Mendel's First Law or Law of Segregation of Factors determines that each characteristic is conditioned by two factors that are separated in the formation of gametes.
Segregation is a consequence of the location of genes on chromosomes and their behavior during gamete formation, through the meiosis process.
The monk Gregor Mendel carried out his studies with the aim of understanding how different characteristics were transmitted from one generation to another.
Pea Experiments
Gregor Mendel conducted his experiments using peas for the following reasons:
- Easy to grow and develop in a short period;
- Production of many seeds;
- Fast reproductive cycle;
- Ease of controlling plant fertilization;
- Ability to self-fertilize.
Their experiments analyzed seven characteristics of peas: flower color, flower position on stem, seed color, seed texture, pod shape, pod color and plant height.
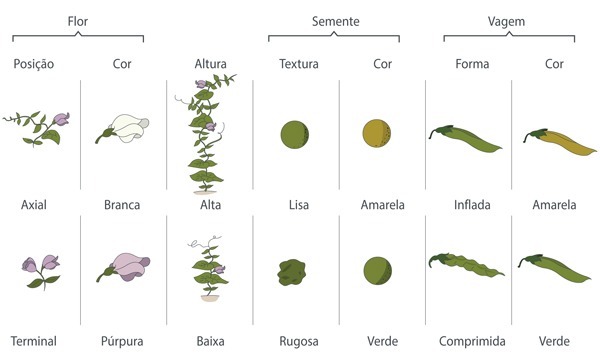
By observing the color of the seeds, Mendel realized that the yellow seed lineage always produced 100% of their offspring with yellow seeds. And the same with the green seeds.
The strains did not show variations, constituting pure strains. In other words, the pure strains kept their characteristics throughout the generations.
the findings of Gregor Mendel are considered the starting point for genetic studies. His contribution to the area was immense, which led him to be considered the "father of Genetics".
Crossings
Because he was interested in how traits were passed from one generation to another, Mendel performed another kind of experiment.
This time, he crossed between pure lines of yellow seeds and green seeds, which constituted the Parental Generation.
As a result of this crossing, 100% of the seeds were yellow - F1 generation.
Mendel concluded that the yellow seed was dominant over the green seed. Thus, the concept of dominant and recessive genes in genetics.
As all the seeds generated were yellow (Generation F1), Mendel performed self-fertilization between them.
The results surprised Mendel, in the new strain (Generation F2) green seeds appeared again, in a 3:1 ratio (yellow: green). That is, it was observed that for every four plants, three had the dominant characteristic and one the recessive characteristic.
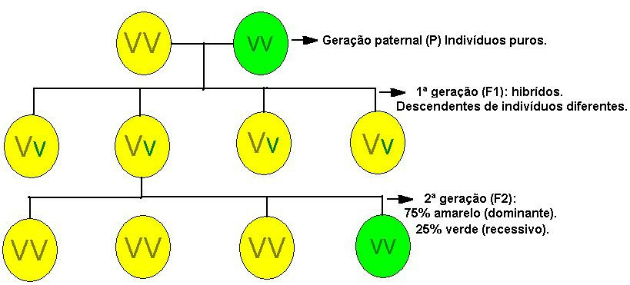
Mendel concluded that seed color was determined by two factors: one factor for generating yellow seeds, which is dominant, and another factor for generating green seeds, which is recessive.
Thus, Mendel's 1st Law can be stated as follows:
"All the characteristics of an individual are determined by genes that are separated during the formation of gametes, and thus, father and mother transmit only one gene to their descendants".
Mendel's First and Second Law
Mendel's First Law says that each characteristic is conditioned by two factors that separate in the formation of gametes.
In this case, Mendel studied only the transmission of a single characteristic. For example, he crossed yellow seeds with green seeds.
THE Mendel's Second Law it is based on the combined transmission of two or more characteristics. For example, he crossed green, rough seeds with yellow, smooth seeds.
Taken together, Mendel's Laws explain how hereditary traits are transmitted from one generation to another.
Through cross-breeding studies of plants with different characteristics, it was possible to prove that they maintain their integrity over generations.
Exercise solved
1. (FUC-MT) Crossing green peas vv with yellow peas Vv, the descendants will be:
a) 100% vv, green;
b) 100% VV, yellow;
c) 50% Vv, yellow; 50% vv, green;
d) 25% Vv, yellow; 50% vv, green; 25% VV, yellow;
e) 25% vv, green; 50% Vv, yellow; 25% VV, green.
Resolution
To resolve the issue, a cross between recessive green peas (vv) and dominant heterozygous yellow peas (Vv) should be performed:
Vv x vv → the originated genotypes are: vv vv vv vv
soon we have 50% of Vv (yellow peas) and 50% vv (green peas).
Reply: Letter C) 50% Vv, yellow; 50% vv, green.
Exercises with resolution and comments
1. (Unifor-CE) A student, when starting the course in Genetics, noted the following:
I. Each hereditary character is determined by a pair of factors, and as these separate in the formation of gametes, each gamete receives only one factor from the pair.
II. Each pair of alleles present in diploid cells separates in meiosis, so that each haploid cell receives only one allele of the pair.
III. Before cell division begins, each DNA molecule duplicates itself, and in mitosis the two resulting molecules separate, going to different cells.
Mendel's first law is expressed in:
a) I, only.
b) II, only.
c) I and II only.
d) II and III only.
e) I, II and III.
Alternative c) I and II only.
Considering the given statements and the statements of Mendel's First Law, we know that each characteristic is conditioned by two factors that are separated in the formation of gametes, one of which is of maternal origin and the other of paternal origin.
Haploid cells are those that have only one chromosomal set, so they do not appear in pairs. This is because diploid cells were separated during meiosis.
2. (PUC-SP) - It is known that, in a certain breed of cat, the uniform black coat is conditioned by a dominant B gene and the uniform white coat by its recessive b allele. From the crossing of a pair of black cats, both heterozygous, it is expected that they will be born:
a) 100% black cats.
b) 100% white cats.
c) 25% black cats, 50% tabby and 25% white.
d) 75% black cats and 25% white cats.
e) 100% tabby cats.
Alternative d) 75% black cats and 25% white cats.
Based on the information given in the question, we have the following alleles:
Uniform black coat - B (Dominant allele)
Uniform white coat - b
From the cross between black cats, we have:
Bb x Bb, with the following proportions: BB, Bb, Bb and bb. Thus, 75% (BB, Bb, Bb) of the cats will have a black coat and 25% (bb) will have a white coat.
3. (Unifesp-2008) Plant A and plant B, with yellow peas and unknown genotypes, were crossed with plants C that produce green peas. The A x C cross originated 100% plants with yellow peas and the B x C cross resulted in 50% plants with yellow peas and 50% green. The genotypes of plants A, B and C are, respectively,
a) Vv, vv, VV.
b) VV, vv, Vv.
c) VV, Vv, vv.
d) vv, VV, Vv.
e) vv, vv, vv
Alternative c) VV, Vv, vv.
Plants A and B produce yellow peas and in the cross they produced 100% yellow peas. This indicates that the trait is conditioned by a dominant allele (VV or Vv).
In the crossing between plant B and C, 50% of yellow pea plants and 50% of green pea plants were originated.
Therefore, the characteristic green pea is conditioned by a recessive allele (vv) and it must be present in plant B and plant C.
So we have:
Plant A (VV) - homozygous yellow pea.
Plant B (Vv) - heterozygous yellow pea.
Plant C (vv) - homozygous green pea.