Active transport is what takes place across the cell membrane energy-using.
In this case, the transport of substances takes place from the lowest to the highest concentration. That is, against a concentration gradient.
Among the substances that can be actively transported across the membrane are: sodium, potassium, iron, hydrogen, calcium and some types of sugars and amino acids.
Active Transport vs. Passive Transport: Remember, no passive transportno energy is wasted and substances are transported down the contraction gradient.
Active Transport Types
Active transport can be classified according to the energy source used to carry out the process.
Primary Active Transport
In this type of transport, energy is derived from the breakdown of ATP or another phosphate compound with energy.
An example is the Sodium and Potassium Pump, which occurs in every cell in the body.
How does the Sodium and Potassium Pump work?
Some proteins present in plasma membrane act as “pumps” of ions.
In this case, they capture sodium ions from the cytoplasm and transport them out of the cell.
Meanwhile, they also capture potassium ions from the medium and transport them to the cytoplasm.
For every three sodium ions pumped out of the cell, only two potassium ions are pumped into the cytoplasm.
The sodium and potassium pump occurs continuously and is essential for the cells to function.
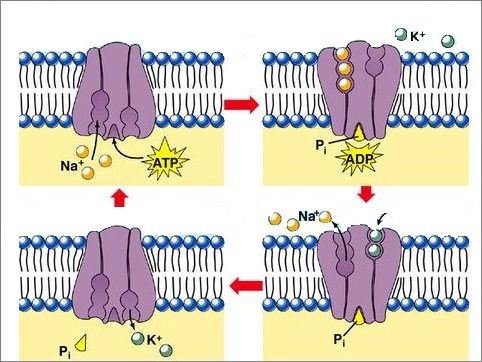 Sodium and Potassium Pump Operation
Sodium and Potassium Pump Operation
Secondary Active Transport
Also called coupled transport.
This type of transport is called secondary because it does not directly use the metabolic energy of ATP and depends on transport proteins found in the membrane.
The energy to carry out this type of transport depends on the energy used by the sodium and potassium pump.
The sodium and potassium pump generates different concentrations of these ions between the two sides of the membrane.
Sodium, when transported out of the cell during primary transport, is concentrated in this region. This gradient represents energy storage.
Thus, sodium will always be moving into the cell, as it will go in favor of its concentration gradient.
Other substances can take advantage of this concentration gradient and be transported along with sodium.
When they are transported in the same direction, it is called co-transport or sim-transport.
When it occurs in the opposite direction, it is called counter-transport or anti-transport.
 Types of secondary transport
Types of secondary transport
Block Transport
This type of transport occurs when cells transfer large amounts of substances into or out of the intracellular environment.
It is characteristic for involving morphological changes in the cell.
can be by endocytosis or exocytosis:
endocytosis: transport in quantity of substances to the interior of the cell.
can occur by phagocytosis, when the cell engulfs solid particles. and by pinocytosis, when the cell encloses small particles or liquids.
exocytosis: transport of substances, in quantity, out of the cell.
Learn more about the subject, read also:
- Passive Transport
- Simple Broadcast
- Diffusion facilitated
- Osmosis
- Selective Permeability
- Exercises on Plasma Membrane



