Cytology or Cell Biology is the branch of biology that studies cells.
The word cytology comes from the Greek kytos, cell and logos, study.
Cytology focuses on the study of cells, covering their structure and metabolism.
The birth of cytology and the invention of the microscope are related facts. In 1663, Robert Hooke cut a piece of cork and observed it under a microscope. He noticed that there were compartments, which he called cells.
From then on, cytology began to develop as a science. The advancement of microscopes contributed to the structures of cells being observed and studied.
Cell Theory
The establishment of the Cell Theory was possible thanks to the development of microscopy.
Cell Theory presents important postulates for the study of Cytology:
- All living things are made up of cells;
- The essential activities that characterize life take place inside cells;
- New cells form by dividing preexisting cells through cell division;
- The cell is the smallest unit of life.
Learn more about Cell Theory.
Cell Types
At cells can be divided into two types: the prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
prokaryotes
The main characteristic of the prokaryote cell is the absence of a karyotheque delimiting the cell nucleus. The nucleus of the prokaryote cell is not individualized.
At prokaryotic cells they are the most primitive and have simpler cell structures. This cell type can be found in bacteria.
eukaryotes
At eukaryotic cells are more complex. These have caryotheque individualizing the nucleus, in addition to various types of organelles.
Examples of eukaryotic cells are the animal cells and the plant cells.
Know more:
- cell types
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
- animal and plant cell
Cell Parts
Eukaryotic cells have differentiated morphological parts. The main parts of the cell are: plasma membrane, cytoplasm and cell nucleus.
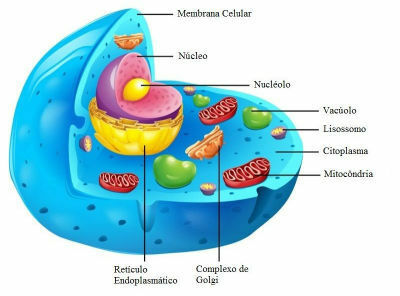
Structures present in the animal eukaryotic cell
Plasma membrane
The plasma membrane or cell membrane is a thin, porous cell structure. It has the function of protecting cellular structures by serving as an envelope for all cells.
The plasma membrane acts as a filter, allowing the passage of small substances and preventing or hindering the passage of large substances. We call this condition Selective Permeability.
Learn more about Plasma membrane.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is the most voluminous portion of the cell, where cell organelles are found.
The cytoplasm of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells is filled with a viscous and semi-transparent matrix, the hyloplasm or cytosol.
Organelles are small organs in the cell. Each organelle performs a different function.
Know what the Cell Organelles are:
Mitochondria: Its function is to carry out the cellular respiration, which produces most of the energy used in cellular functions.
Endoplasmic Reticulum: There are 2 types of endoplasmic reticulum, smooth and rough.
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is responsible for lipid production that will make up cell membranes.
The rough endoplasmic reticulum has the function of performing the protein synthesis.
Golgi Complex: The main functions of the golgi complex are are modify, store and export proteins synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum. It also gives rise to lysosomes and sperm acrosomes.
Lysosomes: Are responsible for intracellular digestion. These organelles act as sacs of digestive enzymes, digesting nutrients and destroying unwanted substances.
Ribosomes: The function of ribosomes is assist protein synthesis in the cells.
peroxisomes: The function of peroxisomes is the fatty acid oxidation for cholesterol synthesis and cellular respiration.
Learn more about Cell Organelles.
Cell Core
The cell nucleus represents the command region of cell activities.
In the nucleus is the organism's genetic material, DNA. It is in the nucleus that cell division takes place, an important process for cell growth and reproduction.
Know more:
- Cell Core
- Cell Division
- Cell exercises