The propagation or transmission of heat can occur in three ways:
- thermal conduction
- Thermal Convection
- Thermal Irradiation
What is heat?
It is worth remembering that heat, also called heat energy, is a concept in the field of physics that determines the exchange of thermal energy between two bodies.
This energy transfer is intended to achieve the thermal balance between two bodies, that is, the same temperature.
Thus, a warmer body transfers heat to a cooler body until both are at the same temperature.
Types of Heat Propagation
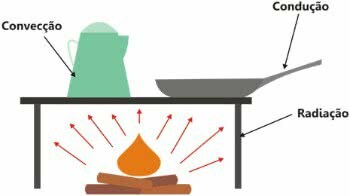
Illustration of the three forms of heat transmission
thermal conduction: Heat energy is transmitted through solid bodies that heat up, either by the heat of the fire, or by contact with a hotter one. Thus, when we heat a solid body, the kinetic energy increases and, consequently, the agitation of the molecules.
Thermal Convection: this type of heat transfer occurs in substances that are in a liquid or gaseous state. Circular currents called "convection currents" are created, which are determined by the difference in density between the hottest and coldest fluid.
Thermal Irradiation: through the electromagnetic waves or heat waves of a body, the transfer of thermal energy occurs. In this case, an object's electrical particles increase, as does its kinetic energy.
Examples of Heat Propagation
thermal conduction
- Heating a metal bar
- Heating a metal spoon placed in a pan
- Heating a pan's metal handle
- Warming up a cup of tea or coffee
- Heating of clothes by electric iron
Thermal Convection
- Heating liquids in a pan
- fridge and freezer
- Air conditioning
- Heaters
- Atmospheric air currents
Thermal Irradiation
- Solar energy
- Solar boards
- Bake food in the oven
- Fire from the fireplaces
- Plant greenhouses
Read too:
- Heat and Temperature
- Calorimetry
- Specific heat
- latent heat
- Sensitive heat
- Thermal energy
- Physics Formulas
Entrance Exam Exercises with Feedback
1. (UFTM) Regarding heat transmission processes, consider:
I. in convection, heat is transferred from one place to another using the fluids themselves as agents;
II. in conduction, the transfer of kinetic energy between particles occurs;
III. in irradiation, heat is transmitted in the form of electromagnetic waves.
It is correct what is contained in
a) I, only.
b) II, only.
c) I and II only.
d) II and III only.
e) I, II and III.
Alternative e) I, II and III.
2. (UNISINOS-RS) Health professionals recommend the use of light clothing for physical exercise, such as walking or jogging, especially in summer. The preference for light clothes is due to the fact that they:
a) absorb less thermal radiation than dark clothing.
b) reflect less thermal radiation than dark clothing.
c) absorb more thermal radiation than dark clothes.
d) prevent the formation of convection currents more easily than dark clothing.
e) they favor the conduction of heat because they have greater thermal conductivity than dark clothes.
Alternative a) absorb less thermal radiation than dark clothes.
3. (Mackenzie) One of the reasons that the water, close to the free surface of some lakes, freezes in winter, in regions of low temperatures, is the fact that when it is cooled, in the approximate range of 4 °C to 0 °C, it undergoes a process of dilation. With that its volume ____________ and its density ____________.
Ignoring the effects of thermal irradiation, during this cooling, the water at the bottom of the lake cannot reach the free surface, as it no longer occurs at ____________ and its temperature will decrease due to the process in____________.
The information that correctly fills in the gaps, in reading order, are, respectively:
a) increases, decreases, thermal convection and thermal conduction.
b) decreases, increases, thermal convection and thermal conduction.
c) increases, decreases, thermal conduction and thermal convection.
d) decreases, increases, thermal conduction and thermal convection.
e) increases, increases, thermal conduction and thermal convection.
Alternative a) increases, decreases, thermal convection and thermal conduction.
4. (PUC-MG) A thermos has silver and double walls with a vacuum in the intermediate space. The advantage of making thermos bottles like this is because the silver walls:
a) absorb heat and vacuum is a great thermal insulator.
b) are highly reflective and vacuum, an excellent thermal insulator.
c) absorb heat and vacuum is an excellent conductor.
d) are highly reflective and vacuum is an excellent conductor.
Alternative b) are highly reflective and vacuum, a great thermal insulator.
5. (CFT-MG) Modern stainless steel pans have stainless steel handles, which are a __________ heat conductor. They don't burn people's hands because they have a hollow shape, facilitating heat exchange by __________ from the air through them.
The option that correctly and respectively completes the gaps is
a) bad / irradiation.
b) good / irradiation.
c) good / convection.
d) bad / convection.
Alternative c) good / convection.