Simple diffusion is a type of passive transport of substances across the cell membrane.
It is a process that occurs from the region where the particles are more concentrated to regions where their concentration is lower, until an equilibrium in concentrations is reached.
Thus, diffusion occurs in favor of a concentration gradient. With this, there is no waste of energy and no need for a carrier for substances.
Diffusion is due to the fact that the particles are in constant motion. For this to happen, two fundamental conditions must exist:
- The cell membrane must be permeable to the substance to be transported;
- There must be differences in the concentration of this substance between the cell and the external environment.
Diffusion is an important process for cells, as it allows the entry of substances essential to cell metabolism and also allows the exit of excretions.
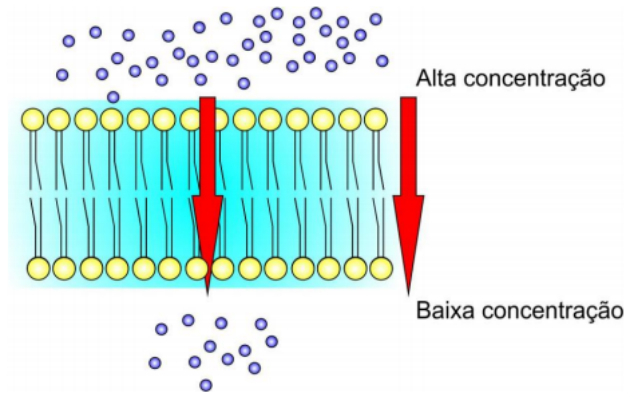
Simple Broadcast Example
An example of simple diffusion is the breathing process. Upon reaching the pulmonary alveoli, oxygen diffuses into the blood from the capillaries. Meanwhile, the carbon dioxide present in the blood from the capillaries diffuses into the alveoli.
This situation of gas exchange occurs due to the differences in concentration between the two gases in the pulmonary alveoli, from the more concentrated to the less concentrated medium.
Difference between Simple and Facilitated Diffusion
THE facilitated diffusion and simple diffusion deal with the same process of passive transport of substances across the cell membrane.
The difference is that in the facilitated diffusion there is the help of proteins, the permeases. These proteins act as carriers of substances, they capture the molecules and facilitate their entry into the cell.
Learn more about the two types of transport across the membrane, read also:
- Active Transport
- Passive Transport
Differences between Simple Diffusion and Osmosis
THE osmosis it is a special type of diffusion as it only deals with the passage of water across the cell membrane.
Osmosis is the passage of water from a less concentrated (hypotonic) medium to a more concentrated (hypertonic) medium.
Expand your knowledge, learn more about:
- Selective Permeability
- Sodium and Potassium Pump


