Plants have different types of roots as a result of the adaptive changes they undergo to stay in the environment.
Types
Learn about the main types of plant roots:
underground root
The subterranean roots are divided into fasciculate and pivoting:
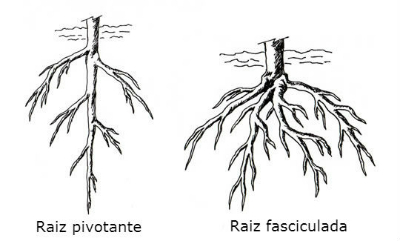
fasciculated roots
The fasciculate roots are found in monocotyledonous plants. They originate from a point from which thin branches of approximately the same size depart.
Examples: cane, corn and grass.
pivoting roots
Pivoting or axial roots are characterized by a larger taproot, from which lateral roots depart. They are found in dicot plants.
Examples: beans, coffee, ipe.
Root adaptations
Roots may also have certain specializations that contribute to carrying out their functions.
tuberous roots

Tuberous roots store a large amount of reserve substances, especially starch. Because of this characteristic, some of them are edible.
Examples: sweet potatoes, carrots, beets, yams, cassava.
sucking roots

Sucking or haustor roots occur in parasitic plants. They get this name because they penetrate the trunk of another plant to extract its sap.
Examples: birdweed and lead vine.
Roots anchors

Anchor roots have the stem as a starting point. Its structure is fixed to the soil, which facilitates the increase in the plant's absorption area.
They are commonly found in waterlogged soils such as mangroves.
Example: fig tree.
tabular roots

The tabular roots are flat and look like planks. They have the function of increasing the stability of the plant in the soil and are common in large trees.
Examples: chicha do cerrado.
aquatic root

Aquatic roots are found in plants that live in water. They aid in the absorption of nutrients.
Examples: water lily and water hyacinth.
Learn more, read also:
- plant parts
- plant kingdom
- Botany: the study of plants
Root Functions
The plant root has the following functions:
- Fixation of the plant in the soil;
- Absorption of nutrients, minerals and water;
- Reserve of water and nutrients.
Root parts
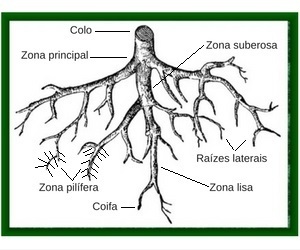
- Coif: Function to protect the root from friction with the soil and the attack of microorganisms. It is characterized by the existence of small cells with the ability to rapidly multiply. This is the root growth mechanism.
- smooth zone: Also called the growing zone, it is the part where vertical elongation and root growth take place.
- piliferous zone: Also known as the absorption zone. Its function is to absorb water and mineral salts from the soil that will form the plant's sap. It is characterized by the presence of hairs responsible for absorption.
- Suberous zone: It is the branch of the root, responsible for the increase in the absorption area. From it, secondary roots are formed, which have the function of fixing the plant to the ground.
- Collection or lap: It is the transition from the root to the stem.
Learn about the other parts of the plant. Read too:
- Types of Flowers and Their Functions
- All about Leaves
- Types of Fruits
- Stem Types