.
already the verb to be is used when the meaning of the sentence is related to the verbs "to be" or "to be". Thus, the answers to the questions are:
a) are - Are you married? (Are you married?)
b) do - Do you have any children? (Do you have kids?)
c) do - Where do you work? (Where do you work?)
d) are - What are their names? (What are their names?)
e) do - What do you do? (What do you do?)
question 9
In the sentences below, insert the frequency adverbs in parentheses in the correct place.
a) Do you work late? (often)
b) I’m exhausted. (always)
c) I finish at four in the morning. (usually)
d) I work till six. (once a week)
Frequency adverbs are used between the subject and the verb, except when the main verb of the sentence is the to be. Check out the correct answers:
a) Do you often work late? (Do you usually work late?)
b) I'm always exhausted. (I'm always exhausted.)
c) I usually finish at four in the morning. (I usually finish at four in the morning.)
d) I work till six once a week. (I work until six once a week.)
question 10
Read the sentences below regarding grammar rules about using the Simple Present.
I. When conjugating in the Simple Present a verb ending in y preceded by a consonant, just add the -s in the inflections of grammatical people he, she and it.
II. O Simple Present it is used to speak of habits and routines, and universal truths.
III. In the interrogative form of the Simple Present, the main verb is not inflected. It is used in the infinitive without the I'm.
It is correct what is stated in:
a) I and III
b) I and II
c) II and III
d) I, II and III
e) n.d.a.
Correct answer: c) II and III
The statement of sentence I is incorrect, since when conjugating in the Simple Present a verb ending in y preceded by a consonant, it is necessary to add -yes, and not just -s, in the inflections of grammatical people he, she and it.
For more exercises on the Simple Present, See too Simple Present exercises



