THE artistic gymnastics, also called Olympic gymnastics, is a sport that involves a set of movements.
These movements require precision, strength, flexibility, agility, coordination and balance. Therefore, body control is one of the main characteristics of these athletes.

artistic gymnastics movements
Those who practice artistic gymnastics are called gymnasts. Although initially it was only practiced by men, today this modality is present in both categories (male and female).
Did you know?
In the beginning, this modality was called Olympic gymnastics. Only later, with the inclusion of rhythmic sports gymnastics and trampoline gymnastics, did it come to be called artistic gymnastics.
History
The history of artistic gymnastics is older than we think. It is believed that the Greeks practiced various movements and acrobatics on some devices in order to achieve physical perfection.
Greek gymnastics was a preparation of the body both for the practice of other sports and for military training.
At the beginning of the 19th century, the German pedagogue Friedrich Ludwig Christoph Jahn (1778-1852) was one of those responsible for transforming artistic gymnastics into a sport modality.

Portrait of Friedrich Ludwig Christoph Jahn
He founded gym clubs for young people and those interested in the sport and also created several equipment that are still used today.
For this reason, it is called by some the “father of gymnastics”. Since the practice was seen as dangerous, Jahn was arrested and gymnastics was banned.
Fortunately, fans of this sport did not allow its extinction. Thus, some Germans took the sport to other parts of Europe and the world.
In 1881 the European Gymnastics Federation was founded, which resulted in the consolidation of this sport.
Since 1896, artistic gymnastics has been present in the Olympic Games. It started at the Athens Games and at the Pan American Games it has been in since 1951.
As far as the female category is concerned, it was only in the 1928 Olympics in Holland that women began to compete. Today this group has great representation in Brazil and in the world.
Artistic Gymnastics in Brazil
Artistic gymnastics arrived in Brazil at the end of the 19th century. Brought by European immigrants, it was in the states of the southern region that it began.
In 1858, the Joinville Gymnastics Society was founded in Santa Catarina. Ten years later, another organization of this modality was founded in Porto Alegre: Sociedade de Ginástica de Porto Alegre (Sogipa).
At the beginning of the 20th century, Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo began to practice Olympic gymnastics in clubs in the city. The first national championship took place in 1950 between athletes from São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro and Rio Grande do Sul.
On November 25, 1978, the Brazilian Gymnastics Confederation (CBG) was created, the body responsible for the sport in the country.
Soon, she joined the International Gymnastics Federation (FIG), responsible for organizing world competitions.
The first Brazilian Olympic competition was held in Moscow in 1980. Since then, this modality has been growing in the country. Noteworthy are gymnasts Daiane dos Santos and Diego Hipólito, both world champions.
Read too: Olympics and Fitness.
Rules
Usually the artistic gymnastics tests focus on the perfection of the movements. In an oré-determined sequence, gymnasts perform a series of movements that occur on the apparatus and on the floor.
Gadgets
In addition to ground movements and jumps performed by gymnasts, Olympic gymnastics brings together various equipment. Gymnasts use a kind of splint on their hands to perform these movements.
For the female and male categories, the equipment used is different. Thus, for male practice, the main devices are:
pommel horse

Gymnast performing movements on pommel horse
Rings

gymnast in the rings
Parallel bars

Gymnast in the parallel bar test
Fixed Bars

Gymnast in fixed bar competition
For female practice, the main devices are:
Asymmetric Bars

Gymnast in asymmetrical bar test
Balance Bars
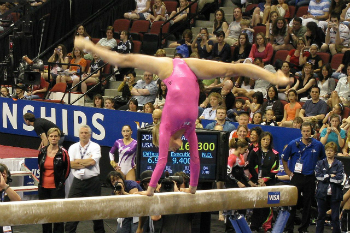
Gymnast on balance bars
Jump and Solo
Both women and men perform ground movements and jumps.
Through a short initial run, athletes develop the momentum needed to take a jump. Finally, they put their feet on a mattress.

gymnast after the jump
In the ground test, turns, jumps, steps and acrobatic movements are performed by both groups. They cannot cross the boundary of the square-shaped court with 40 feet on a side.
Men have 70 seconds to perform the movements. As for women, they have 90 seconds.
In the male solo event there is no music to accompany the movements. In the feminine, in turn, there is a musical background.

Gymnast on the floor
The judges award marks related to the execution of each movement according to the degree of difficulty. If gymnasts make mistakes, some points are taken away.
Also know about the Rhythmic gymnastics and Acrobatic gymnastics.

