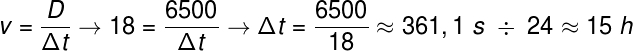In physics, the average velocity relates to the space traveled by a body in a given period of time.
To calculate the average speed in the questions use the formula Vm = distance/time. The International System unit for this quantity is m/s (meters per second).
question 1
(FCC) What is the average speed, in km/h, of a person walking 1200 m in 20 min?
a) 4.8
b) 3.6
c) 2.7
d) 2.1
e) 1.2
Correct alternative: b) 3.6.
1st step: transform meters into kilometers.
Knowing that 1 km corresponds to 1000 meters, we have:
2nd step: turn minutes into hours.
3rd step: calculate the average speed in km/h.
Therefore, the average speed is 3.6 km/h.
See too: Average speed
question 2
Alonso decided to take a tour of the nearby towns in the region where he lives. To get to know the places, he spent 2 hours traveling a distance of 120 km. What speed was Alonso on his ride?
a) 70 km/h
b) 80 km/h
c) 60 km/h
d) 90 km/h
Correct alternative: c) 60 km.
Average speed is expressed mathematically by:
Where,
V is the average speed; it is space covered;
is the time spent.
Replacing the statement data in the formula, we have:
Therefore, to get to know the region, Alonso traveled with an average speed of 60 km/h.
question 3
(Cesgranrio) A person, running, travels 4.0 km with an average speed of 12 km/h. The journey time is:
a) 3.0 min
b) 8.0 min
c) 20 min
d) 30 min
e) 33 min
Correct alternative: c) 20 min.
1st step: calculate the time spent in hours using the speed formula.
2nd step: convert from hours to minutes.
Therefore, the journey time is 20 minutes.
See too: Kinematics Formulas
question 4
Laura was walking in the park at a speed of 10 m/s on her bicycle. Performing the unit conversion, what would this speed be if we expressed it in kilometers per hour?
a) 12 km/h
b) 10 km/h
c) 24 km/h
d) 36 km/h
Correct alternative: d) 36 km/h.
The fastest way to convert m/s to km/h, and vice versa, is using the following relationship:
Therefore:
Note how the value of 3.6 was arrived at to multiply the speed, in m/s, and transform it into km/h.
Another way to perform the calculation is this:
Knowing that 1 km corresponds to 1000 m and 1 h represents 3600 seconds, we can, through the rule of three, find the values that we will apply in the formula.
1st step: conversion of distance from meters to kilometers.
2nd step: time conversion from seconds to hours.
3rd step: application of the values in the speed formula.
In different ways we arrive at the same result, which is 36 km/h.
question 5
(Unitau) A car maintains a constant speed of 72.0 km/h. In one hour and ten minutes it travels, in kilometers, the distance of:
a) 79.2
b) 80.0
c) 82.4
d) 84.0
e) 90.0
Correct alternative: d) 84.0.
1st step: calculate the time in minutes that corresponds to 1h 10min.
Step 2: Calculate the distance covered using the simple rule of three.
If the climbing speed is 72 km/h, it means that in 1 hour, or 60 minutes, the car has covered 72 km. For 70 minutes, we have:
Therefore, the distance covered is 84 kilometers.
question 6
Starting from time zero, a vehicle leaves the initial position of 60 meters and reaches the final position of 10 meters after 5 seconds. What is the vehicle's average speed to complete this route?
a) 10 m/s
b) – 10 m/s
c) 14 m/s
d) null
Correct alternative: b) – 10 m/s.
1st step: determine the space traveled.
For this, we subtract the final position from the initial position.
Note that the offset is negative. When this occurs, it means that the object made a movement in the opposite direction to the positive orientation of the trajectory, that is, the path was made in the decreasing direction of the positions.
2nd step: determine the time taken to complete the route.
As we did in the previous step, let's also subtract the final value from the initial one.
3rd step: calculate the average speed.
Now we need to enter the values found earlier in the formula and perform the division.
See the representation of this displacement in the image below.

