The main Brazilian ecosystems are: Amazon, Caatinga, Cerrado, Atlantic Forest, Cocais Forest, Pantanal, Araucaria Forest, Mangue and Pampas.
The ecosystem refers to the set formed by biotic communities and abiotic factors that interact in a given region.
Any environment where there is interaction between abiotic factors and living beings is an ecosystem.
Map of Brazilian ecosystems
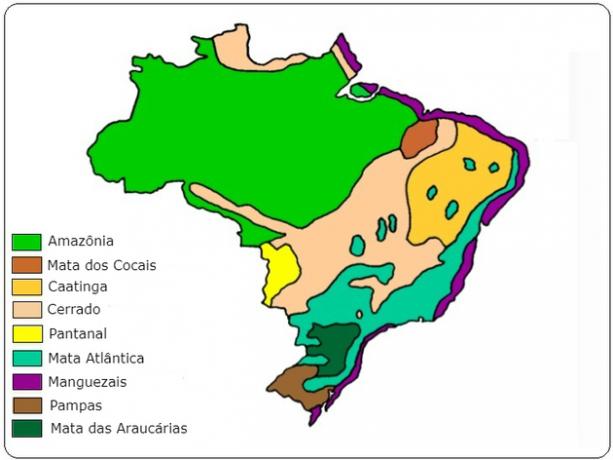
Brazil has a vast territory, the types of climate and soil are very varied, which gives different environmental conditions.
These factors favor the emergence of different ecosystems. See below the main characteristics and images of Brazilian ecosystems.
Amazon

The Amazon constitutes the largest remaining area of tropical forests in the world. It occupies about 49.29% of the Brazilian territory.
- Location: Covers the states of Acre, Amapá, Amazonas, Pará, Roraima, Rondônia and a portion of Mato Grosso, Maranhão and Tocantins.
- Climate conditionsAttractions: Hot and humid climate, with temperatures ranging from 20ºC to 41ºC throughout the year. Rainfall is greater than 1800 mm/year. The humidity in the region presents indexes from 80 to 100%.
- FloraAttractions: Brazil nut, rubber, kapok, guarana and a variety of epiphytic plants.
- FaunaAttractions: insects, amphibians, pythons, anacondas, sloths, manatees, porpoises, jaguars and arapaima.
Know more about:
- Amazon
- Amazon river
- Tropical forest
- Endangered animals in the Amazon rainforest
Caatinga

The Caatinga represents 10% of the Brazilian territory. One of its main characteristics is its plants that have adapted to the lack of water in the environment.
The survival of Caatinga plants is their resistance in periods of drought, as they store water in their trunks and leaves.
- Location: Covers the states of Piauí, Ceará, Rio Grande do Norte, Paraíba, Paraíba, Pernambuco, Sergipe, Alagoas, Bahia and North of Minas Gerais.
- Climate conditions: Semi-arid climate, with rainfall rates between 500 mm to 700 mm per year and temperature between 24ºC and 26ºC.
- Flora: The vegetation is formed by plants adapted to the dry climate. Plants have leaves turned into thorns, impermeable cuticles and stems that store water. These characteristics correspond to xeromorphic plants. Examples are the cacti (mandacaru and facheiro).
- FaunaAttractions: Some typical animals of the Caatinga are the preá, deer, calango, iguanas, jaguars and black monkey.
See also:
- Caatinga
- Caatinga climate
- Caatinga flora
- Caatinga Animals
thick

The Cerrado is a savanna-type biome, with small and spaced trees.
This is considered one of the Brazilian ecosystems that has been suffering most from deforestation caused by the advance of agricultural plantations.
- Location: It occupies the central region of Brazil. It covers the states of Minas Gerais, Goiás, Tocantins, Mato Grosso, Mato Grosso do Sul and west of São Paulo and Paraná.
- Climate conditions: The climate is relatively hot. Annual temperatures range from 21ºC to 27ºC. It has a dry season, with the possibility of the vegetation catching fire naturally.
- Flora: The trees have a thick bark, twisted trunks and deep roots. There is a predominance of grasses and herbaceous plants. The highlights are the ipê, peroba-do-campo and pequi.
- Fauna: Some characteristic animals are opossums, anteaters, maned wolves, agouti, tapirs, armadillos and puma.
Read too:
- thick
- Animals of the Cerrado
- Logging
- terrestrial ecosystem
Atlantic forest

