The sodium and potassium pump is a type of active transport that takes place in every cell in the body.
The process occurs due to differences in concentrations of sodium ions (Na+) and potassium (K+) inside and outside the cell.
To maintain the difference in concentration of the two ions in the cell's internal and external environment, it is necessary to use energy in the form of ATP. Thus, the sodium and potassium pump is a type of active transport.
The sodium and potassium pump is directly related to the transmission of nerve impulses and muscle contraction.
Sodium and Potassium Pump Operation
Under normal conditions, the concentration of Na+ it is lower inside the cell than in the extracellular environment. Meanwhile, the concentration of K+ it is higher inside the cell than in the extracellular environment.
In this situation, of course, the Na+ enter the cell and the K+ leaves the cell, by diffusion. This is because solutes tend to stay in concentration balances.
However, to carry out its metabolism, the cell needs to maintain the differences in concentration between the two ions. This means that Na
+ needs to remain at a low concentration inside the cell and the K+ in high concentration.The operation of the sodium and potassium pump is possible due to two basic conditions:
(1) The presence of transmembrane proteins throughout the entire plasma membrane. These proteins contain specific sites for binding Na ions.+ and K+;
(2) ATP expenditure, as the cell needs to maintain the concentration difference between the ions. Therefore, the sodium and potassium pump is a type of Active Transport.
Transmembrane proteins expel Na+ that enters the cell and look for the K+ coming out of the cell.
At each activation of the sodium and potassium pump, 3 Na+ bind to their specific sites on the protein. ATP also binds to the protein and loses a phosphate radical, turning into ADP. This causes a change in the conformation of the protein that releases Na ions+ in the extracellular environment.
At the same time, the 2K+ bind to the protein at their specific sites. The phosphate is released and the protein returns to its original conformation, releasing the K ions+ inside the cell.
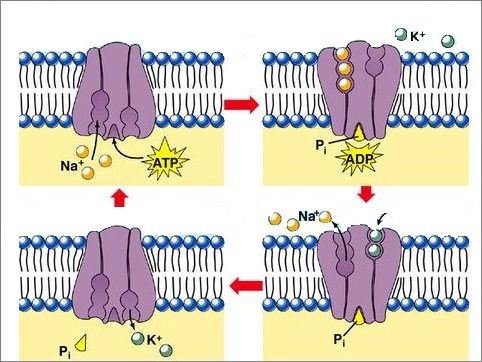
Diagram of the operation of the sodium and potassium pump
Also understand how the Nervous Impulse Transmission.