question 7
(UEL) A small animal moves with an average speed equal to 0.5 m/s. The speed of this animal in km/day is:
a) 13.8
b) 48.3
c) 43.2
d) 4.30
e) 1.80
Correct alternative: c) 43.2.
1st step: convert the unit of meters into kilometers.
2nd step: convert the unit of seconds into day.
Knowing that:
1 hour has 3600 seconds because
1 day has 86400 seconds because
Therefore:
3rd step: calculate the average speed in km/day.
Note another way to do this calculation:
The animal's average speed is 0.5 m/s, that is, in 1 second the animal travels 0.5 m. We find the distance covered in one day as follows:
If 1 km is 1000 m, just divide 43 200 meters by 1000 and we will find that the average speed is 43.2 km/day.
See too: Uniform Movement
question 8
Pedro and Maria went out for a drive. They left São Paulo at 10 am towards Braúna, located 500 km from the capital.
As the journey was long, they made two 15-minute stops for gas and also spent 45 minutes for lunch. Upon arriving at the final destination, Maria looked at her watch and saw that it was 6 pm.
What is the average speed of the trip?
a) 90 km/h
b) 105 km/h
c) 62.5 km/h
d) 72.4 km/h
Correct alternative: c) 62.5 km/h
For the calculation of the average speed, the time that must be taken into account is the initial instant and the final instant, regardless of how many stops were made. Therefore:
Now, in possession of the amount of time spent, we can calculate the average speed.
question 9
(FGV) In a formula 1 race the fastest lap was done in 1 min and 20 s at an average speed of 180 km/h. Can it be said that the length of the runway, in meters, is?
a) 180
b) 4000
c) 1800
d) 14400
e) 2160
Correct alternative: b) 4000.
To convert the speed from km/h to m/s we use the conversion factor 3.6.
Therefore, 180 km/h corresponds to 50 m/s.
Knowing that 1 min contains 60 s, then the fastest lap time is:
1min20s = 60 s + 20 s = 80 s
Using the speed formula we can calculate the length of the track.
Another way to resolve the issue is:
1st step: convert the time given in seconds.
2nd step: convert the distance into meters.
3rd step: transform the average speed unit to m/s.
4th step: calculate the length of the track.
Knowing that 1 minute corresponds to 60 seconds and adding to the remaining 20 seconds, we have:
We performed the following calculation to calculate the runway length:
Therefore, the length of the track is 4000 meters.
question 10
Carla left her home in the direction of her relatives' house, at a distance of 280 km. Half of the route she made with a speed of 70 km/h and, in the other half of the way, she decided to reduce the speed even more, completing the route with 50 km/h.
What was the average speed performed on the course?
a) 100 km/h
b) 58.33 km/h
c) 80 km/h
d) 48.22 km/h
Correct alternative: b) 58.33 km/h.
As the total displacement performed by Carla was 280 km, we can say that the sections performed at different speeds were 140 km each.
The first step in solving this question is to calculate the time it took to cover each section with the speed applied.
1st step: calculate the time in the first part of the route with a speed of 70 km/h
2nd step: calculate the time on the second part of the route at a speed of 50 km/h
3rd step: calculate the total time to make the 280 km displacement
4th step: calculate the average speed of the journey
Therefore, the average speed of the course was 58.33 km/h.
question 11
(Mackenzie) Mr. José leaves his house walking at a constant speed of 3.6 km/h, heading to the supermarket, which is 1.5 km away. His son Fernão, 5 minutes later, runs to his father, taking the wallet he had forgotten. Knowing that the boy meets his father the moment he arrives at the supermarket, we can say that Fernão's average speed was equal to:
a) 5.4 km/h
b) 5.0 km/h
c) 4.5 km/h
d) 4.0 km/h
e) 3.8 km/h
Correct alternative: c) 4.5 km/h.
If Mr. José and his son go towards the supermarket, then it means that the distance covered () for both is equal.
As the two arrive at the supermarket at the same time, the final time is the same. What changes from one to the other is the initial time, as Fernão goes to meet his father 5 minutes after he left.
