Nucleic acids are macromolecules made up of nucleotides that form two important components of cells, DNA and RNA.
They receive this name because they have an acidic character and because they are found in the nucleus of the cell.
Nucleic acids are essential for all cells, as it is from the DNA and RNA molecules that they are Once the proteins are synthesized, the cells multiply and the mechanism of transmission of the characteristics still occurs. hereditary.
Furthermore, nucleotides are important in several processes, such as the synthesis of some carbohydrates and lipids and the regulation of intermediary metabolism, activating or inhibiting enzymes.
Structure
As we have seen, nucleic acids are made up of nucleotides, which have three basic components: a phosphate group, a pentose, and a nitrogenous base.
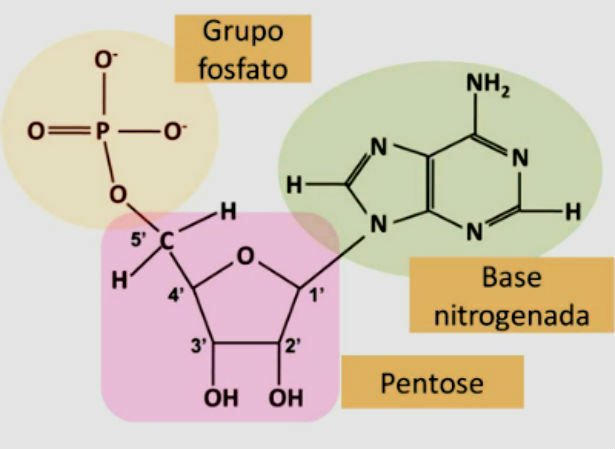
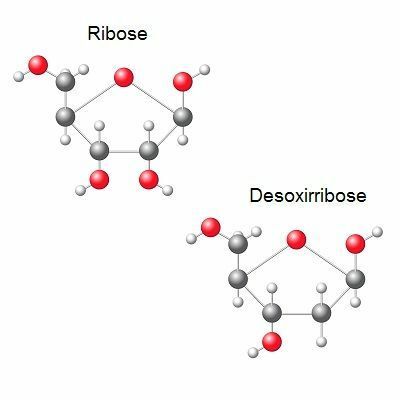
You nucleotides they are joined through phosphodiester bonds between the sugar and the phosphate group. Pentose is a sugar with five carbons. DNA is called deoxyribose, while the RNA it is called ribose.
When there is only one nitrogenous base linked to a carbohydrate from the group of pentoses, a nucleoside. Thanks to the addition of the phosphate group to the nucleosides, the molecules start to have negative charges and become nucleotides, presenting an acidic character.
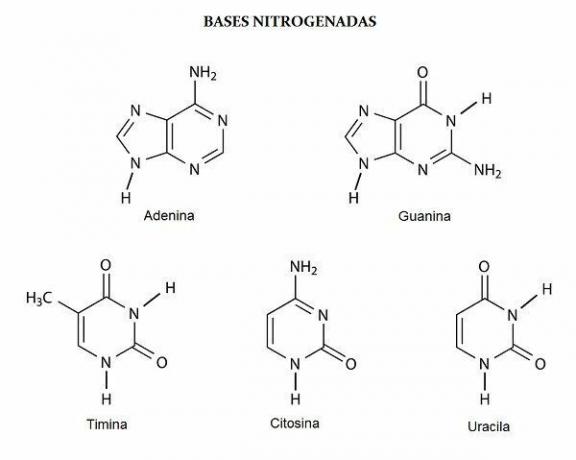
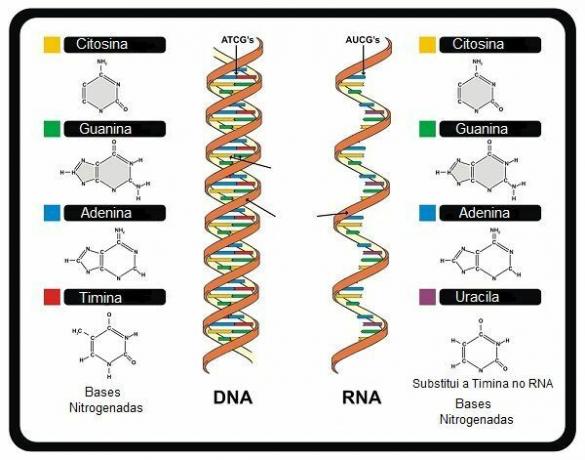
At nitrogen bases they are cyclic structures and exist in two types: the puric and the pyrimidine types. Both DNA and RNA have the same purines: a adenine (A) and the guanine (G). The change occurs in relation to pyrimidines, the cytosine (C) is common between the two, but the second base varies, in DNA there is thymine (T) and in RNA there is uracil (U).
Therefore, there are two types of nucleic acids: o deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) it's the ribonucleic acid or RNA (ribonucleic acid). Both are macromolecules composed of chains of hundreds or thousands of linked nucleotides.
Learn more, read also:
- Differences between DNA and RNA
- DNA replication
- DNA exercises