Also called the Atlantic Forest, it is one of the most devastated ecosystems in Brazil.
It is estimated that there are only 5% of its original vegetation. Approximately 70% of the Brazilian population lives in the area of this biome.
- Location: It extends from Rio Grande do Norte to Rio Grande do Sul.
- Climate conditions: Wet subtropical climate in the south and humid tropical climate in the north.
- Flora: Plants have broad, evergreen leaves. The vegetation is rich in epiphytic plants. The characteristic plants of this ecosystem are the ipe, pau-brasil, jacarandá, jequitibá and palm trees.
- Fauna: The representative animals of the Atlantic Forest are the ocelots, marmosets, golden lion tamarins, toucans and parrots.
Learn more about:
- Atlantic forest
- Atlantic Forest Animals
- Biotic and abiotic factors
Cocais Forest

The Mata dos Cocais is considered a “transition forest” and is located between the humid forests of the Amazon and the Caatinga.
This ecosystem was already extensively explored, even in the colonial period, for the extraction of specific products, such as babassu oil and carnauba wax. Over time, soy plantations have taken on an extensive dimension, which contributes to the destruction of the environment.
- Location: It covers the states of Maranhão, Piauí and Rio Grande do Norte.
- Climate conditions: It has high levels of rain, ranging from 1500 mm to 2200 mm. The average annual temperature is 26ºC.
- Flora: The most characteristic species of these ecosystems is the palm tree. martian orbignya, the babassu. This palm tree has economic importance for the population, as its seeds are extracted an oil and the leaves are used to cover houses.
- Fauna: It presents several species of birds, mammals, reptiles, amphibians, insects, The characteristic animals are the red macaw, harpy eagle, giant otter, wild cat, capuchin, maned wolf, dolphin, guan, paca, cotias, flag acará, among others.
See also:
- Cocais Forest
- Biomes of the world
wetland

The wetland is considered the largest flooded plain in Brazil. This occurs in certain periods of the year, where certain areas can be partially or totally submerged.
It is one of the biomes with the greatest diversity of animals and plants.
- Location: West of Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul.
- Climate conditions: Continental Tropical Climate. In summer, temperatures reach 32ºC, while in winter, they reach 21ºC.
- Flora: It has few endemic species, that is, typical of this ecosystem. The caranda palm is the most representative.
- Fauna: The fauna is diverse. There are molluscs, crustaceans and fish, such as dorado, pau, jaú, surubim and piranhas. In addition to tuiuiús, socós, sara-curas, alligators, capybaras, jaguars and deer.
Learn more about:
- wetland
- Pantanal Animals
- aquatic ecosystem
Araucaria Forest

It gets its name since the region is full of Paraná pine (Araucaria angustifolia), known as Araucaria.
The Mata das Araucárias presents, in a well defined way, the different seasons of the year, that is, the winters are cold and the summers are hot
- Location: It covers the states of Rio Grande do Sul, Santa Catarina, Paraná and São Paulo.
- Climate conditions: It has low temperatures in winter. The rainfall index is 1400 mm annually.
- Flora: The most representative species is the Araucaria, which can reach up to 25 m in height. Ferns and epiphytic plants can also be found.
- Fauna: There are mammals, birds, reptiles and insects.
Also read about:
- Araucaria Forest
- Brazilian Biomes
Mangroves

Mangroves are coastal biomes with shrubby vegetation that develops in a muddy and salty soil.
For the environment, this is an important ecosystem as it prevents the beaches from silting up, acting as a barrier.
- Location: It extends along the entire Brazilian coast. However, it can penetrate several kilometers into the continent, following the course of rivers, whose waters meet, the salt waters during high tide.
- Flora: There are three main species of mangroves, the red mangrove, with a predominance of the species Rhizophora mangle; white mangrove, with a predominance of the species racemose lagoon it's the black mangrove, with a predominance of the species Schauerian Avicennia.
- Fauna: Crabs, molluscs and birds such as herons predominate.
You may also be interested in:
- Mangrove
- ecosystem
Pampas

Also called southern fields or fields. Represents a type of prairie.
Occurs in places where the relief region has rounded tops. Livestock is considered the main economic activity.
- Location: It predominates in the North of Rio Grande do Sul.
- Climate conditions: The Pampa's climate is subtropical with four well-defined seasons.
- Flora: Predominance of grasses and shrubs. Some plants are laurel, cedar, fork grass, carpet grass, pau-de-leite, cat's claw, field aloe, cacti, timbaúva, araucarias, algarrobo, dwarf palm.
- Fauna: jaguar, ocelot, capuchin monkey, howler monkey, anteater, rhea, partridge, partridge, lapwing, clay pigeon, pampas deer, guinea pig, tuco-tucos, toucans, sairas, gaturamos.
Know more about:
- Pampas
- Pampa animals