Based on this information, we can calculate Fernão's velocity as follows:
1st step: apply the average speed formula to find out the time spent by Mr. José.
2nd step: convert from hours to minutes.
3rd step: calculate Fernão's average speed.
Knowing that Fernão left the house 5 minutes after his father, the time taken by him to get to the supermarket was approximately 20 minutes or 0.333 h.
We apply the data in the average speed formula.
Therefore, Fernão's average speed was equal to 4.5 km/h.
question 12
(UFPA) Maria left Mosqueiro at 6:30 am, from a point on the road where the kilometer mark indicated km 60. She arrived in Belém at 7:15 am, where the kilometer mark of the road indicated km 0. The average speed, in kilometers per hour, of Maria's car, on its journey from Mosqueiro to Belém, was:
a) 45
b) 55
c) 60
d) 80
e) 120
Correct alternative: d) 80.
1st step: calculate time spent in hours
2nd step: calculate the average speed.
Therefore, the average speed of Maria's car was 80 km/h.
question 13
(Fatec) An elevator moves upwards and travels 40 m in 20 s. It then returns to the starting position taking the same amount of time. The average scalar speed of the elevator throughout the entire journey is:
a) 0 m/s
b) 2 m/s
c) 3 m/s
d) 8 m/s
e) 12 m/s
Correct alternative: a) 0 m/s
The formula for calculating average speed is:
If the elevator went up, from the ground, but returned to the initial position, it means that its displacement was equal to zero and, therefore, its speed corresponds to 0 m/s, as
See too: Uniform Movement - Exercises
question 14
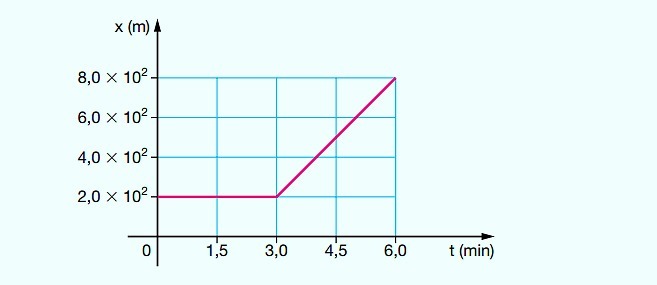
(UFPE) The graph represents the position of a particle as a function of time. What is the average particle velocity, in meters per second, between instants t 2.0 min and t 6.0 min?
a) 1.5
b) 2.5
c) 3.5
d) 4.5
e) 5.5
Correct alternative: b) 2.5.
1st step: calculate the average speed between 2.0 min and 6.0 min.
2nd step: transform the unit from m/min into m/s.
Therefore, the mean particle velocity between time t 2.0 min and t 6.0 min was 2.5 m/s.
See too: Kinematics - Exercises
question 15
(UEPI) In its trajectory, an interstate bus traveled 60 km in 80 min, after a 10 min stop, it continued travel for another 90 km at an average speed of 60 km/h and, finally, after 13 min of stop, it covered another 42 km in 30 min. The true statement about the movement of the bus, from the beginning to the end of the trip, is that it:
a) covered a total distance of 160 km
b) spent a total time equal to triple the time spent on the first trip segment
c) developed an average speed of 60.2 km/h
d) did not change its average speed as a result of stops
e) would have developed an average speed of 57.6 km/h if it had not made stops
Correct alternative: e) would have developed an average speed of 57.6 km/h if it had not made stops.
a) WRONG. The route that the bus took was 192 km, because
b) WRONG. For the total time to be triple the time of the first stretch, the time taken should be 240 minutes, but the trajectory was performed in 223 minutes.
thick. The average speed developed was 51.6 km/h, since 223 minutes correspond to approximately 3.72 h.
d) WRONG. The average velocity was modified, since the calculation of this quantity takes into account only the final and initial instants. Thus, the longer the time to complete a journey, the lower the average speed.
it's right. Two stops were made, 10 and 13 minutes, which delayed the trip by 23 minutes. If this time was not spent, the average speed would be approximately 57.6 km/h.